Java 静态方法、类、变量和块的基础知识
已发表: 2019-12-13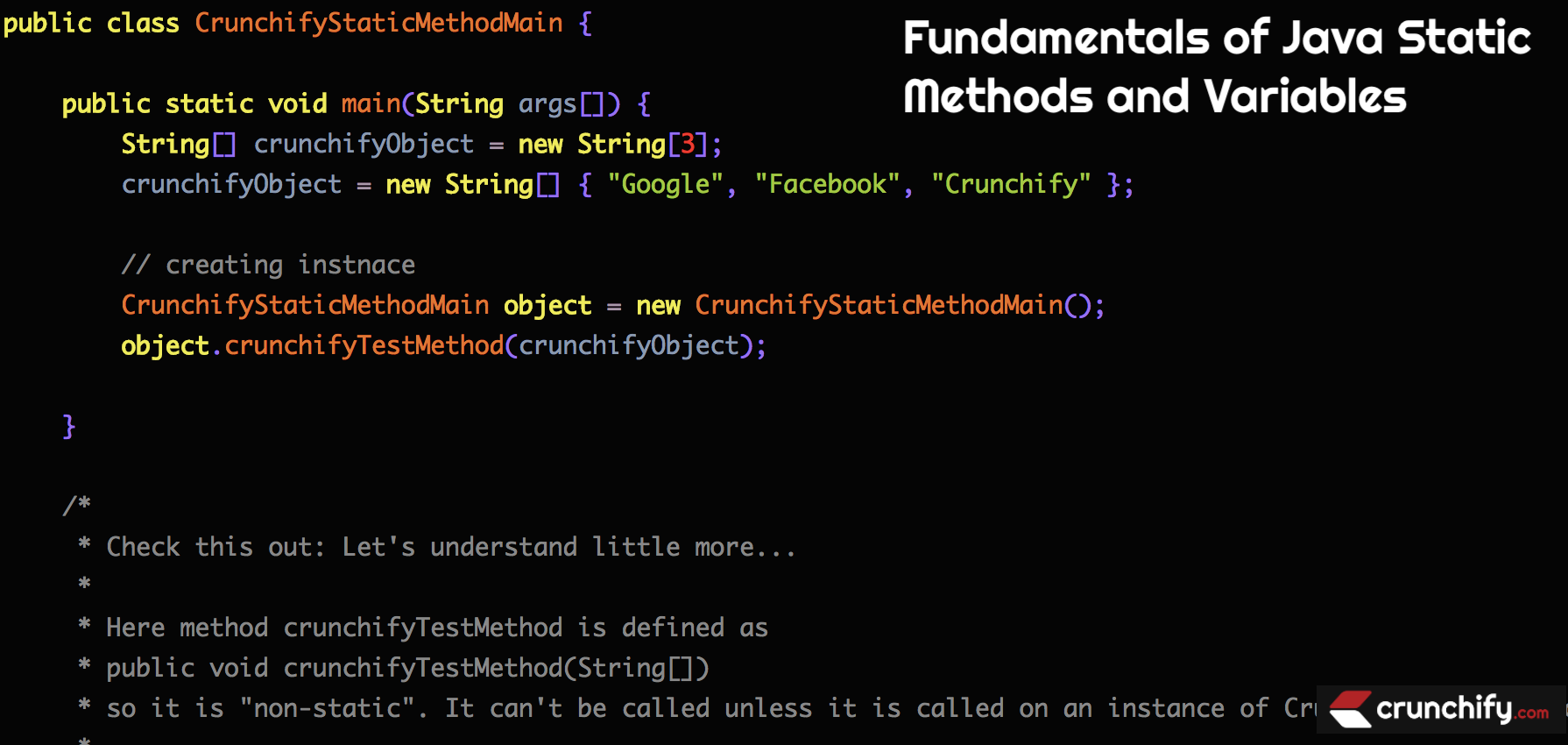
Java中的静态是什么?
- static 关键字可以与类、变量、方法和块一起使用。
- 静态成员不属于任何特定实例。
- 静态成员仅属于该类。
- 将成员设为静态后,您可以在没有任何对象的情况下访问它。
您有以下任何问题吗?
- 你能写下 Java 静态方法的最佳实践吗?
- 什么是接口中的 Java 静态方法?
- 对 Java 静态方法与单例有疑问吗?
- Java 静态方法与实例方法的性能
- Java 静态方法和变量
- Java 静态方法与非静态方法
- 抽象类中的 Java 静态方法
static 关键字可用于 3 种场景:
- 静态变量
- 静态方法
- 静态代码块。
静态变量(“静态”关键字 = 类变量)
在 Java 中,可以使用“ static ”关键字声明变量。
示例: static int y = 0;
当使用关键字static声明变量时,它被称为class variable 。 所有实例共享同一个变量副本。 类变量可以直接用类访问,而不需要创建实例。
没有“静态”关键字 = 实例变量
没有static keyword ,它被称为instance variable ,并且类的每个实例都有自己的变量副本。
示例:静态 int crunchify_variable_name ;
- 静态变量在类的所有实例之间共享。
- 当您想要进行大量内存管理时,您需要它的主要原因之一。
- 对于所有静态变量——只有一个副本可供您使用。
- 您绝对不需要类对象来访问静态变量。
- 直接用就行了。 你不需要
object.StaticVariable
- 直接用就行了。 你不需要
什么是静态块?
静态块是Java class中的语句块,将在类首次加载到 JVM 时执行。
你可以覆盖Java中的私有方法吗?
- 嗯,不。 私有方法不能被覆盖,因为它不能在类外使用。
为什么我们不能覆盖 Java 中的静态方法?
- 静态方法也不能被覆盖,因为它是类而不是对象的一部分
我们可以在静态上下文中访问非静态变量吗?
- 为了能够从您的静态方法访问非静态变量,它们需要是静态成员变量。
静态方法的详细信息
- 如何识别? 只需先检查一下。 你需要一个类对象来访问静态方法吗? 如果你不需要一个对象,那么它就是静态方法。
- 您需要使用 static 关键字来指定静态方法
- 如果该方法在运行时不会在整个项目中发生变化,则最好使用关键字 static。
- 您不能覆盖静态方法。
我们来看看下面的例子:
示例 1:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyStaticMethodMain { public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { String [ ] crunchifyObject = new String [ 3 ] ; crunchifyObject = new String [ ] { "Google" , "Facebook" , "Crunchify" } ; // creating instnace CrunchifyStaticMethodMain object = new CrunchifyStaticMethodMain ( ) ; object . crunchifyTestMethod ( crunchifyObject ) ; } /* * Check this out: Let's understand little more... * * Here method crunchifyTestMethod is defined as * public void crunchifyTestMethod(String[]) * so it is "non-static". It can't be called unless it is called on an instance of CrunchifyStaticMethodMain. * * If you declared your method as * public static void crunchifyTestMethod(int[]) * then you could call: CrunchifyStaticMethodMain.crunchifyTestMethod(arr); within main without having created an instance for it. */ public void crunchifyTestMethod ( String [ ] crunchifyObject ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyObject . length ; i ++ ) System . out . println ( crunchifyObject [ i ] ) ; } } |
查看above code block中的解释。 我们必须创建 Class 的实例来访问非静态方法。
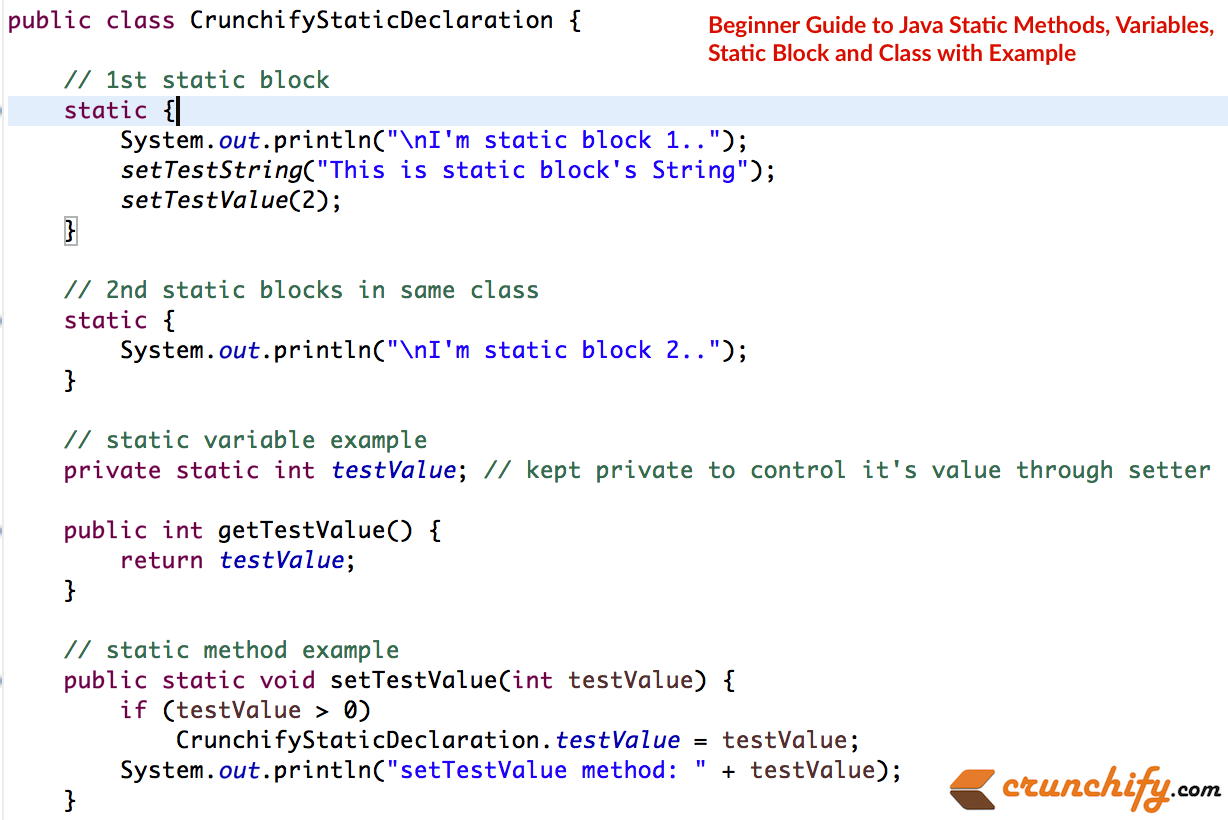
示例 2:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyStaticDeclaration { // 1st static block static { System . out . println ( "\nI'm static block 1.." ) ; setTestString ( "This is static block's String" ) ; setTestValue ( 2 ) ; } // 2nd static blocks in same class static { System . out . println ( "\nI'm static block 2.." ) ; } // static variable example private static int testValue ; // kept private to control it's value through setter public int getTestValue ( ) { return testValue ; } // static method example public static void setTestValue ( int testValue ) { if ( testValue > 0 ) CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testValue = testValue ; System . out . println ( "setTestValue method: " + testValue ) ; } public static String testString ; /** * @return the testString */ public static String getTestString ( ) { return testString ; } /** * @param testString the testString to set */ public static void setTestString ( String testString ) { CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString = testString ; System . out . println ( "setTestString method: " + testString ) ; } // static util method public static int subValue ( int i , int . . . js ) { int sum = i ; for ( int x : js ) sum -= x ; return sum ; } } |
现在让我们进行测试:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyStaticExample { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . setTestValue ( 5 ) ; // non-private static variables can be accessed with class name CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString = "\nAssigning testString a value" ; CrunchifyStaticDeclaration csd = new CrunchifyStaticDeclaration ( ) ; System . out . println ( csd . getTestString ( ) ) ; // class and instance static variables are same System . out . print ( "\nCheck if Class and Instance Static Variables are same: " ) ; System . out . println ( CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString == csd . testString ) ; System . out . println ( "Why? Because: CrunchifyStaticDeclaration.testString == csd.testString" ) ; } } |
输出:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
I 'm static block 1.. setTestString method: This is static block' s String setTestValue method : 2 I ' m static block 2.. setTestValue method : 5 Assigning testString a value Check if Class and Instance Static Variables are same : true Why ? Because : CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString == csd . testString |
我希望你真的能得到关于静态方法、变量和块的好信息。

如果您在运行以上程序时遇到任何问题或在理解 Java 中的静态关键字时遇到问题,请告诉我们。
