자바: 팩토리 디자인-메소드 패턴 | 객체 지향 디자인 | 디자인 패턴
게시 됨: 2013-06-28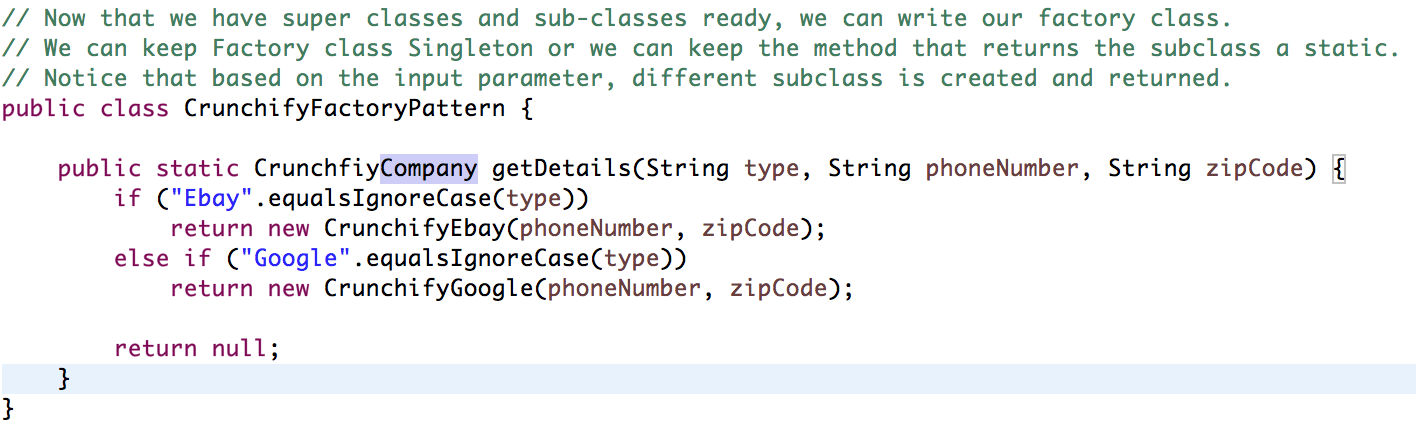
Factory Design Pattern은 Creational Design 패턴 중 하나로 JDK는 물론 Spring MVC, Struts와 같은 프레임워크에서도 널리 사용됩니다. 팩토리 메소드 패턴 은 팩토리 개념을 구현하기 위한 객체 지향 생성 디자인 패턴으로, 생성될 객체의 정확한 클래스를 지정하지 않고 객체(제품) 생성 문제를 다룬다. 이 패턴의 본질은 " 객체를 생성하기 위한 인터페이스를 정의하되, 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스가 인스턴스화할 클래스를 결정하게 하십시오. Factory 메서드를 사용하면 클래스가 인스턴스화를 하위 클래스로 연기할 수 있습니다 .

먼저 자바에서 팩토리 패턴을 구현하는 방법을 알아봅시다. 이 패턴을 구현하기 위해 5개의 클래스를 만들 것입니다.
- 슈퍼 클래스(CrunchfiyCompany.java)
- 팩토리 패턴의 슈퍼 클래스는 인터페이스, 추상 클래스 또는 일반 자바 클래스가 될 수 있습니다. 이 예에서는 테스트 목적으로
toString()메서드를 재정의한 추상 클래스로 슈퍼 클래스가 있습니다.
- 팩토리 패턴의 슈퍼 클래스는 인터페이스, 추상 클래스 또는 일반 자바 클래스가 될 수 있습니다. 이 예에서는 테스트 목적으로
- 하위 클래스1(CrunchifyEbay.java)
- 클래스가 CrunchfiyCompany 클래스를 확장하고 있음을 주목하십시오.
- 하위 클래스2(CrunchifyGoogle.java)
- 클래스가 CrunchfiyCompany 클래스를 확장하고 있음을 주목하십시오.
- 팩토리 클래스(CrunchifyFactoryPattern.java)
- 이제 슈퍼 클래스와 서브 클래스가 준비되었으므로 팩토리 클래스를 작성할 수 있습니다.
- Factory 클래스를 Singleton으로 유지하거나 하위 클래스를 정적으로 반환하는 메서드를 유지할 수 있습니다.
- 입력 매개변수에 따라 다른 하위 클래스가 생성되고 반환됩니다.
- 테스트 클래스(CrunchifyFactoryPatternTest.java)
- 위의 팩토리 패턴 구현을 사용하는 단순 테스트 클라이언트 프로그램입니다.
기타 반드시 읽어야 할 사항:
- 스레드로부터 안전한 Java의 빠른 싱글톤 구현
- Java에서 데몬 스레드란 무엇입니까? 첨부된 예
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ // Super class in factory pattern can be an interface, abstract class or a // normal java class. For our example, we have super class as abstract class // with overridden toString() method for testing purpose. public abstract class CrunchfiyCompany { public abstract String getPhoneNumber ( ) ; public abstract String getZipCode ( ) ; @Override public String toString ( ) { return "Phone #= " + this . getPhoneNumber ( ) + ", Zip Code= " + this . getZipCode ( ) ; } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ // Notice that the class is extending CrunchfiyCompany class. public class CrunchifyEbay extends CrunchfiyCompany { private String phoneNumber ; private String zipCode ; public CrunchifyEbay ( String phoneNumber , String zipCode ) { this . phoneNumber = phoneNumber ; this . zipCode = zipCode ; } @Override public String getPhoneNumber ( ) { return this . phoneNumber ; } @Override public String getZipCode ( ) { return this . zipCode ; } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ // Notice that the class is extending CrunchfiyCompany class. public class CrunchifyGoogle extends CrunchfiyCompany { private String phoneNumber ; private String zipCode ; public CrunchifyGoogle ( String phoneNumber , String zipCode ) { this . phoneNumber = phoneNumber ; this . zipCode = zipCode ; } @Override public String getPhoneNumber ( ) { return this . phoneNumber ; } @Override public String getZipCode ( ) { return this . zipCode ; } } |

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchfiyCompany ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchifyEbay ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchifyGoogle ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ // Now that we have super classes and sub-classes ready, we can write our factory class. // We can keep Factory class Singleton or we can keep the method that return the subclass a static. // Notice that based on the input parameter, different subclass is created and returned. public class CrunchifyFactoryPattern { public static CrunchfiyCompany getDetails ( String type , String phoneNumber , String zipCode ) { if ( "Ebay" . equalsIgnoreCase ( type ) ) return new CrunchifyEbay ( phoneNumber , zipCode ) ; else if ( "Google" . equalsIgnoreCase ( type ) ) return new CrunchifyGoogle ( phoneNumber , zipCode ) ; return null ; } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchfiyCompany ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchifyFactoryPattern ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ // Simple Test client program that uses above factory pattern implementation. public class CrunchifyFactoryPatternTest { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { CrunchfiyCompany eBay = CrunchifyFactoryPattern . getDetails ( "Ebay" , "408.123.4567" , "98765" ) ; CrunchfiyCompany google = CrunchifyFactoryPattern . getDetails ( "Google" , "519.123.4567" , "56789" ) ; System . out . println ( "Factory eBay Config::" + eBay ) ; System . out . println ( "Factory Google Config::" + google ) ; } } |
|
1 2 |
Factory eBay Config : : Phone #= 408.123.4567, Zip Code= 98765 Factory Google Config : : Phone #= 519.123.4567, Zip Code= 56789 |
팩토리 패턴을 사용하는 다른 예는?
- java.util.Calendar, ResourceBundle 및 NumberFormat
getInstance()메소드는 팩토리 패턴을 사용합니다. - Boolean, Integer 등과 같은 래퍼 클래스의
valueOf()메서드
공장 패턴의 이점:
- 여러 하위 클래스가 있는 수퍼 클래스가 있고 입력에 따라 하위 클래스 중 하나를 반환해야 할 때 사용됩니다. 이 패턴은 클라이언트 프로그램에서 팩토리 클래스로 클래스를 인스턴스화하는 책임을 집니다.
- 팩토리 패턴은 구현이 아닌 인터페이스에 대한 코드 접근 방식을 제공합니다.
- 팩토리 패턴은 클라이언트 코드에서 실제 구현 클래스의 인스턴스화를 제거하여 더 강력하고 덜 결합되고 확장하기 쉽게 만듭니다. 예를 들어, 클라이언트 프로그램이 이를 인식하지 못하기 때문에 PC 클래스 구현을 쉽게 변경할 수 있습니다.
- 팩토리 패턴은 상속을 통해 구현과 클라이언트 클래스 간의 추상화를 제공합니다.
단점:
- 팩토리는 객체 패밀리에 사용되어야 합니다. 클래스가 공통 기본 클래스 또는 인터페이스를 확장하지 않으면 팩토리 디자인 템플릿에서 사용할 수 없습니다.
모든 Java 웹 개발, Spring MVC 자습서 목록입니다.
