如何序列化反序列化Java中的对象列表? Java 序列化示例
已发表: 2013-07-15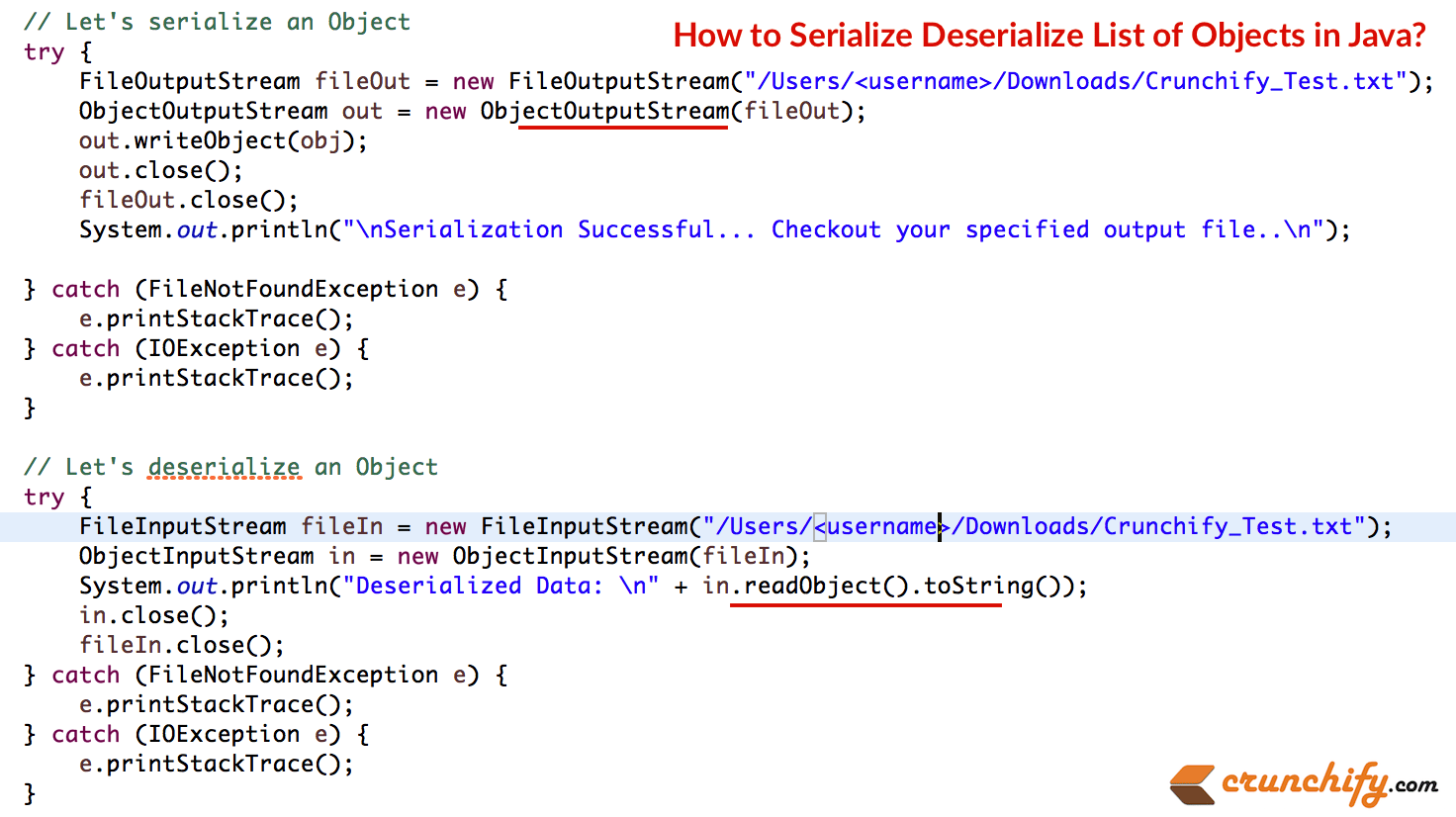
Java 提供了一种称为对象序列化的机制,其中对象可以表示为字节序列,其中包括对象的数据以及有关对象类型和存储在对象中的数据类型的信息。
序列化的对象写入文件后,可以从文件中读取并进行反序列化,即表示对象及其数据的类型信息和字节可用于在内存中重新创建对象。
最令人印象深刻的是整个过程是独立于 JVM 的,这意味着一个对象可以在一个平台上序列化并在完全不同的平台上反序列化。
如何在 Java 中创建一个简单的内存缓存(轻量级缓存)
类ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream是包含序列化和反序列化对象的方法的高级流。
如果您有以下任何问题,以下教程也将起作用:
- 如何使用 JSON 序列化和反序列化对象
- 如何在java示例中序列化和反序列化对象
- Java序列化反序列化对象到xml字符串
- 序列化和反序列化二叉树
- Java中的序列化列表
这是一个完整的例子。 这些是步骤:
- 创建实现可序列化的类 Item()。
- 在 Main – 创建 2 个项目对象。
- 将其添加到 ArrayList。
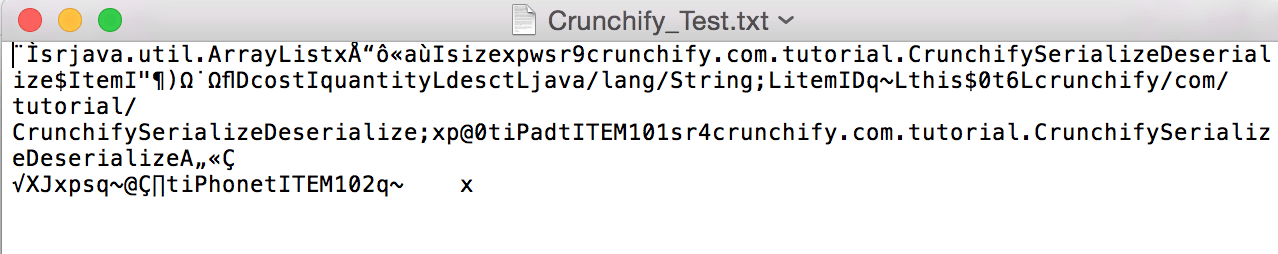
- 序列化 ArrayList。 签出文件以查看对象的字节流。 (下图)
- 反序列化同一文件中的字节流以查看 Object.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import java . io . FileInputStream ; import java . io . FileNotFoundException ; import java . io . FileOutputStream ; import java . io . IOException ; import java . io . ObjectInputStream ; import java . io . ObjectOutputStream ; import java . io . Serializable ; import java . util . ArrayList ; import java . util . List ; @SuppressWarnings ( "serial" ) public class CrunchifySerializeDeserialize implements Serializable { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws ClassNotFoundException { int i ; Item [ ] items = new Item [ 2 ] ; CrunchifySerializeDeserialize c = new CrunchifySerializeDeserialize ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { items [ i ] = c . new Item ( ) ; // create array } // hard-coded values of id, desc, cost, qty items [ 0 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM101" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM102" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setDesc ( "iPad" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setDesc ( "iPhone" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setCost ( 499 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setCost ( 599 ) ; items [ 0 ] . setQuantity ( 1 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setQuantity ( 3 ) ; System . out . println ( "Item Details....." ) ; for ( Item d : items ) { System . out . print ( d . getItemID ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getDesc ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getCost ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( "\t" + d . getQuantity ( ) ) ; } List <Item> obj ; obj = new ArrayList <Item> ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { obj . add ( items [ i ] ) ; } // Let's serialize an Object try { FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream ( fileOut ) ; out . writeObject ( obj ) ; out . close ( ) ; fileOut . close ( ) ; System . out . println ( "\nSerialization Successful... Checkout your specified output file..\n" ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } // Let's deserialize an Object try { FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream ( fileIn ) ; System . out . println ( "Deserialized Data: \n" + in . readObject ( ) . toString ( ) ) ; in . close ( ) ; fileIn . close ( ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } public class Item implements Serializable { private String itemID ; private String desc ; private double cost ; private int quantity ; public Item ( ) { itemID = "" ; desc = "" ; cost = 0 ; quantity = 0 ; } public Item ( String id , String d , double c , int q ) { itemID = id ; desc = d ; cost = c ; quantity = q ; } /** * @return the itemID */ public String getItemID ( ) { return itemID ; } /** * @param itemID * the itemID to set */ public void setItemID ( String itemID ) { this . itemID = itemID ; } /** * @return the desc */ public String getDesc ( ) { return desc ; } /** * @param desc * the desc to set */ public void setDesc ( String desc ) { this . desc = desc ; } /** * @return the cost */ public double getCost ( ) { return cost ; } /** * @param cost * the cost to set */ public void setCost ( double cost ) { this . cost = cost ; } /** * @return the quantity */ public int getQuantity ( ) { return quantity ; } /** * @param quantity * the quantity to set */ public void setQuantity ( int quantity ) { this . quantity = quantity ; } /* * @see java.lang.Object#toString() */ @Override public String toString ( ) { return "Item [itemcrayon-h"> + itemID + ", desc=" + desc + ", cost=" + cost + ", quantity=" + quantity + "]" ; } } } |
输出:

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Item Details . . . . . ITEM101 iPad 499.0 1 ITEM102 iPhone 599.0 3 Serialization Successful . . . Checkout your specified output file . . Deserialized Data : [ Item [ itemID = ITEM101 , desc = iPad , cost = 499.0 , quantity = 1 ] , Item [ itemID = ITEM102 , desc = iPhone , cost = 599.0 , quantity = 3 ] ] |
您可能感兴趣的所有 Java 教程和 Spring MVC 教程的列表。
