Todo en uno Java Regex, Matcher Pattern y Regular Expressions Tutorial
Publicado: 2021-09-29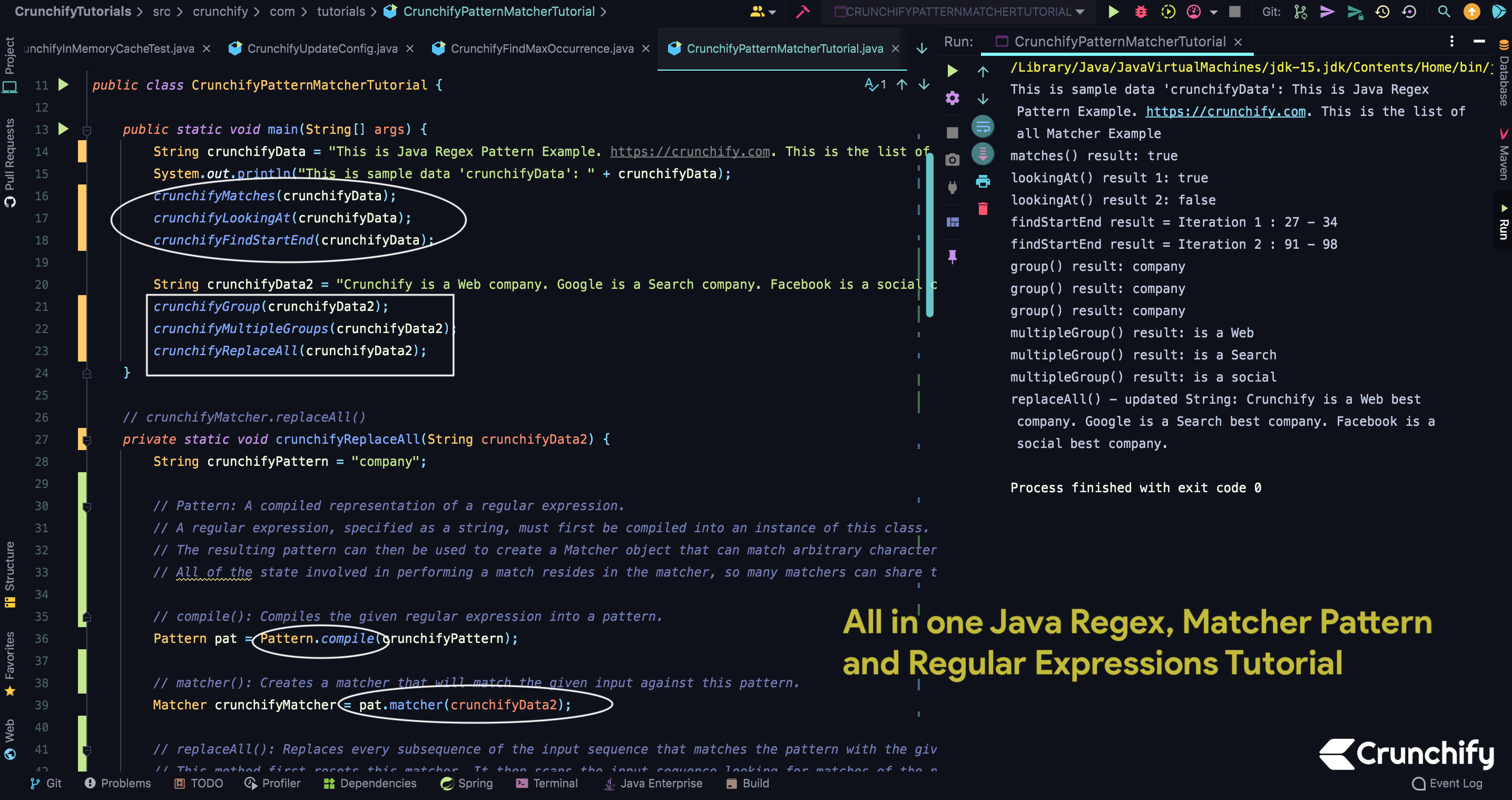
En este tutorial repasaremos la lista de API de Matcher ( java.util.regex.Matcher ). Hace algún tiempo escribí un tutorial sobre Java Regex que cubre una amplia variedad de muestras.
Regular Expression es un patrón de búsqueda para String. java.util.regex Clases para hacer coincidir secuencias de caracteres con patrones especificados por expresiones regulares en Java.
Este tutorial funciona mejor si tiene alguna de las siguientes preguntas:
- Expresiones regulares de Java – Tutorial
- Tutoriales de expresiones regulares de Java
- ¿Qué es la expresión regular en Java?
- ¿Qué es un patrón en Java?
- Ejemplo de comparación de patrones de Java y caracteres especiales de expresiones regulares de Java
Empecemos.
- Crear clase
CrunchifyPatternMatcherTutorial.java - Cree diferentes métodos para verificar las siguientes API de Matcher:
- partidos()
- mirando a()
- buscarInicioFinal()
- grupo()
- multipleGroups()
- reemplaza todo()
- Imprime el resultado de cada API.
partidos()
matches() intenta hacer coincidir la cadena completa con el patrón. Devuelve true si, y only if , toda la secuencia de la región coincide con el patrón de este comparador.
mirando a()
La funcionalidad lookingAt() es exactamente igual que matches() excepto que intenta hacer coincidir la secuencia de entrada, comenzando al principio de la región, contra el patrón. Devuelve verdadero si, y solo si, un prefijo de la secuencia de entrada coincide con el patrón de este comparador.
buscar (), iniciar () y finalizar ()
find() intenta encontrar la siguiente subsecuencia de la secuencia de entrada que coincida con el patrón. start() intenta devolver el índice de inicio de la coincidencia anterior y end() intenta devolver el índice final de la coincidencia anterior.
grupo()
group() devuelve la subsecuencia de entrada que coincide con la coincidencia anterior. Es como una coincidencia entre start() y end().
grupos múltiples
multiplegroups podrían representarse mediante “(String) (String)”.
Ejemplo: String crunchifyPattern = "(is) (.+?) (.+?) " ;
reemplaza todo()
replaceAll() reemplaza cada subsecuencia de la secuencia de entrada que coincide con el patrón con la cadena de reemplazo dada.
Aquí hay un ejemplo completo:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . util . regex . Matcher ; import java . util . regex . Pattern ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * All in one Java Regex, Matcher Pattern and Regular Expressions Tutorial. */ public class CrunchifyPatternMatcherTutorial { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { String crunchifyData = "This is Java Regex Pattern Example. https://crunchify.com. This is the list of all Matcher Example" ; System . out . println ( "This is sample data 'crunchifyData': " + crunchifyData ) ; crunchifyMatches ( crunchifyData ) ; crunchifyLookingAt ( crunchifyData ) ; crunchifyFindStartEnd ( crunchifyData ) ; String crunchifyData2 = "Crunchify is a Web company. Google is a Search company. Facebook is a social company." ; crunchifyGroup ( crunchifyData2 ) ; crunchifyMultipleGroups ( crunchifyData2 ) ; crunchifyReplaceAll ( crunchifyData2 ) ; } // crunchifyMatcher.replaceAll() private static void crunchifyReplaceAll ( String crunchifyData2 ) { String crunchifyPattern = "company" ; // Pattern: A compiled representation of a regular expression. // A regular expression, specified as a string, must first be compiled into an instance of this class. // The resulting pattern can then be used to create a Matcher object that can match arbitrary character sequences against the regular expression. // All of the state involved in performing a match resides in the matcher, so many matchers can share the same pattern. // compile(): Compiles the given regular expression into a pattern. Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; // matcher(): Creates a matcher that will match the given input against this pattern. Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData2 ) ; // replaceAll(): Replaces every subsequence of the input sequence that matches the pattern with the given replacement string. // This method first resets this matcher. It then scans the input sequence looking for matches of the pattern. Characters that are not part of any match are appended directly to the result string; each match is replaced in the result by the replacement string. // The replacement string may contain references to captured subsequences as in the appendReplacement method. String updatedString = crunchifyMatcher . replaceAll ( "best company" ) ; System . out . println ( "replaceAll() - updated String: " + updatedString ) ; } private static void crunchifyMultipleGroups ( String crunchifyData2 ) { String crunchifyPattern = "(is) (.+?) (.+?) " ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData2 ) ; // find(): Attempts to find the next subsequence of the input sequence that matches the pattern. while ( crunchifyMatcher . find ( ) ) { // group(): Returns the input subsequence matched by the previous match. // For a matcher m with input sequence s, the expressions m.group() and s.substring(m.start(), m. end()) are equivalent. // Note that some patterns, for example a*, match the empty string. // This method will return the empty string when the pattern successfully matches the empty string in the input. System . out . println ( "multipleGroup() result: " + crunchifyMatcher . group ( ) ) ; } } // crunchifyMatcher.group() private static void crunchifyGroup ( String crunchifyData2 ) { String crunchifyPattern = "company" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData2 ) ; while ( crunchifyMatcher . find ( ) ) { System . out . println ( "group() result: " + crunchifyMatcher . group ( ) ) ; } } // crunchifyMatcher.find() - start() - end() private static void crunchifyFindStartEnd ( String crunchifyData ) { String crunchifyPattern = "Example" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; int totalCount = 0 ; while ( crunchifyMatcher . find ( ) ) { totalCount ++ ; // start(): Returns the start index of the previous match. // end(): Returns the offset after the last character matched. System . out . println ( "findStartEnd result = Iteration " + totalCount + " : " + crunchifyMatcher . start ( ) + " - " + crunchifyMatcher . end ( ) ) ; } } // crunchifyMatcher.lookingAt() private static void crunchifyLookingAt ( String crunchifyData ) { String crunchifyPattern = "This is Java" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; // lookingAt(): Attempts to match the input sequence, starting at the beginning of the region, against the pattern. boolean isLookingAt = crunchifyMatcher . lookingAt ( ) ; System . out . println ( "lookingAt() result 1: " + isLookingAt ) ; crunchifyPattern = " is Java" ; pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; isLookingAt = crunchifyMatcher . lookingAt ( ) ; System . out . println ( "lookingAt() result 2: " + isLookingAt ) ; } // crunchifyMatcher.matches() public static void crunchifyMatches ( String crunchifyData ) { String crunchifyPattern = ".*https://.*" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; boolean isMatched = crunchifyMatcher . matches ( ) ; System . out . println ( "matches() result: " + isMatched ) ; } } |
Resultado de la consola de Eclipse:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
This is sample data 'crunchifyData' : This is Java Regex Pattern Example . https : //crunchify.com. This is the list of all Matcher Example matches ( ) result : true lookingAt ( ) result 1 : true lookingAt ( ) result 2 : false findStartEnd result = Iteration 1 : 27 - 34 findStartEnd result = Iteration 2 : 90 - 97 group ( ) result : company group ( ) result : company group ( ) result : company multipleGroup ( ) result : is a Web multipleGroup ( ) result : is a Search multipleGroup ( ) result : is a social replaceAll ( ) - updated String : Crunchify is a Web best company . Google is a Search best company . Facebook is a social best company . |
Avíseme si tiene alguna pregunta sobre el programa anterior.

