Java에서 객체 목록을 직렬화 해제하는 방법은 무엇입니까? 자바 직렬화 예
게시 됨: 2013-07-15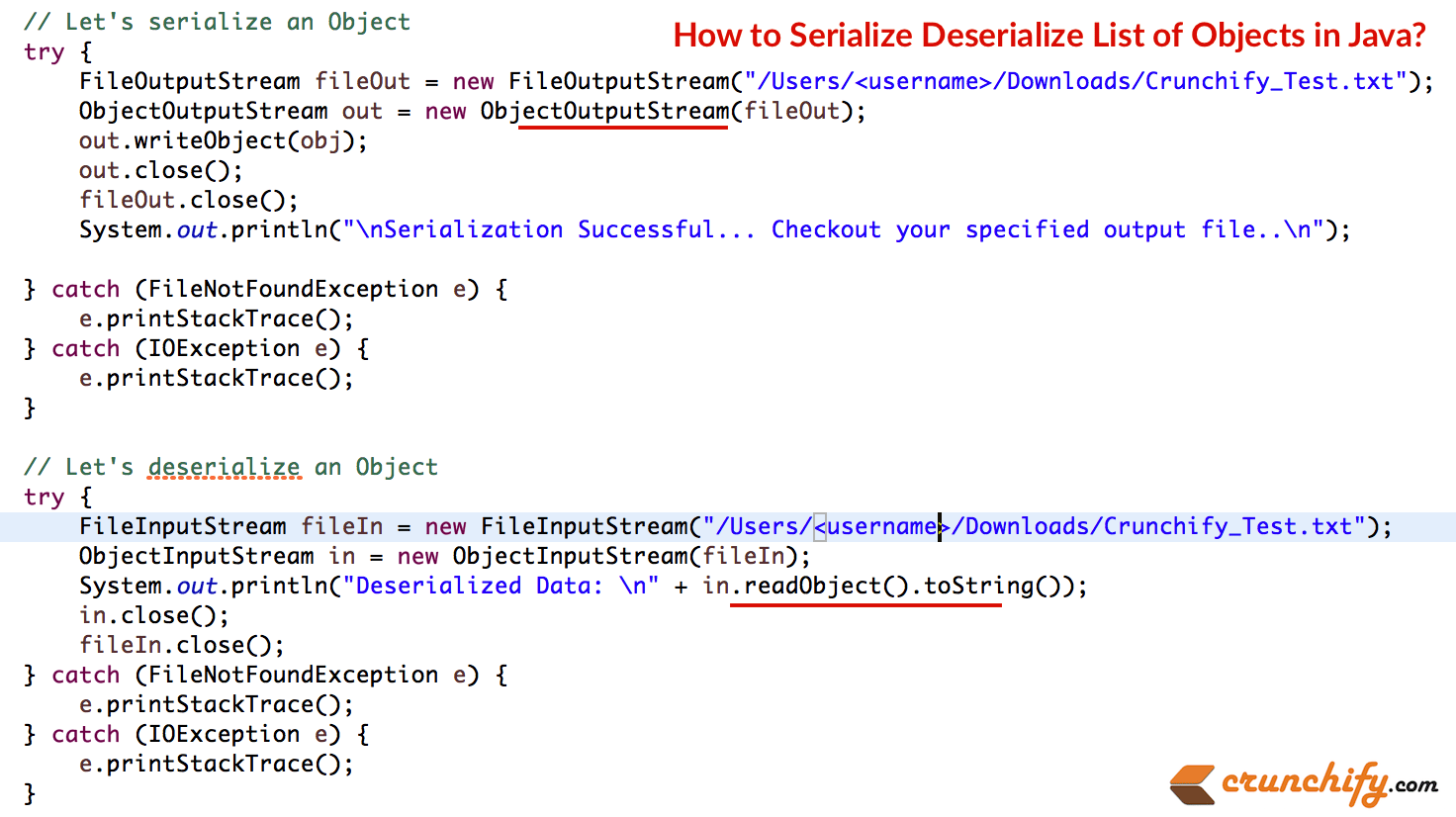
Java는 객체 직렬화라고 하는 메커니즘을 제공합니다. 여기서 객체의 데이터는 물론 객체의 유형 및 객체에 저장된 데이터 유형에 대한 정보를 포함하는 바이트 시퀀스로 객체를 나타낼 수 있습니다.
직렬화된 개체가 파일에 작성된 후에는 파일에서 읽고 역직렬화할 수 있습니다. 즉, 개체와 해당 데이터를 나타내는 유형 정보와 바이트를 사용하여 메모리에 개체를 다시 만들 수 있습니다.
가장 인상적인 것은 전체 프로세스가 JVM에 독립적이라는 것입니다. 즉, 개체를 한 플랫폼에서 직렬화하고 완전히 다른 플랫폼에서 역직렬화할 수 있습니다.
Java에서 단순 인 메모리 캐시를 만드는 방법(경량 캐시)
ObjectInputStream 및 ObjectOutputStream 클래스는 개체 직렬화 및 역직렬화를 위한 메서드가 포함된 상위 수준 스트림입니다.
아래 튜토리얼은 아래 질문이 있는 경우에도 작동합니다.
- JSON을 사용하여 객체를 직렬화 및 역직렬화하는 방법
- Java 예제에서 개체를 직렬화 및 역직렬화하는 방법
- Java 직렬화 객체를 xml 문자열로 직렬화 해제
- 이진 트리 직렬화 및 역직렬화
- Java에서 목록 직렬화
다음은 완전한 예입니다. 단계는 다음과 같습니다.
- Serializable을 구현하는 Class Item()을 생성합니다.
- 메인에서 – 2개의 아이템 객체를 생성합니다.
- ArrayList에 추가합니다.
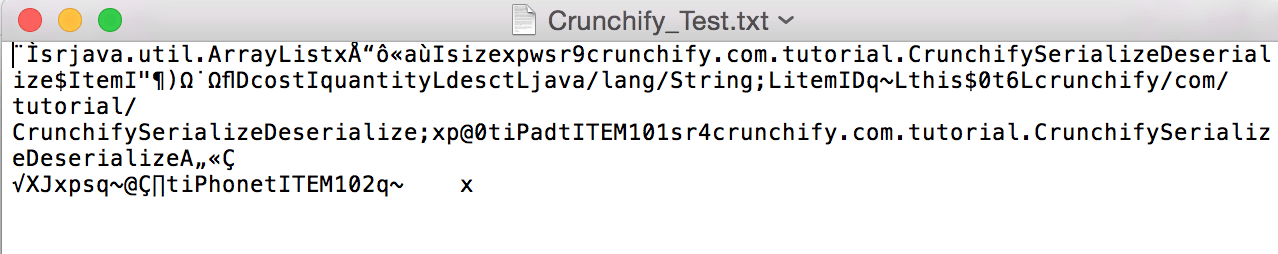
- ArrayList를 직렬화하십시오. 객체의 바이트스트림을 보려면 파일을 체크아웃하십시오. (아래 이미지)
- 동일한 파일에서 바이트스트림을 역직렬화하여 Object를 확인합니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import java . io . FileInputStream ; import java . io . FileNotFoundException ; import java . io . FileOutputStream ; import java . io . IOException ; import java . io . ObjectInputStream ; import java . io . ObjectOutputStream ; import java . io . Serializable ; import java . util . ArrayList ; import java . util . List ; @SuppressWarnings ( "serial" ) public class CrunchifySerializeDeserialize implements Serializable { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws ClassNotFoundException { int i ; Item [ ] items = new Item [ 2 ] ; CrunchifySerializeDeserialize c = new CrunchifySerializeDeserialize ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { items [ i ] = c . new Item ( ) ; // create array } // hard-coded values of id, desc, cost, qty items [ 0 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM101" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM102" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setDesc ( "iPad" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setDesc ( "iPhone" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setCost ( 499 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setCost ( 599 ) ; items [ 0 ] . setQuantity ( 1 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setQuantity ( 3 ) ; System . out . println ( "Item Details....." ) ; for ( Item d : items ) { System . out . print ( d . getItemID ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getDesc ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getCost ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( "\t" + d . getQuantity ( ) ) ; } List <Item> obj ; obj = new ArrayList <Item> ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { obj . add ( items [ i ] ) ; } // Let's serialize an Object try { FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream ( fileOut ) ; out . writeObject ( obj ) ; out . close ( ) ; fileOut . close ( ) ; System . out . println ( "\nSerialization Successful... Checkout your specified output file..\n" ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } // Let's deserialize an Object try { FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream ( fileIn ) ; System . out . println ( "Deserialized Data: \n" + in . readObject ( ) . toString ( ) ) ; in . close ( ) ; fileIn . close ( ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } public class Item implements Serializable { private String itemID ; private String desc ; private double cost ; private int quantity ; public Item ( ) { itemID = "" ; desc = "" ; cost = 0 ; quantity = 0 ; } public Item ( String id , String d , double c , int q ) { itemID = id ; desc = d ; cost = c ; quantity = q ; } /** * @return the itemID */ public String getItemID ( ) { return itemID ; } /** * @param itemID * the itemID to set */ public void setItemID ( String itemID ) { this . itemID = itemID ; } /** * @return the desc */ public String getDesc ( ) { return desc ; } /** * @param desc * the desc to set */ public void setDesc ( String desc ) { this . desc = desc ; } /** * @return the cost */ public double getCost ( ) { return cost ; } /** * @param cost * the cost to set */ public void setCost ( double cost ) { this . cost = cost ; } /** * @return the quantity */ public int getQuantity ( ) { return quantity ; } /** * @param quantity * the quantity to set */ public void setQuantity ( int quantity ) { this . quantity = quantity ; } /* * @see java.lang.Object#toString() */ @Override public String toString ( ) { return "Item [itemcrayon-h"> + itemID + ", desc=" + desc + ", cost=" + cost + ", quantity=" + quantity + "]" ; } } } |
산출:

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Item Details . . . . . ITEM101 iPad 499.0 1 ITEM102 iPhone 599.0 3 Serialization Successful . . . Checkout your specified output file . . Deserialized Data : [ Item [ itemID = ITEM101 , desc = iPad , cost = 499.0 , quantity = 1 ] , Item [ itemID = ITEM102 , desc = iPhone , cost = 599.0 , quantity = 3 ] ] |
관심이 있을 수 있는 모든 Java 자습서 및 Spring MVC 자습서 목록입니다.
