如何在 Java 中从头开始实现 LinkedList 类
已发表: 2013-06-19
如果您实际上正在构建一个真正的生产系统,那么是的,如果您需要的东西在那里可用,您通常只需使用标准库中的东西。 也就是说,不要认为这是一个毫无意义的练习。
了解事物是如何工作的很好, understanding linked lists是了解更复杂数据结构的重要一步,其中许多数据结构在标准库中不存在。
创建链接列表的方式与 Java 集合 API 的创建方式之间存在一些差异。
Collections API 试图遵循更复杂的接口。 您的 LinkedList 将始终包含至少一个元素。
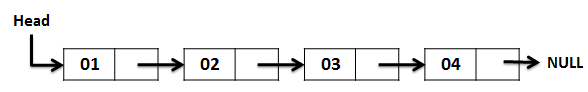
通过这种设置,您可以在需要空列表时使用 null。 将“下一个”视为“列表的其余部分”。 事实上,很多人会称它为tail而不是“下一个”。
这是一个单链表的示意图:
另一个必须阅读:
- 如何在 Java 中遍历 LinkedList 实例?
- Java:如何找到 LinkedList 的中间元素?
从头开始在 Java 中创建链表的最佳方法是什么?
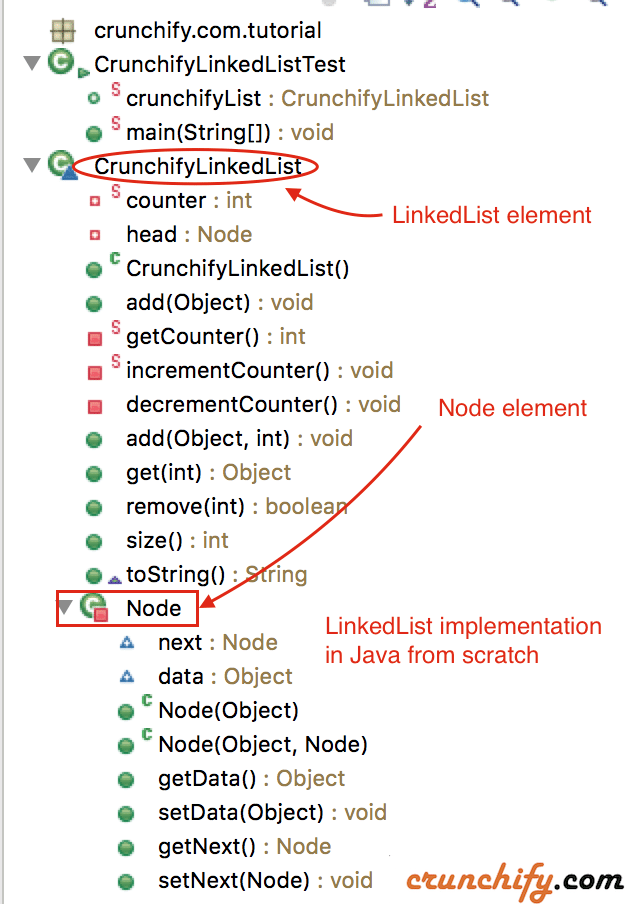
好吧,这里是 Java 中 LinkedList 类的最简单实现。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 |
package crunchify . com . tutorial ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * version: 1.2 * last updated: 11/10/2015 */ public class CrunchifyLinkedListTest { public static CrunchifyLinkedList crunchifyList ; public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { // Default constructor - let's put "0" into head element. crunchifyList = new CrunchifyLinkedList ( ) ; // add more elements to LinkedList crunchifyList . add ( "1" ) ; crunchifyList . add ( "2" ) ; crunchifyList . add ( "3" ) ; crunchifyList . add ( "4" ) ; crunchifyList . add ( "5" ) ; /* * Please note that primitive values can not be added into LinkedList directly. They must be converted to their * corresponding wrapper class. */ System . out . println ( "Print: crunchifyList: \t\t" + crunchifyList ) ; System . out . println ( ".size(): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList . size ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( ".get(3): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList . get ( 3 ) + " (get element at index:3 - list starts from 0)" ) ; System . out . println ( ".remove(2): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList . remove ( 2 ) + " (element removed)" ) ; System . out . println ( ".get(3): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList . get ( 3 ) + " (get element at index:3 - list starts from 0)" ) ; System . out . println ( ".size(): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList . size ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( "Print again: crunchifyList: \t" + crunchifyList ) ; } } class CrunchifyLinkedList { private static int counter ; private Node head ; // Default constructor public CrunchifyLinkedList ( ) { } // appends the specified element to the end of this list. public void add ( Object data ) { // Initialize Node only incase of 1st element if ( head == null ) { head = new Node ( data ) ; } Node crunchifyTemp = new Node ( data ) ; Node crunchifyCurrent = head ; // Let's check for NPE before iterate over crunchifyCurrent if ( crunchifyCurrent ! = null ) { // starting at the head node, crawl to the end of the list and then add element after last node while ( crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ! = null ) { crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ; } // the last node's "next" reference set to our new node crunchifyCurrent . setNext ( crunchifyTemp ) ; } // increment the number of elements variable incrementCounter ( ) ; } private static int getCounter ( ) { return counter ; } private static void incrementCounter ( ) { counter ++ ; } private void decrementCounter ( ) { counter -- ; } // inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list public void add ( Object data , int index ) { Node crunchifyTemp = new Node ( data ) ; Node crunchifyCurrent = head ; // Let's check for NPE before iterate over crunchifyCurrent if ( crunchifyCurrent ! = null ) { // crawl to the requested index or the last element in the list, whichever comes first for ( int i = 0 ; i < index && crunchifyCurrent.getNext() != null; i ++ ) { crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ; } } // set the new node's next-node reference to this node's next-node reference crunchifyTemp . setNext ( crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ) ; // now set this node's next-node reference to the new node crunchifyCurrent . setNext ( crunchifyTemp ) ; // increment the number of elements variable incrementCounter ( ) ; } public Object get ( int index ) // returns the element at the specified position in this list. { // index must be 1 or higher if ( index < 0 ) return null ; Node crunchifyCurrent = null ; if ( head ! = null ) { crunchifyCurrent = head . getNext ( ) ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++ ) { if ( crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) == null ) return null ; crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ; } return crunchifyCurrent . getData ( ) ; } return crunchifyCurrent ; } // removes the element at the specified position in this list. public boolean remove ( int index ) { // if the index is out of range, exit if ( index < 1 | | index > size ( ) ) return false ; Node crunchifyCurrent = head ; if ( head ! = null ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++ ) { if ( crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) == null ) return false ; crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ; } crunchifyCurrent . setNext ( crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) . getNext ( ) ) ; // decrement the number of elements variable decrementCounter ( ) ; return true ; } return false ; } // returns the number of elements in this list. public int size ( ) { return getCounter ( ) ; } public String toString ( ) { String output = "" ; if ( head ! = null ) { Node crunchifyCurrent = head . getNext ( ) ; while ( crunchifyCurrent ! = null ) { output += "[" + crunchifyCurrent . getData ( ) . toString ( ) + "]" ; crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent . getNext ( ) ; } } return output ; } private class Node { // reference to the next node in the chain, or null if there isn't one. Node next ; // data carried by this node. could be of any type you need. Object data ; // Node constructor public Node ( Object dataValue ) { next = null ; data = dataValue ; } // another Node constructor if we want to specify the node to point to. @SuppressWarnings ( "unused" ) public Node ( Object dataValue , Node nextValue ) { next = nextValue ; data = dataValue ; } // these methods should be self-explanatory public Object getData ( ) { return data ; } @SuppressWarnings ( "unused" ) public void setData ( Object dataValue ) { data = dataValue ; } public Node getNext ( ) { return next ; } public void setNext ( Node nextValue ) { next = nextValue ; } } } |
几样东西:
这里我们只在adding 1st element时初始化Node 。

|
1 2 3 4 |
// Initialize Node only incase of 1st element if ( head == null ) { head = new Node ( data ) ; } |
结果:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Print : crunchifyList : [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] . size ( ) : 5 . get ( 3 ) : 4 ( get element at index : 3 - list starts from 0 ) . remove ( 2 ) : true ( element removed ) . get ( 3 ) : 5 ( get element at index : 3 - list starts from 0 ) . size ( ) : 4 Print again : crunchifyList : [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] |
对此实现的增强包括使其成为double-linked list ,添加从中间或末尾insert和delete的方法,以及添加get和sort方法。
来自 Laurence Gonsalves 的 Stack Overflow 的参考答案。 您可能对所有 Java 教程的列表感兴趣。
