Javaでオブジェクトのリストをシリアル化する方法は? Javaシリアル化の例
公開: 2013-07-15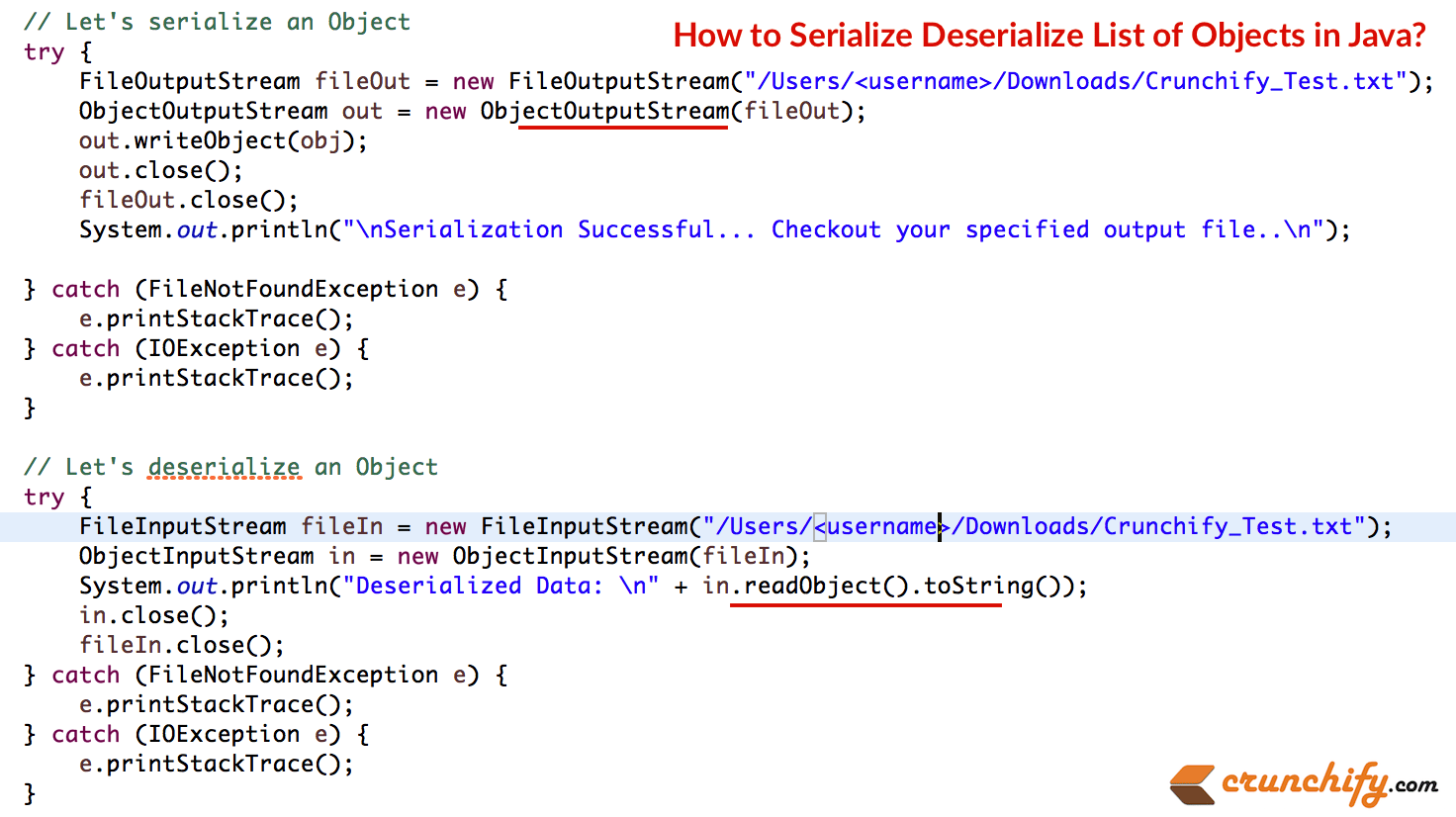
Javaは、オブジェクトのタイプとオブジェクトに格納されているデータのタイプに関する情報だけでなく、オブジェクトのデータを含むバイトのシーケンスとしてオブジェクトを表すことができる、オブジェクトのシリアル化と呼ばれるメカニズムを提供します。
シリアル化されたオブジェクトがファイルに書き込まれた後、ファイルから読み取って逆シリアル化できます。つまり、オブジェクトとそのデータを表すタイプ情報とバイトを使用して、メモリ内にオブジェクトを再作成できます。
最も印象的なのは、プロセス全体がJVMに依存しないことです。つまり、オブジェクトを1つのプラットフォームでシリアル化し、まったく異なるプラットフォームで逆シリアル化できます。
Javaでシンプルなメモリ内キャッシュを作成する方法(軽量キャッシュ)
クラスObjectInputStreamおよびObjectOutputStreamは、オブジェクトをシリアル化および逆シリアル化するためのメソッドを含む高レベルのストリームです。
以下の質問がある場合は、以下のチュートリアルも機能します。
- JSONを使用してオブジェクトをシリアル化および逆シリアル化する方法
- Javaの例でオブジェクトをシリアル化および逆シリアル化する方法
- Javaシリアル化逆シリアル化オブジェクトをxml文字列に
- 二分木のシリアル化と逆シリアル化
- Javaでリストをシリアル化する
これが完全な例です。 手順は次のとおりです。
- Serializableを実装するClassItem()を作成します。
- メイン–2つのアイテムオブジェクトを作成します。
- ArrayListに追加します。
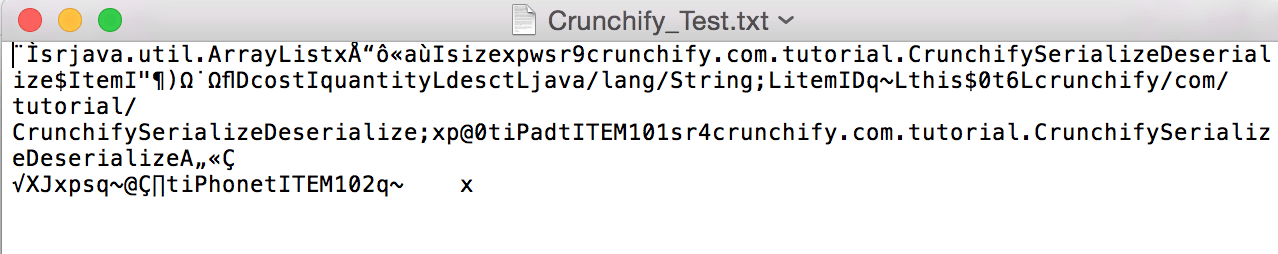
- ArrayListをシリアル化します。 オブジェクトのバイトストリームを確認するためのチェックアウトファイル。 (下の画像)
- 同じファイルからバイトストリームを逆シリアル化して、オブジェクトを表示します。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import java . io . FileInputStream ; import java . io . FileNotFoundException ; import java . io . FileOutputStream ; import java . io . IOException ; import java . io . ObjectInputStream ; import java . io . ObjectOutputStream ; import java . io . Serializable ; import java . util . ArrayList ; import java . util . List ; @SuppressWarnings ( "serial" ) public class CrunchifySerializeDeserialize implements Serializable { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws ClassNotFoundException { int i ; Item [ ] items = new Item [ 2 ] ; CrunchifySerializeDeserialize c = new CrunchifySerializeDeserialize ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { items [ i ] = c . new Item ( ) ; // create array } // hard-coded values of id, desc, cost, qty items [ 0 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM101" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM102" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setDesc ( "iPad" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setDesc ( "iPhone" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setCost ( 499 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setCost ( 599 ) ; items [ 0 ] . setQuantity ( 1 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setQuantity ( 3 ) ; System . out . println ( "Item Details....." ) ; for ( Item d : items ) { System . out . print ( d . getItemID ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getDesc ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getCost ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( "\t" + d . getQuantity ( ) ) ; } List <Item> obj ; obj = new ArrayList <Item> ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { obj . add ( items [ i ] ) ; } // Let's serialize an Object try { FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream ( fileOut ) ; out . writeObject ( obj ) ; out . close ( ) ; fileOut . close ( ) ; System . out . println ( "\nSerialization Successful... Checkout your specified output file..\n" ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } // Let's deserialize an Object try { FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream ( fileIn ) ; System . out . println ( "Deserialized Data: \n" + in . readObject ( ) . toString ( ) ) ; in . close ( ) ; fileIn . close ( ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } public class Item implements Serializable { private String itemID ; private String desc ; private double cost ; private int quantity ; public Item ( ) { itemID = "" ; desc = "" ; cost = 0 ; quantity = 0 ; } public Item ( String id , String d , double c , int q ) { itemID = id ; desc = d ; cost = c ; quantity = q ; } /** * @return the itemID */ public String getItemID ( ) { return itemID ; } /** * @param itemID * the itemID to set */ public void setItemID ( String itemID ) { this . itemID = itemID ; } /** * @return the desc */ public String getDesc ( ) { return desc ; } /** * @param desc * the desc to set */ public void setDesc ( String desc ) { this . desc = desc ; } /** * @return the cost */ public double getCost ( ) { return cost ; } /** * @param cost * the cost to set */ public void setCost ( double cost ) { this . cost = cost ; } /** * @return the quantity */ public int getQuantity ( ) { return quantity ; } /** * @param quantity * the quantity to set */ public void setQuantity ( int quantity ) { this . quantity = quantity ; } /* * @see java.lang.Object#toString() */ @Override public String toString ( ) { return "Item [itemcrayon-h"> + itemID + ", desc=" + desc + ", cost=" + cost + ", quantity=" + quantity + "]" ; } } } |
出力:

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Item Details . . . . . ITEM101 iPad 499.0 1 ITEM102 iPhone 599.0 3 Serialization Successful . . . Checkout your specified output file . . Deserialized Data : [ Item [ itemID = ITEM101 , desc = iPad , cost = 499.0 , quantity = 1 ] , Item [ itemID = ITEM102 , desc = iPhone , cost = 599.0 , quantity = 3 ] ] |
興味があるかもしれないすべてのJavaチュートリアルとSpringMVCチュートリアルのリスト。
