พื้นฐานของ Java Static Method, Class, Variable และ Block
เผยแพร่แล้ว: 2019-12-13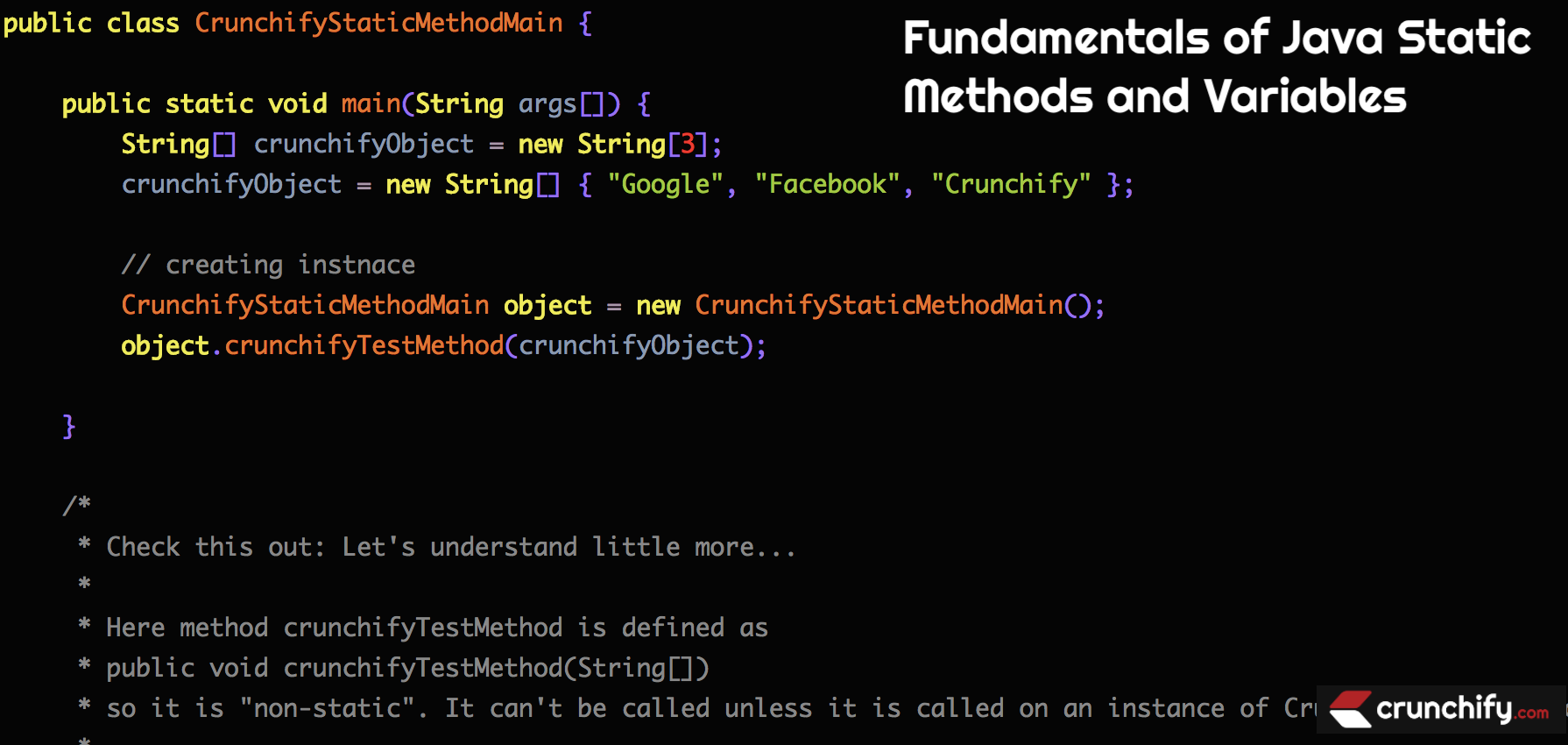
สแตติกใน Java คืออะไร?
- คำหลักแบบสแตติกสามารถใช้กับคลาส ตัวแปร เมธอด และบล็อก
- สมาชิกแบบคงที่ไม่ได้อยู่ในอินสแตนซ์ใด ๆ ที่เฉพาะเจาะจง
- สมาชิกแบบคงที่เป็นของชั้นเรียนเท่านั้น
- เมื่อคุณทำให้สมาชิกเป็นแบบคงที่ คุณจะสามารถเข้าถึงได้โดยไม่ต้องมีวัตถุใดๆ
คุณมีคำถามด้านล่างหรือไม่?
- คุณช่วยเขียนแนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดของ Java static method ได้ไหม?
- วิธีสแตติก Java ในอินเทอร์เฟซคืออะไร
- มีคำถามเกี่ยวกับวิธีการสแตติก Java เทียบกับซิงเกิลตัน?
- วิธีสแตติก Java เทียบกับประสิทธิภาพของวิธีอินสแตนซ์
- เมธอดและตัวแปรสแตติกของ Java
- วิธีการแบบคงที่ของ Java กับแบบไม่คงที่
- วิธีการแบบคงที่ของ Java ในคลาสนามธรรม
คำหลักคงที่สามารถใช้ได้ใน 3 สถานการณ์:
- ตัวแปรคงที่
- วิธีการแบบคงที่
- บล็อกคงที่ของรหัส
ตัวแปรคงที่ (“คงที่” คำสำคัญ = ตัวแปรคลาส)
ใน Java Variables สามารถประกาศได้ด้วยคีย์เวิร์ด “ static ”
ตัวอย่าง: static int y = 0;
เมื่อมีการประกาศตัวแปรด้วยคีย์เวิร์ด static จะเรียกว่า class variable อินสแตนซ์ทั้งหมดใช้สำเนาของตัวแปรเดียวกัน สามารถเข้าถึงตัวแปรคลาสได้โดยตรงกับคลาส โดยไม่ต้องสร้างอินสแตนซ์
ไม่มีคีย์เวิร์ด "คงที่" = ตัวแปรอินสแตนซ์
หากไม่มี static keyword จะเรียกว่า instance variable และแต่ละอินสแตนซ์ของคลาสจะมีสำเนาของตัวแปรเป็นของตัวเอง
ตัวอย่าง: คงที่ int crunchify_variable_name ;
- ตัวแปรสแตติกถูกใช้ร่วมกันในทุกอินสแตนซ์ของคลาส
- หนึ่งในเหตุผลหลักที่คุณต้องการเมื่อต้องการจัดการหน่วยความจำจำนวนมาก
- สำหรับตัวแปรสแตติกทั้งหมด – จะมีเพียงสำเนาเดียวที่คุณสามารถใช้ได้
- คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องมีคลาสอ็อบเจ็กต์เพื่อเข้าถึงตัวแปรสแตติก
- เพียงแค่ใช้โดยตรง คุณไม่จำเป็นต้อง
object.StaticVariable
- เพียงแค่ใช้โดยตรง คุณไม่จำเป็นต้อง
บล็อกแบบคงที่คืออะไร?
สแตติกบล็อก เป็นบล็อกของคำสั่งภายใน Java class ที่จะดำเนินการเมื่อโหลดคลาสใน JVM เป็นครั้งแรก
คุณสามารถแทนที่วิธีการส่วนตัวใน Java ได้หรือไม่?
- ดีไม่มี วิธีส่วนตัวไม่สามารถแทนที่ได้ เนื่องจากไม่สามารถใช้นอกชั้นเรียนได้
เหตุใดเราจึงไม่สามารถแทนที่วิธีการแบบคงที่ใน Java ได้
- วิธีสแตติกไม่สามารถแทนที่ได้เนื่องจากเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของคลาสแทนที่จะเป็นอ็อบเจกต์
เราสามารถเข้าถึงตัวแปรที่ไม่คงที่ในบริบทคงที่ได้หรือไม่?
- เพื่อให้สามารถเข้าถึงตัวแปรที่ไม่คงที่จากวิธีการแบบคงที่ของคุณ พวกเขาจะต้องเป็นตัวแปรสมาชิกแบบคงที่
รายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับวิธีการคงที่
- จะระบุได้อย่างไร? ตรวจสอบสิ่งนี้ก่อน คุณต้องการคลาสอ็อบเจ็กต์เพื่อเข้าถึงเมธอดแบบคงที่หรือไม่? หากคุณไม่ต้องการวัตถุก็เป็นวิธีคงที่
- คุณต้องใช้คำหลักแบบคงที่เพื่อระบุวิธีการแบบคงที่
- ควรใช้คำสำคัญแบบคงที่หากวิธีการนั้นจะไม่เปลี่ยนแปลงตลอดทั้งโครงการของคุณในขณะใช้งานจริง
- คุณไม่สามารถแทนที่วิธีการแบบคงที่
ลองมาดูตัวอย่างด้านล่าง:
ตัวอย่าง-1:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyStaticMethodMain { public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { String [ ] crunchifyObject = new String [ 3 ] ; crunchifyObject = new String [ ] { "Google" , "Facebook" , "Crunchify" } ; // creating instnace CrunchifyStaticMethodMain object = new CrunchifyStaticMethodMain ( ) ; object . crunchifyTestMethod ( crunchifyObject ) ; } /* * Check this out: Let's understand little more... * * Here method crunchifyTestMethod is defined as * public void crunchifyTestMethod(String[]) * so it is "non-static". It can't be called unless it is called on an instance of CrunchifyStaticMethodMain. * * If you declared your method as * public static void crunchifyTestMethod(int[]) * then you could call: CrunchifyStaticMethodMain.crunchifyTestMethod(arr); within main without having created an instance for it. */ public void crunchifyTestMethod ( String [ ] crunchifyObject ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyObject . length ; i ++ ) System . out . println ( crunchifyObject [ i ] ) ; } } |
ตรวจสอบคำอธิบายใน above code block เราต้องสร้างอินสแตนซ์ของ Class เพื่อเข้าถึงวิธีการที่ไม่คงที่
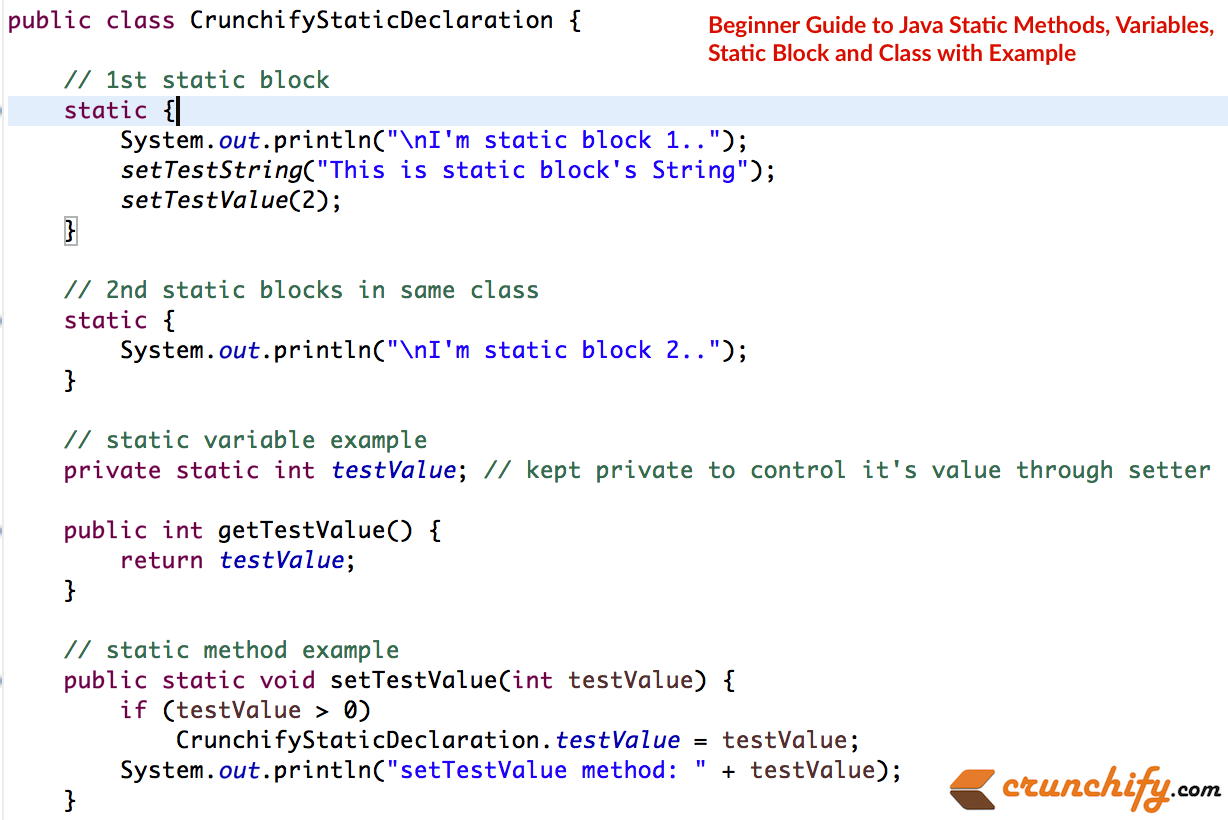
ตัวอย่าง-2:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyStaticDeclaration { // 1st static block static { System . out . println ( "\nI'm static block 1.." ) ; setTestString ( "This is static block's String" ) ; setTestValue ( 2 ) ; } // 2nd static blocks in same class static { System . out . println ( "\nI'm static block 2.." ) ; } // static variable example private static int testValue ; // kept private to control it's value through setter public int getTestValue ( ) { return testValue ; } // static method example public static void setTestValue ( int testValue ) { if ( testValue > 0 ) CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testValue = testValue ; System . out . println ( "setTestValue method: " + testValue ) ; } public static String testString ; /** * @return the testString */ public static String getTestString ( ) { return testString ; } /** * @param testString the testString to set */ public static void setTestString ( String testString ) { CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString = testString ; System . out . println ( "setTestString method: " + testString ) ; } // static util method public static int subValue ( int i , int . . . js ) { int sum = i ; for ( int x : js ) sum -= x ; return sum ; } } |
ตอนนี้มาทำแบบทดสอบกัน:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyStaticExample { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . setTestValue ( 5 ) ; // non-private static variables can be accessed with class name CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString = "\nAssigning testString a value" ; CrunchifyStaticDeclaration csd = new CrunchifyStaticDeclaration ( ) ; System . out . println ( csd . getTestString ( ) ) ; // class and instance static variables are same System . out . print ( "\nCheck if Class and Instance Static Variables are same: " ) ; System . out . println ( CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString == csd . testString ) ; System . out . println ( "Why? Because: CrunchifyStaticDeclaration.testString == csd.testString" ) ; } } |
เอาท์พุท:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
I 'm static block 1.. setTestString method: This is static block' s String setTestValue method : 2 I ' m static block 2.. setTestValue method : 5 Assigning testString a value Check if Class and Instance Static Variables are same : true Why ? Because : CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString == csd . testString |
ฉันหวังว่าคุณจะได้รับข้อมูลที่ดีเกี่ยวกับวิธีการคงที่ ตัวแปร และบล็อก

แจ้งให้เราทราบหากคุณประสบปัญหาใดๆ ในการใช้งานโปรแกรมข้างต้น หรือมีปัญหาในการทำความเข้าใจคำหลักแบบคงที่ใน Java
