كيف تسلسل إلغاء تسلسل قائمة الكائنات في جافا؟ مثال على تسلسل جافا
نشرت: 2013-07-15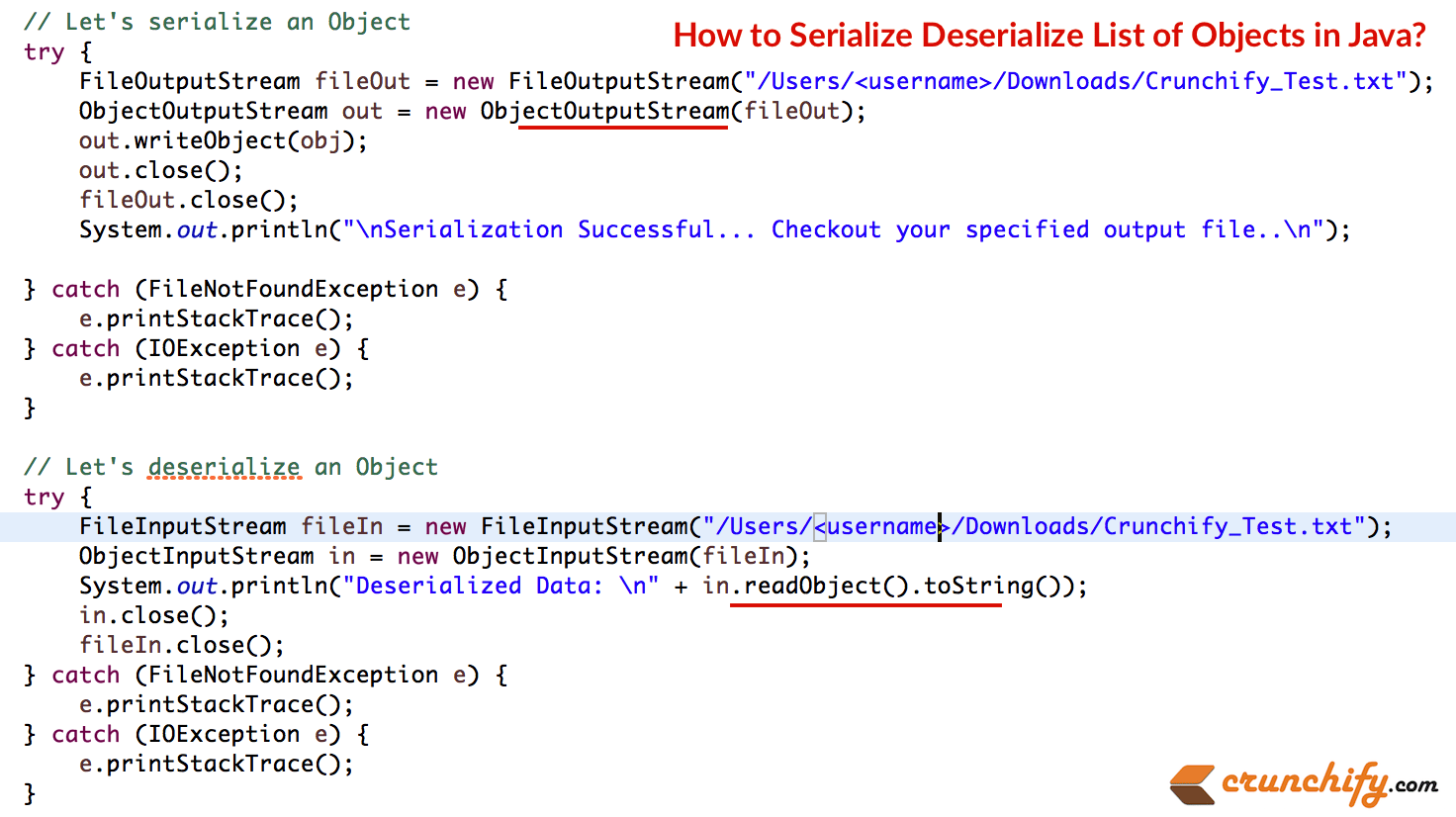
توفر Java آلية تسمى تسلسل الكائن حيث يمكن تمثيل الكائن على شكل تسلسل من البايت يتضمن بيانات الكائن بالإضافة إلى معلومات حول نوع الكائن وأنواع البيانات المخزنة في الكائن.
بعد كتابة الكائن المتسلسل في ملف ، يمكن قراءته من الملف وإلغاء التسلسل ، أي يمكن استخدام معلومات النوع والبايتات التي تمثل الكائن وبياناته لإعادة إنشاء الكائن في الذاكرة.
الأمر الأكثر إثارة للإعجاب هو أن العملية بأكملها مستقلة عن JVM ، مما يعني أنه يمكن إجراء تسلسل للكائن على منصة واحدة وإلغاء التسلسل على منصة مختلفة تمامًا.
كيفية إنشاء ذاكرة تخزين مؤقت بسيطة في الذاكرة في Java (ذاكرة تخزين مؤقت خفيفة الوزن)
تعتبر الفئات ObjectInputStream و ObjectOutputStream تدفقات عالية المستوى تحتوي على طرق لتسلسل كائن وإلغاء تسلسله.
سيعمل البرنامج التعليمي أدناه أيضًا إذا كان لديك أي من الأسئلة التالية:
- كيفية إجراء تسلسل وإلغاء تسلسل كائن باستخدام JSON
- كيفية إجراء تسلسل وإلغاء تسلسل كائن في مثال جافا
- جافا تسلسل إلغاء تسلسل الكائن إلى سلسلة xml
- تسلسل شجرة ثنائية وإلغاء تسلسلها
- تسلسل القائمة في جافا
هنا مثال كامل. هذه هي الخطوات:
- قم بإنشاء عنصر فئة () والذي يقوم بتنفيذ Serializable.
- بشكل رئيسي - إنشاء كائنين من عناصر العنصر.
- أضفه إلى ArrayList.
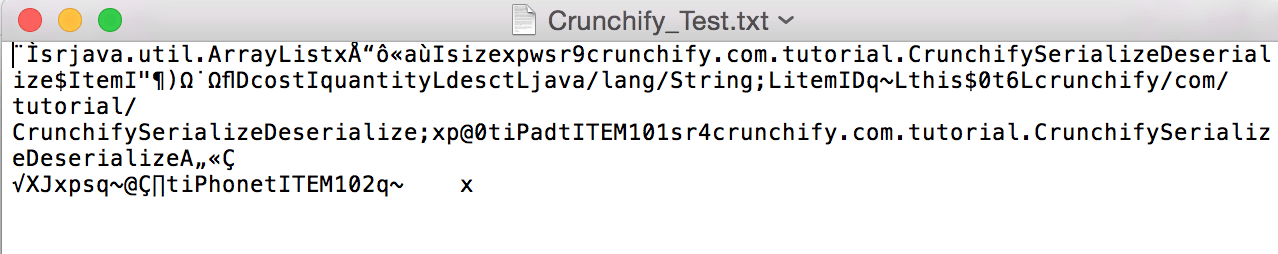
- تسلسل ArrayList. ملف الخروج لرؤية bytestream لكائن. (الصورة أدناه)
- قم بإلغاء تسلسل سلسلة البايت من نفس الملف لرؤية الكائن.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import java . io . FileInputStream ; import java . io . FileNotFoundException ; import java . io . FileOutputStream ; import java . io . IOException ; import java . io . ObjectInputStream ; import java . io . ObjectOutputStream ; import java . io . Serializable ; import java . util . ArrayList ; import java . util . List ; @SuppressWarnings ( "serial" ) public class CrunchifySerializeDeserialize implements Serializable { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws ClassNotFoundException { int i ; Item [ ] items = new Item [ 2 ] ; CrunchifySerializeDeserialize c = new CrunchifySerializeDeserialize ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { items [ i ] = c . new Item ( ) ; // create array } // hard-coded values of id, desc, cost, qty items [ 0 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM101" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM102" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setDesc ( "iPad" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setDesc ( "iPhone" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setCost ( 499 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setCost ( 599 ) ; items [ 0 ] . setQuantity ( 1 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setQuantity ( 3 ) ; System . out . println ( "Item Details....." ) ; for ( Item d : items ) { System . out . print ( d . getItemID ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getDesc ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getCost ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( "\t" + d . getQuantity ( ) ) ; } List <Item> obj ; obj = new ArrayList <Item> ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { obj . add ( items [ i ] ) ; } // Let's serialize an Object try { FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream ( fileOut ) ; out . writeObject ( obj ) ; out . close ( ) ; fileOut . close ( ) ; System . out . println ( "\nSerialization Successful... Checkout your specified output file..\n" ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } // Let's deserialize an Object try { FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream ( fileIn ) ; System . out . println ( "Deserialized Data: \n" + in . readObject ( ) . toString ( ) ) ; in . close ( ) ; fileIn . close ( ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } public class Item implements Serializable { private String itemID ; private String desc ; private double cost ; private int quantity ; public Item ( ) { itemID = "" ; desc = "" ; cost = 0 ; quantity = 0 ; } public Item ( String id , String d , double c , int q ) { itemID = id ; desc = d ; cost = c ; quantity = q ; } /** * @return the itemID */ public String getItemID ( ) { return itemID ; } /** * @param itemID * the itemID to set */ public void setItemID ( String itemID ) { this . itemID = itemID ; } /** * @return the desc */ public String getDesc ( ) { return desc ; } /** * @param desc * the desc to set */ public void setDesc ( String desc ) { this . desc = desc ; } /** * @return the cost */ public double getCost ( ) { return cost ; } /** * @param cost * the cost to set */ public void setCost ( double cost ) { this . cost = cost ; } /** * @return the quantity */ public int getQuantity ( ) { return quantity ; } /** * @param quantity * the quantity to set */ public void setQuantity ( int quantity ) { this . quantity = quantity ; } /* * @see java.lang.Object#toString() */ @Override public String toString ( ) { return "Item [itemcrayon-h"> + itemID + ", desc=" + desc + ", cost=" + cost + ", quantity=" + quantity + "]" ; } } } |
انتاج:

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Item Details . . . . . ITEM101 iPad 499.0 1 ITEM102 iPhone 599.0 3 Serialization Successful . . . Checkout your specified output file . . Deserialized Data : [ Item [ itemID = ITEM101 , desc = iPad , cost = 499.0 , quantity = 1 ] , Item [ itemID = ITEM102 , desc = iPhone , cost = 599.0 , quantity = 3 ] ] |
قائمة بجميع دروس Java التعليمية ودروس Spring MVC التي قد تكون مهتمًا بها.
