Comment sérialiser désérialiser la liste d'objets en Java ? Exemple de sérialisation Java
Publié: 2013-07-15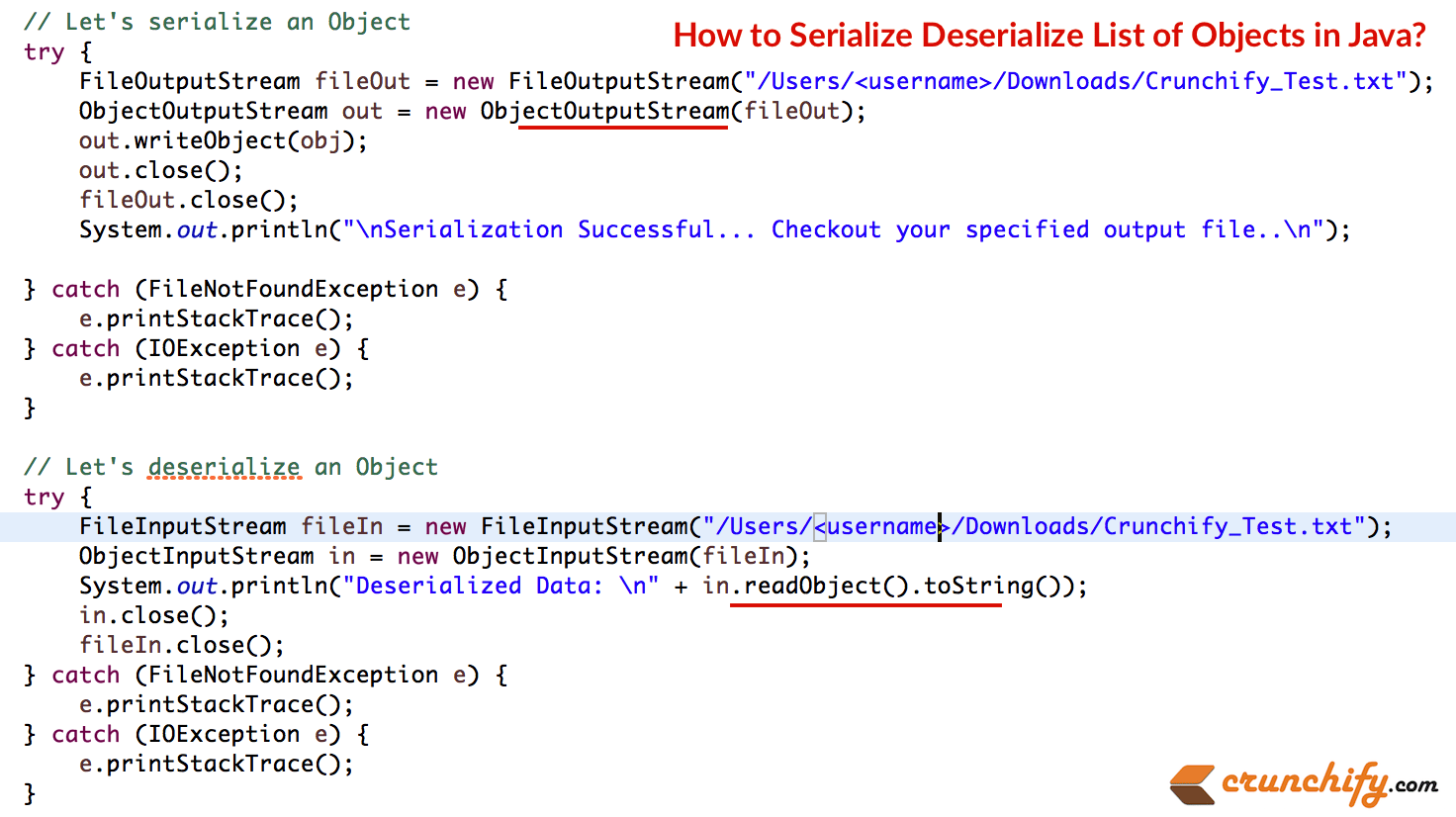
Java fournit un mécanisme, appelé sérialisation d'objet, où un objet peut être représenté comme une séquence d'octets qui inclut les données de l'objet ainsi que des informations sur le type de l'objet et les types de données stockées dans l'objet.
Une fois qu'un objet sérialisé a été écrit dans un fichier, il peut être lu à partir du fichier et désérialisé, c'est-à-dire que les informations de type et les octets qui représentent l'objet et ses données peuvent être utilisés pour recréer l'objet en mémoire.
Le plus impressionnant est que l'ensemble du processus est indépendant de la JVM, ce qui signifie qu'un objet peut être sérialisé sur une plate-forme et désérialisé sur une plate-forme entièrement différente.
Comment créer un cache en mémoire simple en Java (cache léger)
Les classes ObjectInputStream et ObjectOutputStream sont des flux de haut niveau qui contiennent les méthodes de sérialisation et de désérialisation d'un objet.
Le didacticiel ci-dessous fonctionnera également si vous avez l'une des questions ci-dessous :
- Comment sérialiser et désérialiser un objet en utilisant JSON
- Comment sérialiser et désérialiser un objet dans un exemple Java
- Java sérialiser désérialiser l'objet en chaîne xml
- Sérialiser et désérialiser un arbre binaire
- Sérialiser la liste en Java
Voici un exemple complet. Voici les étapes :
- Créez un élément de classe() qui implémente Serializable.
- Dans Main - Créez 2 objets d'article.
- Ajoutez-le à ArrayList.
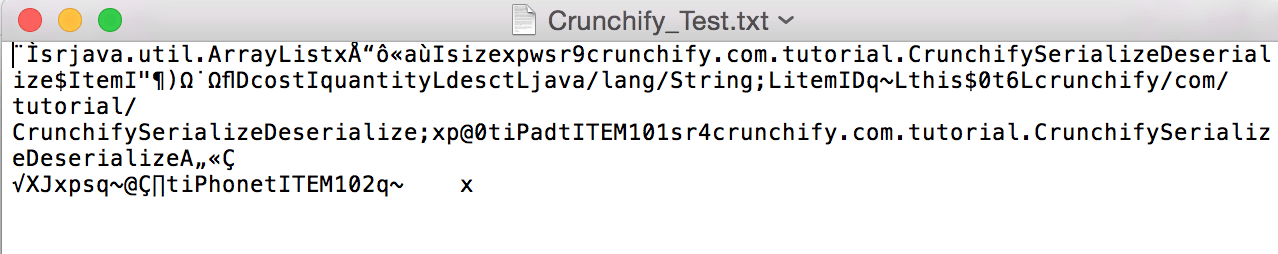
- Sérialisez la ArrayList. Extrayez le fichier pour voir le flux d'octets d'un objet. (Image ci-dessous)
- Désérialisez le flux d'octets du même fichier pour voir Object.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import java . io . FileInputStream ; import java . io . FileNotFoundException ; import java . io . FileOutputStream ; import java . io . IOException ; import java . io . ObjectInputStream ; import java . io . ObjectOutputStream ; import java . io . Serializable ; import java . util . ArrayList ; import java . util . List ; @SuppressWarnings ( "serial" ) public class CrunchifySerializeDeserialize implements Serializable { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws ClassNotFoundException { int i ; Item [ ] items = new Item [ 2 ] ; CrunchifySerializeDeserialize c = new CrunchifySerializeDeserialize ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { items [ i ] = c . new Item ( ) ; // create array } // hard-coded values of id, desc, cost, qty items [ 0 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM101" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM102" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setDesc ( "iPad" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setDesc ( "iPhone" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setCost ( 499 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setCost ( 599 ) ; items [ 0 ] . setQuantity ( 1 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setQuantity ( 3 ) ; System . out . println ( "Item Details....." ) ; for ( Item d : items ) { System . out . print ( d . getItemID ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getDesc ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getCost ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( "\t" + d . getQuantity ( ) ) ; } List <Item> obj ; obj = new ArrayList <Item> ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { obj . add ( items [ i ] ) ; } // Let's serialize an Object try { FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream ( fileOut ) ; out . writeObject ( obj ) ; out . close ( ) ; fileOut . close ( ) ; System . out . println ( "\nSerialization Successful... Checkout your specified output file..\n" ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } // Let's deserialize an Object try { FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream ( fileIn ) ; System . out . println ( "Deserialized Data: \n" + in . readObject ( ) . toString ( ) ) ; in . close ( ) ; fileIn . close ( ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } public class Item implements Serializable { private String itemID ; private String desc ; private double cost ; private int quantity ; public Item ( ) { itemID = "" ; desc = "" ; cost = 0 ; quantity = 0 ; } public Item ( String id , String d , double c , int q ) { itemID = id ; desc = d ; cost = c ; quantity = q ; } /** * @return the itemID */ public String getItemID ( ) { return itemID ; } /** * @param itemID * the itemID to set */ public void setItemID ( String itemID ) { this . itemID = itemID ; } /** * @return the desc */ public String getDesc ( ) { return desc ; } /** * @param desc * the desc to set */ public void setDesc ( String desc ) { this . desc = desc ; } /** * @return the cost */ public double getCost ( ) { return cost ; } /** * @param cost * the cost to set */ public void setCost ( double cost ) { this . cost = cost ; } /** * @return the quantity */ public int getQuantity ( ) { return quantity ; } /** * @param quantity * the quantity to set */ public void setQuantity ( int quantity ) { this . quantity = quantity ; } /* * @see java.lang.Object#toString() */ @Override public String toString ( ) { return "Item [itemcrayon-h"> + itemID + ", desc=" + desc + ", cost=" + cost + ", quantity=" + quantity + "]" ; } } } |
Sortir:

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Item Details . . . . . ITEM101 iPad 499.0 1 ITEM102 iPhone 599.0 3 Serialization Successful . . . Checkout your specified output file . . Deserialized Data : [ Item [ itemID = ITEM101 , desc = iPad , cost = 499.0 , quantity = 1 ] , Item [ itemID = ITEM102 , desc = iPhone , cost = 599.0 , quantity = 3 ] ] |
Liste de tous les tutoriels Java et Spring MVC qui pourraient vous intéresser.
