Java:ファクトリデザイン-メソッドパターン| オブジェクト指向デザイン| デザインパターン
公開: 2013-06-28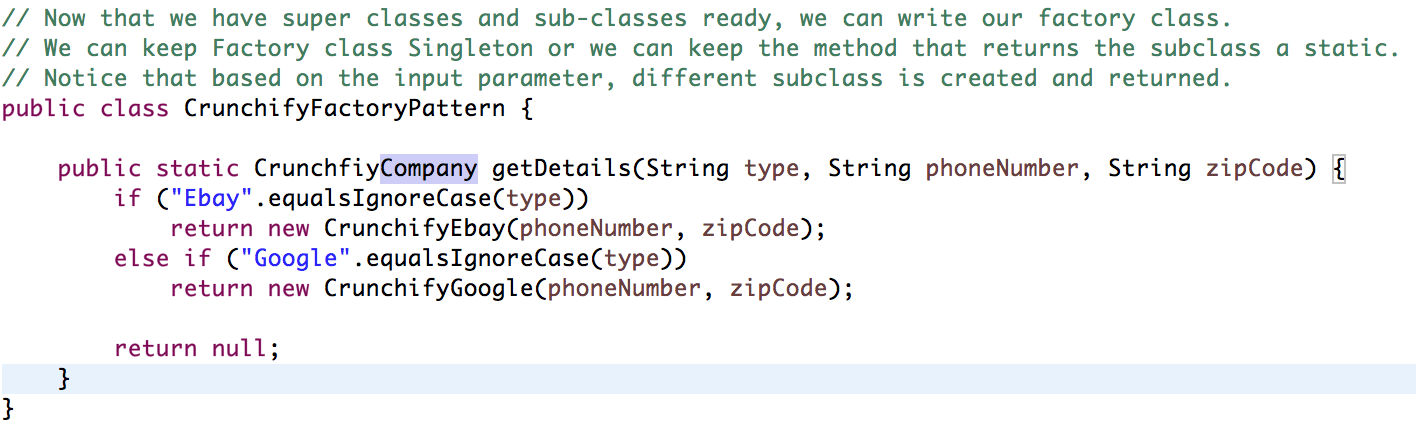
Factory Design Patternは、Creational Designパターンの1つであり、JDKだけでなく、SpringMVCやStrutsなどのフレームワークでも広く使用されています。 ファクトリメソッドパターンは、ファクトリの概念を実装するためのオブジェクト指向の作成デザインパターンであり、作成されるオブジェクトの正確なクラスを指定せずにオブジェクト(製品)を作成する問題に対処します。 このパターンの本質は、「オブジェクトを作成するためのインターフェースを定義しますが、インターフェースを実装するクラスに、インスタンス化するクラスを決定させることです。 Factoryメソッドを使用すると、クラスはインスタンス化をサブクラスに延期できます。

まず、Javaでファクトリパターンを実装する方法を学びましょう。 このパターンを実装するために5つのクラスを作成します。
- スーパークラス(CrunchfiyCompany.java)
- ファクトリパターンのスーパークラスは、インターフェイス、抽象クラス、または通常のJavaクラスにすることができます。 この例では、テスト目的で
toString()メソッドをオーバーライドした抽象クラスとしてスーパークラスがあります。
- ファクトリパターンのスーパークラスは、インターフェイス、抽象クラス、または通常のJavaクラスにすることができます。 この例では、テスト目的で
- サブクラス1(CrunchifyEbay.java)
- クラスがCrunchfiyCompanyクラスを拡張していることに注意してください。
- サブクラス2(CrunchifyGoogle.java)
- クラスがCrunchfiyCompanyクラスを拡張していることに注意してください。
- ファクトリクラス(CrunchifyFactoryPattern.java)
- スーパークラスとサブクラスの準備ができたので、ファクトリクラスを作成できます。
- FactoryクラスをSingletonに保つことも、サブクラスを返すメソッドを静的に保つこともできます。
- 入力パラメーターに基づいて、異なるサブクラスが作成されて返されることに注意してください。
- テストクラス(CrunchifyFactoryPatternTest.java)
- 上記のファクトリパターン実装を使用する単純なテストクライアントプログラム。
他の必読:
- Javaでのスレッドセーフで高速なシングルトン実装
- Javaのデーモンスレッドとは何ですか? 添付例
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ // Super class in factory pattern can be an interface, abstract class or a // normal java class. For our example, we have super class as abstract class // with overridden toString() method for testing purpose. public abstract class CrunchfiyCompany { public abstract String getPhoneNumber ( ) ; public abstract String getZipCode ( ) ; @Override public String toString ( ) { return "Phone #= " + this . getPhoneNumber ( ) + ", Zip Code= " + this . getZipCode ( ) ; } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ // Notice that the class is extending CrunchfiyCompany class. public class CrunchifyEbay extends CrunchfiyCompany { private String phoneNumber ; private String zipCode ; public CrunchifyEbay ( String phoneNumber , String zipCode ) { this . phoneNumber = phoneNumber ; this . zipCode = zipCode ; } @Override public String getPhoneNumber ( ) { return this . phoneNumber ; } @Override public String getZipCode ( ) { return this . zipCode ; } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ // Notice that the class is extending CrunchfiyCompany class. public class CrunchifyGoogle extends CrunchfiyCompany { private String phoneNumber ; private String zipCode ; public CrunchifyGoogle ( String phoneNumber , String zipCode ) { this . phoneNumber = phoneNumber ; this . zipCode = zipCode ; } @Override public String getPhoneNumber ( ) { return this . phoneNumber ; } @Override public String getZipCode ( ) { return this . zipCode ; } } |

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchfiyCompany ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchifyEbay ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchifyGoogle ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ // Now that we have super classes and sub-classes ready, we can write our factory class. // We can keep Factory class Singleton or we can keep the method that return the subclass a static. // Notice that based on the input parameter, different subclass is created and returned. public class CrunchifyFactoryPattern { public static CrunchfiyCompany getDetails ( String type , String phoneNumber , String zipCode ) { if ( "Ebay" . equalsIgnoreCase ( type ) ) return new CrunchifyEbay ( phoneNumber , zipCode ) ; else if ( "Google" . equalsIgnoreCase ( type ) ) return new CrunchifyGoogle ( phoneNumber , zipCode ) ; return null ; } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchfiyCompany ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchifyFactoryPattern ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ // Simple Test client program that uses above factory pattern implementation. public class CrunchifyFactoryPatternTest { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { CrunchfiyCompany eBay = CrunchifyFactoryPattern . getDetails ( "Ebay" , "408.123.4567" , "98765" ) ; CrunchfiyCompany google = CrunchifyFactoryPattern . getDetails ( "Google" , "519.123.4567" , "56789" ) ; System . out . println ( "Factory eBay Config::" + eBay ) ; System . out . println ( "Factory Google Config::" + google ) ; } } |
|
1 2 |
Factory eBay Config : : Phone #= 408.123.4567, Zip Code= 98765 Factory Google Config : : Phone #= 519.123.4567, Zip Code= 56789 |
ファクトリパターンを使用した他の例?
- java.util.Calendar、ResourceBundle、およびNumberFormat
getInstance()メソッドは、ファクトリパターンを使用します。 - ブール、整数などのラッパークラスの
valueOf()メソッド。
ファクトリパターンの利点:
- これは、複数のサブクラスを持つスーパークラスがあり、入力に基づいて、サブクラスの1つを返す必要がある場合に使用されます。 このパターンは、クライアントプログラムからファクトリクラスへのクラスのインスタンス化の責任を負います。
- ファクトリパターンは、実装ではなくインターフェイスのコードへのアプローチを提供します。
- ファクトリパターンは、クライアントコードから実際の実装クラスのインスタンス化を削除し、より堅牢で、結合度が低く、拡張が容易になります。 たとえば、クライアントプログラムはこれを認識しないため、PCクラスの実装を簡単に変更できます。
- ファクトリパターンは、継承を通じて実装クラスとクライアントクラスの間の抽象化を提供します。
欠点:
- ファクトリは、オブジェクトのファミリに使用する必要があります。 クラスが共通の基本クラスまたはインターフェイスを拡張しない場合、ファクトリデザインテンプレートで使用することはできません。
すべてのJavaWeb開発、SpringMVCチュートリアルのリスト。
