多合一 Java 正則表達式、匹配器模式和正則表達式教程
已發表: 2021-09-29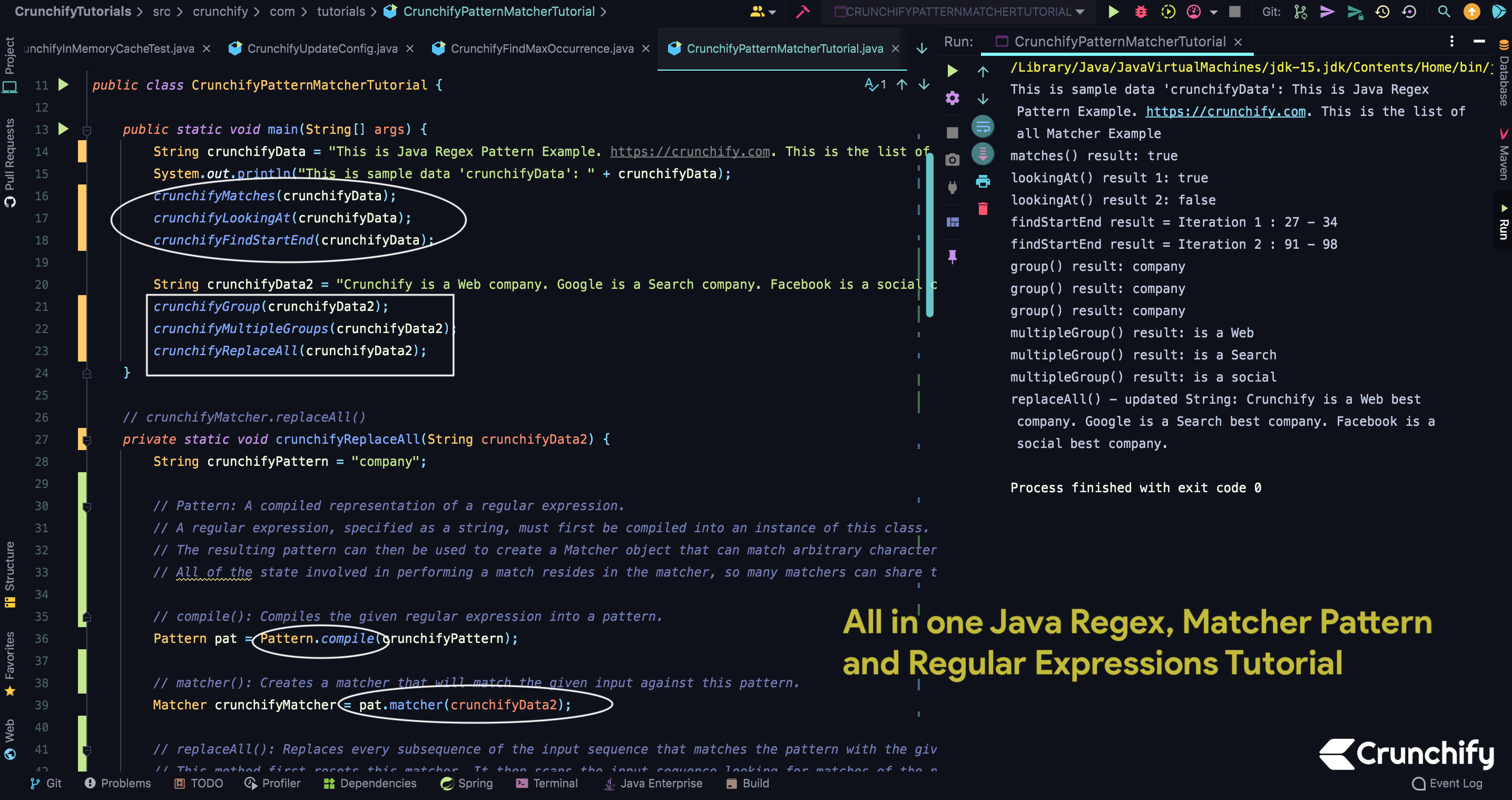
在本教程中,我們將介紹 Matcher ( java.util.regex.Matcher ) API 的列表。 前一段時間,我寫了一篇關於 Java Regex 的教程,其中涵蓋了各種各樣的示例。
正則表達式是字符串的一種搜索模式。 java.util.regex用於將字符序列與 Java 中正則表達式指定的模式進行匹配的類。
如果您有以下任何問題,本教程最有效:
- Java 正則表達式 - 教程
- Java 正則表達式教程
- Java中的正則表達式是什麼?
- Java中的模式是什麼?
- java模式匹配器示例和java正則表達式特殊字符
讓我們開始吧。
- 創建類
CrunchifyPatternMatcherTutorial.java - 創建不同的方法來檢查以下 Matcher API:
- 火柴()
- 看著()
- 查找開始結束()
- 團體()
- 多組()
- 全部替換()
- 打印每個 API 的結果。
火柴()
matches()嘗試將整個字符串與模式匹配。 當且only if整個區域序列與此匹配器的模式匹配時,它才返回true 。
看著()
lookingAt() 功能與matches() 完全相同,只是它嘗試匹配輸入序列,從區域的開頭開始,與模式匹配。 當且僅當輸入序列的前綴與此匹配器的模式匹配時,它才返回 true。
查找(),開始()和結束()
find()嘗試查找與模式匹配的輸入序列的下一個子序列。 start()嘗試返回前一個匹配的開始索引, end()嘗試返回前一個匹配的結束索引。
團體()
group()返回與前一個匹配項匹配的輸入子序列。 這就像 start() 和 end() 之間的匹配。
多組
multiplegroups組可以用“(字符串)(字符串)”表示。
示例: String crunchifyPattern = "(is) (.+?) (.+?) " ;
全部替換()
replaceAll()用給定的替換字符串替換與模式匹配的輸入序列的每個子序列。
這是一個完整的例子:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . util . regex . Matcher ; import java . util . regex . Pattern ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * All in one Java Regex, Matcher Pattern and Regular Expressions Tutorial. */ public class CrunchifyPatternMatcherTutorial { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { String crunchifyData = "This is Java Regex Pattern Example. https://crunchify.com. This is the list of all Matcher Example" ; System . out . println ( "This is sample data 'crunchifyData': " + crunchifyData ) ; crunchifyMatches ( crunchifyData ) ; crunchifyLookingAt ( crunchifyData ) ; crunchifyFindStartEnd ( crunchifyData ) ; String crunchifyData2 = "Crunchify is a Web company. Google is a Search company. Facebook is a social company." ; crunchifyGroup ( crunchifyData2 ) ; crunchifyMultipleGroups ( crunchifyData2 ) ; crunchifyReplaceAll ( crunchifyData2 ) ; } // crunchifyMatcher.replaceAll() private static void crunchifyReplaceAll ( String crunchifyData2 ) { String crunchifyPattern = "company" ; // Pattern: A compiled representation of a regular expression. // A regular expression, specified as a string, must first be compiled into an instance of this class. // The resulting pattern can then be used to create a Matcher object that can match arbitrary character sequences against the regular expression. // All of the state involved in performing a match resides in the matcher, so many matchers can share the same pattern. // compile(): Compiles the given regular expression into a pattern. Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; // matcher(): Creates a matcher that will match the given input against this pattern. Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData2 ) ; // replaceAll(): Replaces every subsequence of the input sequence that matches the pattern with the given replacement string. // This method first resets this matcher. It then scans the input sequence looking for matches of the pattern. Characters that are not part of any match are appended directly to the result string; each match is replaced in the result by the replacement string. // The replacement string may contain references to captured subsequences as in the appendReplacement method. String updatedString = crunchifyMatcher . replaceAll ( "best company" ) ; System . out . println ( "replaceAll() - updated String: " + updatedString ) ; } private static void crunchifyMultipleGroups ( String crunchifyData2 ) { String crunchifyPattern = "(is) (.+?) (.+?) " ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData2 ) ; // find(): Attempts to find the next subsequence of the input sequence that matches the pattern. while ( crunchifyMatcher . find ( ) ) { // group(): Returns the input subsequence matched by the previous match. // For a matcher m with input sequence s, the expressions m.group() and s.substring(m.start(), m. end()) are equivalent. // Note that some patterns, for example a*, match the empty string. // This method will return the empty string when the pattern successfully matches the empty string in the input. System . out . println ( "multipleGroup() result: " + crunchifyMatcher . group ( ) ) ; } } // crunchifyMatcher.group() private static void crunchifyGroup ( String crunchifyData2 ) { String crunchifyPattern = "company" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData2 ) ; while ( crunchifyMatcher . find ( ) ) { System . out . println ( "group() result: " + crunchifyMatcher . group ( ) ) ; } } // crunchifyMatcher.find() - start() - end() private static void crunchifyFindStartEnd ( String crunchifyData ) { String crunchifyPattern = "Example" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; int totalCount = 0 ; while ( crunchifyMatcher . find ( ) ) { totalCount ++ ; // start(): Returns the start index of the previous match. // end(): Returns the offset after the last character matched. System . out . println ( "findStartEnd result = Iteration " + totalCount + " : " + crunchifyMatcher . start ( ) + " - " + crunchifyMatcher . end ( ) ) ; } } // crunchifyMatcher.lookingAt() private static void crunchifyLookingAt ( String crunchifyData ) { String crunchifyPattern = "This is Java" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; // lookingAt(): Attempts to match the input sequence, starting at the beginning of the region, against the pattern. boolean isLookingAt = crunchifyMatcher . lookingAt ( ) ; System . out . println ( "lookingAt() result 1: " + isLookingAt ) ; crunchifyPattern = " is Java" ; pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; isLookingAt = crunchifyMatcher . lookingAt ( ) ; System . out . println ( "lookingAt() result 2: " + isLookingAt ) ; } // crunchifyMatcher.matches() public static void crunchifyMatches ( String crunchifyData ) { String crunchifyPattern = ".*https://.*" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; boolean isMatched = crunchifyMatcher . matches ( ) ; System . out . println ( "matches() result: " + isMatched ) ; } } |
Eclipse 控制台結果:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
This is sample data 'crunchifyData' : This is Java Regex Pattern Example . https : //crunchify.com. This is the list of all Matcher Example matches ( ) result : true lookingAt ( ) result 1 : true lookingAt ( ) result 2 : false findStartEnd result = Iteration 1 : 27 - 34 findStartEnd result = Iteration 2 : 90 - 97 group ( ) result : company group ( ) result : company group ( ) result : company multipleGroup ( ) result : is a Web multipleGroup ( ) result : is a Search multipleGroup ( ) result : is a social replaceAll ( ) - updated String : Crunchify is a Web best company . Google is a Search best company . Facebook is a social best company . |
如果您對上述程序有任何疑問,請告訴我。

