하나의 Java Regex, Matcher 패턴 및 정규식 자습서의 모든 것
게시 됨: 2021-09-29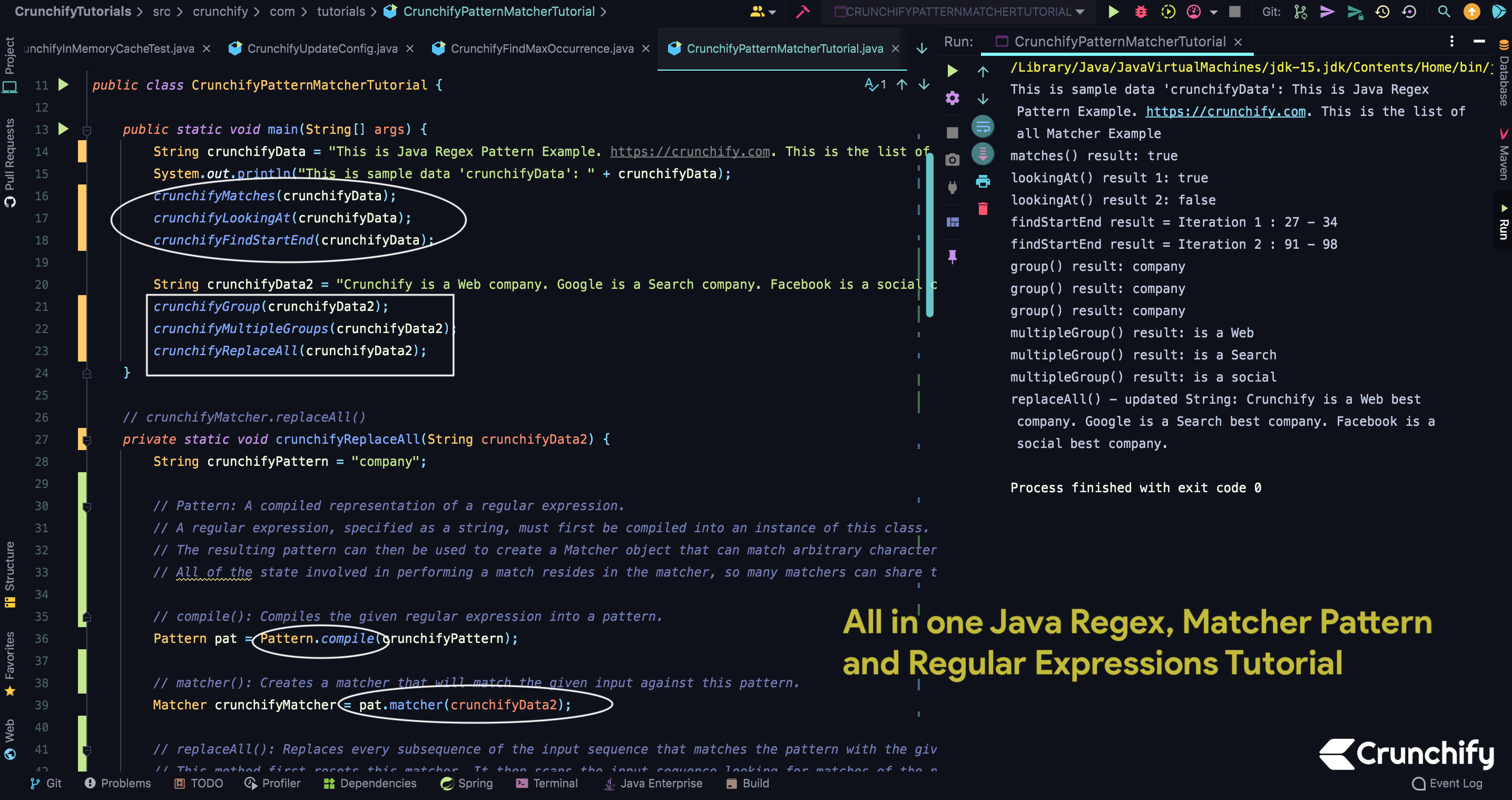
이 튜토리얼에서는 Matcher( java.util.regex.Matcher ) API 목록을 살펴볼 것입니다. 언젠가 나는 다양한 샘플을 다루는 Java Regex에 대한 튜토리얼을 작성했습니다.
정규식은 문자열에 대한 검색 패턴입니다. java.util.regex Java의 정규식으로 지정된 패턴에 대해 문자 시퀀스를 일치시키기 위한 클래스입니다.
이 자습서는 아래 질문 중 하나라도 있는 경우 가장 잘 작동합니다.
- 자바 정규식 – 튜토리얼
- 자바 정규 표현식 튜토리얼
- Java에서 정규 표현식이란 무엇입니까?
- 자바에서 패턴이란?
- Java 패턴 일치자 예제 및 Java 정규식 특수 문자
시작하자.
-
CrunchifyPatternMatcherTutorial.java클래스 생성 - 아래의 Matcher API를 확인하는 다른 메소드를 작성하십시오.
- 성냥()
- 바라보는()
- 찾기 시작 종료()
- 그룹()
- 다중 그룹()
- 전부 교체()
- 각 API의 결과를 출력합니다.
성냥()
matches() 는 패턴에 대해 전체 문자열을 일치시키려고 시도합니다. 전체 영역 시퀀스가 이 매처의 패턴과 일치하는 only if true 를 반환합니다.
바라보는()
lookAt() 기능은 패턴에 대해 영역의 시작 부분에서 시작하여 입력 시퀀스를 일치시키려는 것을 제외하고 Matches()와 정확히 동일합니다. 입력 시퀀스의 접두사가 이 매처의 패턴과 일치하는 경우에만 true를 반환합니다.
찾기(), 시작() 및 끝()
find() 는 패턴과 일치하는 입력 시퀀스의 다음 하위 시퀀스를 찾으려고 시도합니다. start() 는 이전 일치의 시작 인덱스를 반환하려고 시도하고 end() 는 이전 일치의 끝 인덱스를 반환하려고 시도합니다.
그룹()
group() 은 이전 일치 항목과 일치하는 입력 하위 시퀀스를 반환합니다. start()와 end() 사이의 일치와 같습니다.
다중 그룹
multiplegroups 그룹은 "(문자열) (문자열)"로 나타낼 수 있습니다.
샘플: String crunchifyPattern = "(is) (.+?) (.+?) " ;
전부 교체()
replaceAll() 은 패턴과 일치하는 입력 시퀀스의 모든 하위 시퀀스를 주어진 대체 문자열로 바꿉니다.
다음은 완전한 예입니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . util . regex . Matcher ; import java . util . regex . Pattern ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * All in one Java Regex, Matcher Pattern and Regular Expressions Tutorial. */ public class CrunchifyPatternMatcherTutorial { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { String crunchifyData = "This is Java Regex Pattern Example. https://crunchify.com. This is the list of all Matcher Example" ; System . out . println ( "This is sample data 'crunchifyData': " + crunchifyData ) ; crunchifyMatches ( crunchifyData ) ; crunchifyLookingAt ( crunchifyData ) ; crunchifyFindStartEnd ( crunchifyData ) ; String crunchifyData2 = "Crunchify is a Web company. Google is a Search company. Facebook is a social company." ; crunchifyGroup ( crunchifyData2 ) ; crunchifyMultipleGroups ( crunchifyData2 ) ; crunchifyReplaceAll ( crunchifyData2 ) ; } // crunchifyMatcher.replaceAll() private static void crunchifyReplaceAll ( String crunchifyData2 ) { String crunchifyPattern = "company" ; // Pattern: A compiled representation of a regular expression. // A regular expression, specified as a string, must first be compiled into an instance of this class. // The resulting pattern can then be used to create a Matcher object that can match arbitrary character sequences against the regular expression. // All of the state involved in performing a match resides in the matcher, so many matchers can share the same pattern. // compile(): Compiles the given regular expression into a pattern. Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; // matcher(): Creates a matcher that will match the given input against this pattern. Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData2 ) ; // replaceAll(): Replaces every subsequence of the input sequence that matches the pattern with the given replacement string. // This method first resets this matcher. It then scans the input sequence looking for matches of the pattern. Characters that are not part of any match are appended directly to the result string; each match is replaced in the result by the replacement string. // The replacement string may contain references to captured subsequences as in the appendReplacement method. String updatedString = crunchifyMatcher . replaceAll ( "best company" ) ; System . out . println ( "replaceAll() - updated String: " + updatedString ) ; } private static void crunchifyMultipleGroups ( String crunchifyData2 ) { String crunchifyPattern = "(is) (.+?) (.+?) " ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData2 ) ; // find(): Attempts to find the next subsequence of the input sequence that matches the pattern. while ( crunchifyMatcher . find ( ) ) { // group(): Returns the input subsequence matched by the previous match. // For a matcher m with input sequence s, the expressions m.group() and s.substring(m.start(), m. end()) are equivalent. // Note that some patterns, for example a*, match the empty string. // This method will return the empty string when the pattern successfully matches the empty string in the input. System . out . println ( "multipleGroup() result: " + crunchifyMatcher . group ( ) ) ; } } // crunchifyMatcher.group() private static void crunchifyGroup ( String crunchifyData2 ) { String crunchifyPattern = "company" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData2 ) ; while ( crunchifyMatcher . find ( ) ) { System . out . println ( "group() result: " + crunchifyMatcher . group ( ) ) ; } } // crunchifyMatcher.find() - start() - end() private static void crunchifyFindStartEnd ( String crunchifyData ) { String crunchifyPattern = "Example" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; int totalCount = 0 ; while ( crunchifyMatcher . find ( ) ) { totalCount ++ ; // start(): Returns the start index of the previous match. // end(): Returns the offset after the last character matched. System . out . println ( "findStartEnd result = Iteration " + totalCount + " : " + crunchifyMatcher . start ( ) + " - " + crunchifyMatcher . end ( ) ) ; } } // crunchifyMatcher.lookingAt() private static void crunchifyLookingAt ( String crunchifyData ) { String crunchifyPattern = "This is Java" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; // lookingAt(): Attempts to match the input sequence, starting at the beginning of the region, against the pattern. boolean isLookingAt = crunchifyMatcher . lookingAt ( ) ; System . out . println ( "lookingAt() result 1: " + isLookingAt ) ; crunchifyPattern = " is Java" ; pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; isLookingAt = crunchifyMatcher . lookingAt ( ) ; System . out . println ( "lookingAt() result 2: " + isLookingAt ) ; } // crunchifyMatcher.matches() public static void crunchifyMatches ( String crunchifyData ) { String crunchifyPattern = ".*https://.*" ; Pattern pat = Pattern . compile ( crunchifyPattern ) ; Matcher crunchifyMatcher = pat . matcher ( crunchifyData ) ; boolean isMatched = crunchifyMatcher . matches ( ) ; System . out . println ( "matches() result: " + isMatched ) ; } } |
Eclipse 콘솔 결과:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
This is sample data 'crunchifyData' : This is Java Regex Pattern Example . https : //crunchify.com. This is the list of all Matcher Example matches ( ) result : true lookingAt ( ) result 1 : true lookingAt ( ) result 2 : false findStartEnd result = Iteration 1 : 27 - 34 findStartEnd result = Iteration 2 : 90 - 97 group ( ) result : company group ( ) result : company group ( ) result : company multipleGroup ( ) result : is a Web multipleGroup ( ) result : is a Search multipleGroup ( ) result : is a social replaceAll ( ) - updated String : Crunchify is a Web best company . Google is a Search best company . Facebook is a social best company . |
위의 프로그램을 실행하는 데 질문이 있으면 알려주십시오.

