¿Cómo serializar y deserializar la lista de objetos en Java? Ejemplo de serialización de Java
Publicado: 2013-07-15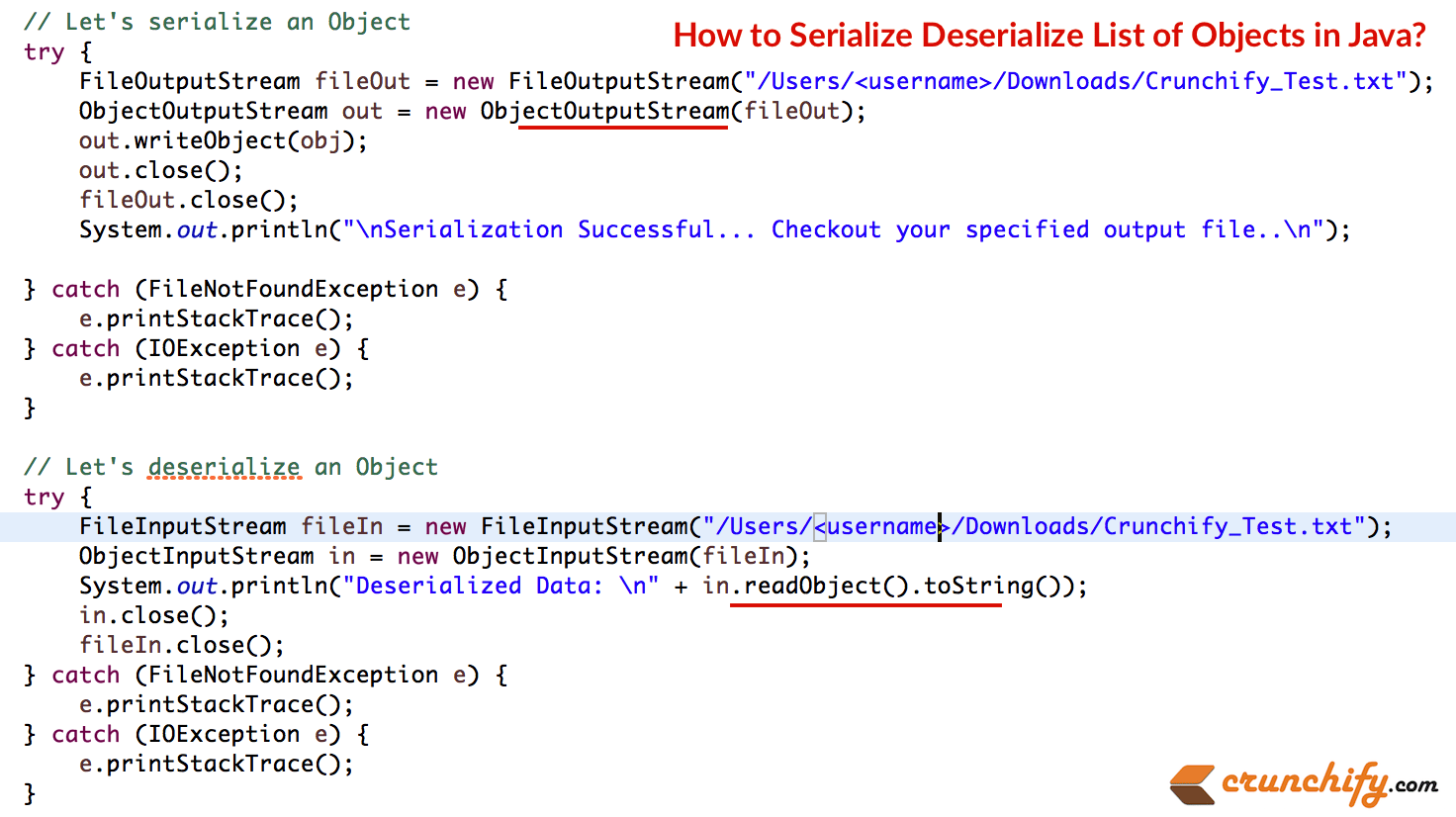
Java proporciona un mecanismo, llamado serialización de objetos, donde un objeto se puede representar como una secuencia de bytes que incluye los datos del objeto, así como información sobre el tipo de objeto y los tipos de datos almacenados en el objeto.
Después de escribir un objeto serializado en un archivo, se puede leer del archivo y deserializar, es decir, la información de tipo y los bytes que representan el objeto y sus datos se pueden usar para recrear el objeto en la memoria.
Lo más impresionante es que todo el proceso es independiente de JVM, lo que significa que un objeto puede serializarse en una plataforma y deserializarse en una plataforma completamente diferente.
Cómo crear un caché en memoria simple en Java (caché ligero)
Las clases ObjectInputStream y ObjectOutputStream son flujos de alto nivel que contienen los métodos para serializar y deserializar un objeto.
El siguiente tutorial funcionará también si tiene alguna de las siguientes preguntas:
- Cómo serializar y deserializar un objeto usando JSON
- Cómo serializar y deserializar un objeto en el ejemplo de Java
- Java serializa deserializa el objeto a la cadena xml
- Serializar y deserializar un árbol binario
- Serializar lista en Java
Aquí hay un ejemplo completo. Estos son los pasos:
- Crear Class Item() que implementa Serializable.
- En principal: cree 2 objetos de artículo.
- Agréguelo a ArrayList.
- Serialice el ArrayList. Archivo de pago para ver el flujo de bytes de un objeto. (Imagen inferior)
- Deserialice el flujo de bytes del mismo archivo para ver Object.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import java . io . FileInputStream ; import java . io . FileNotFoundException ; import java . io . FileOutputStream ; import java . io . IOException ; import java . io . ObjectInputStream ; import java . io . ObjectOutputStream ; import java . io . Serializable ; import java . util . ArrayList ; import java . util . List ; @SuppressWarnings ( "serial" ) public class CrunchifySerializeDeserialize implements Serializable { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws ClassNotFoundException { int i ; Item [ ] items = new Item [ 2 ] ; CrunchifySerializeDeserialize c = new CrunchifySerializeDeserialize ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { items [ i ] = c . new Item ( ) ; // create array } // hard-coded values of id, desc, cost, qty items [ 0 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM101" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setItemID ( "ITEM102" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setDesc ( "iPad" ) ; items [ 1 ] . setDesc ( "iPhone" ) ; items [ 0 ] . setCost ( 499 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setCost ( 599 ) ; items [ 0 ] . setQuantity ( 1 ) ; items [ 1 ] . setQuantity ( 3 ) ; System . out . println ( "Item Details....." ) ; for ( Item d : items ) { System . out . print ( d . getItemID ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getDesc ( ) ) ; System . out . print ( "\t" + d . getCost ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( "\t" + d . getQuantity ( ) ) ; } List <Item> obj ; obj = new ArrayList <Item> ( ) ; for ( i = 0 ; i < items . length ; i ++ ) { obj . add ( items [ i ] ) ; } // Let's serialize an Object try { FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream ( fileOut ) ; out . writeObject ( obj ) ; out . close ( ) ; fileOut . close ( ) ; System . out . println ( "\nSerialization Successful... Checkout your specified output file..\n" ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } // Let's deserialize an Object try { FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream ( "/Users/<UserName>/Downloads/CrunchifyTest/Crunchify_Test1.txt" ) ; ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream ( fileIn ) ; System . out . println ( "Deserialized Data: \n" + in . readObject ( ) . toString ( ) ) ; in . close ( ) ; fileIn . close ( ) ; } catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } public class Item implements Serializable { private String itemID ; private String desc ; private double cost ; private int quantity ; public Item ( ) { itemID = "" ; desc = "" ; cost = 0 ; quantity = 0 ; } public Item ( String id , String d , double c , int q ) { itemID = id ; desc = d ; cost = c ; quantity = q ; } /** * @return the itemID */ public String getItemID ( ) { return itemID ; } /** * @param itemID * the itemID to set */ public void setItemID ( String itemID ) { this . itemID = itemID ; } /** * @return the desc */ public String getDesc ( ) { return desc ; } /** * @param desc * the desc to set */ public void setDesc ( String desc ) { this . desc = desc ; } /** * @return the cost */ public double getCost ( ) { return cost ; } /** * @param cost * the cost to set */ public void setCost ( double cost ) { this . cost = cost ; } /** * @return the quantity */ public int getQuantity ( ) { return quantity ; } /** * @param quantity * the quantity to set */ public void setQuantity ( int quantity ) { this . quantity = quantity ; } /* * @see java.lang.Object#toString() */ @Override public String toString ( ) { return "Item [itemcrayon-h"> + itemID + ", desc=" + desc + ", cost=" + cost + ", quantity=" + quantity + "]" ; } } } |
Producción:

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Item Details . . . . . ITEM101 iPad 499.0 1 ITEM102 iPhone 599.0 3 Serialization Successful . . . Checkout your specified output file . . Deserialized Data : [ Item [ itemID = ITEM101 , desc = iPad , cost = 499.0 , quantity = 1 ] , Item [ itemID = ITEM102 , desc = iPhone , cost = 599.0 , quantity = 3 ] ] |
Lista de todos los Tutoriales de Java y Tutoriales de Spring MVC que podrían interesarle.
