Java에서 처음부터 LinkedList 클래스를 구현하는 방법
게시 됨: 2013-06-19
실제로 실제 프로덕션 시스템을 구축하고 있다면 예, 일반적으로 필요한 것이 사용할 수 있는 경우 표준 라이브러리의 항목을 사용합니다. 즉, 이것을 무의미한 운동으로 생각하지 마십시오.
작동 방식을 이해하는 것이 좋으며 understanding linked lists 을 이해하는 것은 표준 라이브러리에 없는 경우가 많은 보다 복잡한 데이터 구조를 이해하는 데 중요한 단계입니다.
연결 목록을 생성하는 방식과 Java 컬렉션 API가 생성하는 방식 사이에는 몇 가지 차이점이 있습니다.
Collections API는 더 복잡한 인터페이스를 준수하려고 합니다. LinkedList에는 항상 하나 이상의 요소가 있습니다.
이러한 종류의 설정을 사용하면 빈 목록이 필요할 때 null을 사용할 수 있습니다. "다음"을 "나머지 목록"으로 생각하십시오. 사실 많은 사람들은 이것을 "next" 대신 tail 이라고 부를 것입니다.
다음은 단일 LinkedList의 다이어그램입니다.
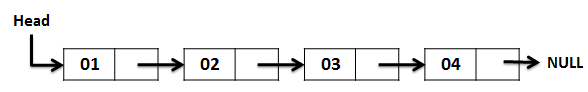
다른 사람은 다음을 읽어야 합니다.
- Java에서 LinkedList 인스턴스를 반복하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
- Java: LinkedList의 중간 요소를 찾는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Java에서 링크드리스트를 처음부터 만드는 가장 좋은 방법은 무엇입니까?
자, 다음은 Java에서 LinkedList 클래스의 가장 간단한 구현입니다.
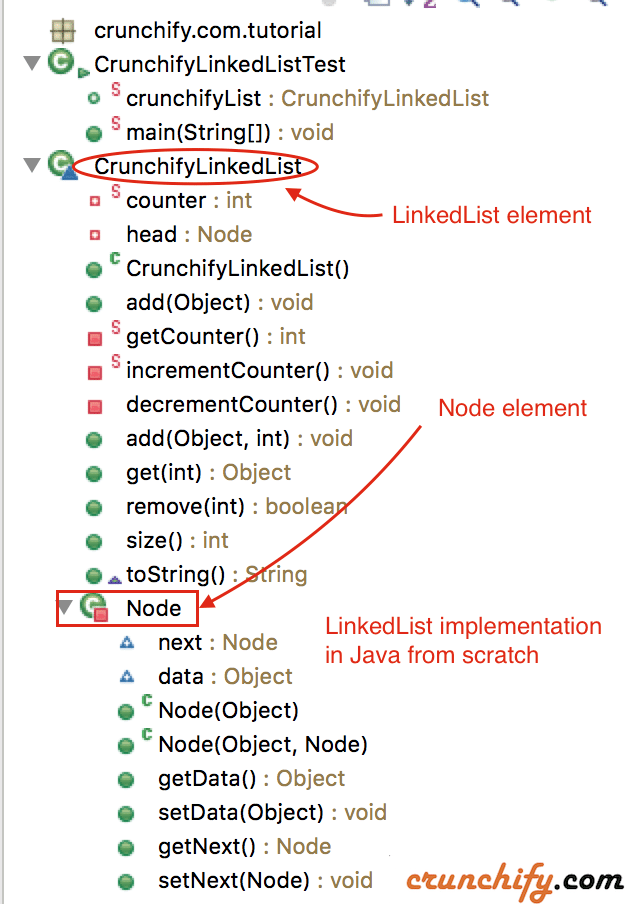
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 |
package crunchify . com . tutorial ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * version: 1.2 * last updated: 11/10/2015 */ public class CrunchifyLinkedListTest { public static CrunchifyLinkedList crunchifyList ; public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { // Default constructor - let's put "0" into head element. crunchifyList = new CrunchifyLinkedList ( ) ; // add more elements to LinkedList crunchifyList . add ( "1" ) ; crunchifyList . add ( "2" ) ; crunchifyList . add ( "3" ) ; crunchifyList . add ( "4" ) ; crunchifyList . add ( "5" ) ; /* * Please note that primitive values can not be added into LinkedList directly. They must be converted to their * corresponding wrapper class. */ System . out . println ( "Print: crunchifyList: \t\t" + crunchifyList ) ; System . out . println ( ".size(): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList . size ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( ".get(3): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList . get ( 3 ) + " (get element at index:3 - list starts from 0)" ) ; System . out . println ( ".remove(2): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList . remove ( 2 ) + " (element removed)" ) ; System . out . println ( ".get(3): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList . get ( 3 ) + " (get element at index:3 - list starts from 0)" ) ; System . out . println ( ".size(): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList . size ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( "Print again: crunchifyList: \t" + crunchifyList ) ; } } class CrunchifyLinkedList { private static int counter ; private Node head ; // Default constructor public CrunchifyLinkedList ( ) { } // appends the specified element to the end of this list. public void add ( Object data ) { // Initialize Node only incase of 1st element if ( head == null ) { head = new Node ( data ) ; } Node crunchifyTemp = new Node ( data ) ; Node crunchifyCurrent = head ; // Let's check for NPE before iterate over crunchifyCurrent if ( crunchifyCurrent ! = null ) { // starting at the head node, crawl to the end of the list and then add element after last node while ( crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ! = null ) { crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ; } // the last node's "next" reference set to our new node crunchifyCurrent . setNext ( crunchifyTemp ) ; } // increment the number of elements variable incrementCounter ( ) ; } private static int getCounter ( ) { return counter ; } private static void incrementCounter ( ) { counter ++ ; } private void decrementCounter ( ) { counter -- ; } // inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list public void add ( Object data , int index ) { Node crunchifyTemp = new Node ( data ) ; Node crunchifyCurrent = head ; // Let's check for NPE before iterate over crunchifyCurrent if ( crunchifyCurrent ! = null ) { // crawl to the requested index or the last element in the list, whichever comes first for ( int i = 0 ; i < index && crunchifyCurrent.getNext() != null; i ++ ) { crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ; } } // set the new node's next-node reference to this node's next-node reference crunchifyTemp . setNext ( crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ) ; // now set this node's next-node reference to the new node crunchifyCurrent . setNext ( crunchifyTemp ) ; // increment the number of elements variable incrementCounter ( ) ; } public Object get ( int index ) // returns the element at the specified position in this list. { // index must be 1 or higher if ( index < 0 ) return null ; Node crunchifyCurrent = null ; if ( head ! = null ) { crunchifyCurrent = head . getNext ( ) ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++ ) { if ( crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) == null ) return null ; crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ; } return crunchifyCurrent . getData ( ) ; } return crunchifyCurrent ; } // removes the element at the specified position in this list. public boolean remove ( int index ) { // if the index is out of range, exit if ( index < 1 | | index > size ( ) ) return false ; Node crunchifyCurrent = head ; if ( head ! = null ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++ ) { if ( crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) == null ) return false ; crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ; } crunchifyCurrent . setNext ( crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) . getNext ( ) ) ; // decrement the number of elements variable decrementCounter ( ) ; return true ; } return false ; } // returns the number of elements in this list. public int size ( ) { return getCounter ( ) ; } public String toString ( ) { String output = "" ; if ( head ! = null ) { Node crunchifyCurrent = head . getNext ( ) ; while ( crunchifyCurrent ! = null ) { output += "[" + crunchifyCurrent . getData ( ) . toString ( ) + "]" ; crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ; } } return output ; } private class Node { // reference to the next node in the chain, or null if there isn't one. Node next ; // data carried by this node. could be of any type you need. Object data ; // Node constructor public Node ( Object dataValue ) { next = null ; data = dataValue ; } // another Node constructor if we want to specify the node to point to. @SuppressWarnings ( "unused" ) public Node ( Object dataValue , Node nextValue ) { next = nextValue ; data = dataValue ; } // these methods should be self-explanatory public Object getData ( ) { return data ; } @SuppressWarnings ( "unused" ) public void setData ( Object dataValue ) { data = dataValue ; } public Node getNext ( ) { return next ; } public void setNext ( Node nextValue ) { next = nextValue ; } } } |
몇 가지:
여기서는 adding 1st element 하는 동안에만 Node 를 초기화합니다.

|
1 2 3 4 |
// Initialize Node only incase of 1st element if ( head == null ) { head = new Node ( data ) ; } |
결과:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Print : crunchifyList : [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] . size ( ) : 5 . get ( 3 ) : 4 ( get element at index : 3 - list starts from 0 ) . remove ( 2 ) : true ( element removed ) . get ( 3 ) : 5 ( get element at index : 3 - list starts from 0 ) . size ( ) : 4 Print again : crunchifyList : [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] |
이 구현의 개선 사항에는 double-linked list 만들기, 중간 또는 끝에서 insert 및 delete 하는 방법 추가, get 및 sort 방법 추가 등이 포함됩니다.
Laurence Gonsalves의 Stack Overflow에서 참조된 답변입니다. 모든 Java 자습서 목록에 관심이 있을 수 있습니다.
