Java静的メソッド、クラス、変数、およびブロックの基礎
公開: 2019-12-13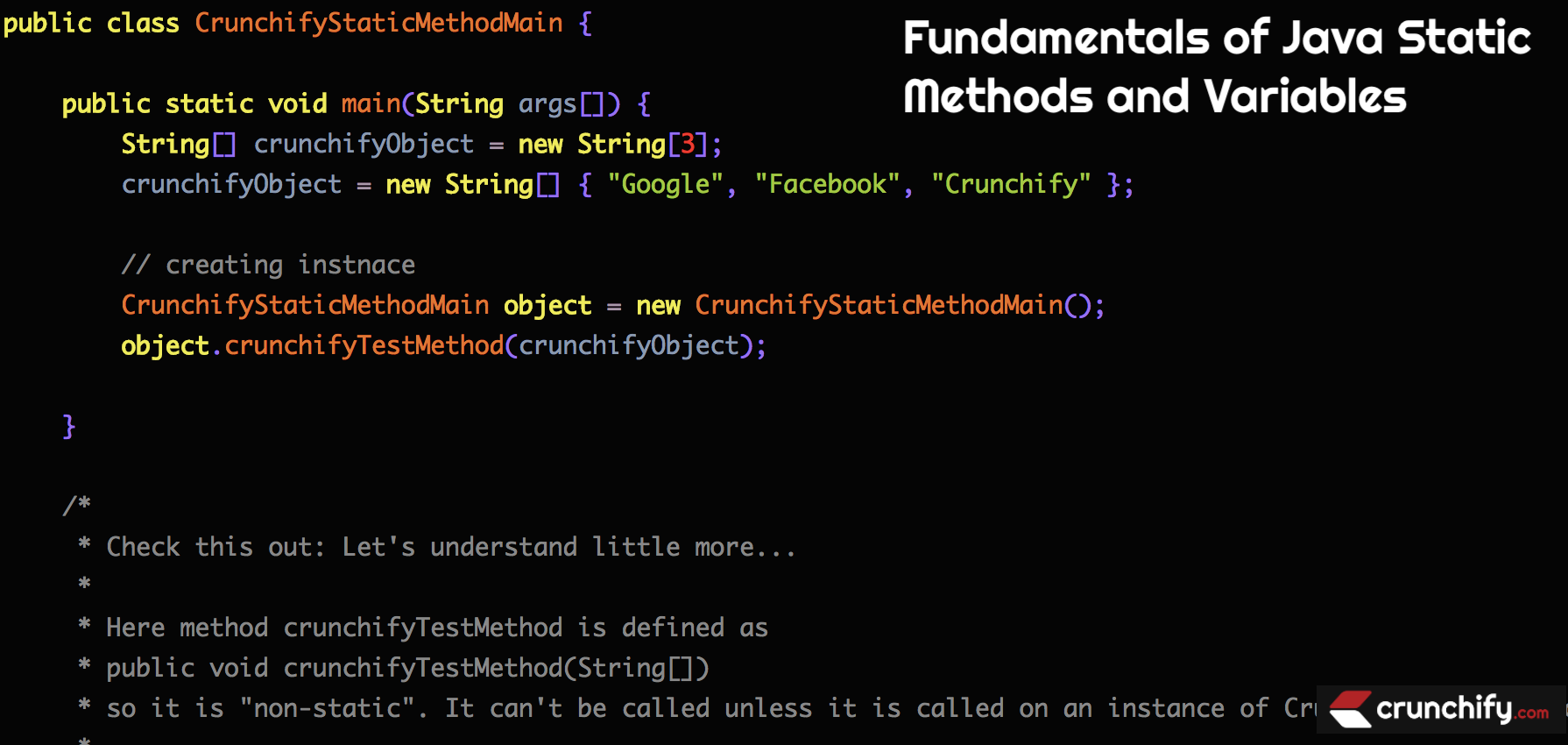
Javaの静的とは何ですか?
- staticキーワードは、クラス、変数、メソッド、およびブロックで使用できます。
- 静的メンバーは、特定のインスタンスのいずれにも属していません。
- 静的メンバーはクラスにのみ属します。
- メンバーを静的にすると、オブジェクトなしでメンバーにアクセスできます。
以下の質問はありますか?
- Java静的メソッドのベストプラクティスを書き留めていただけますか?
- インターフェイスのJava静的メソッドとは何ですか?
- Java静的メソッドとシングルトンについて質問がありますか?
- Java静的メソッドとインスタンスメソッドのパフォーマンス
- Javaの静的メソッドと変数
- Java静的メソッドと非静的メソッド
- 抽象クラスのJava静的メソッド
staticキーワードは、次の3つのシナリオで使用できます。
- 静的変数
- 静的メソッド
- コードの静的ブロック。
静的変数(「静的」キーワード=クラス変数)
Javaでは、変数は「 static 」キーワードで宣言できます。
例: static int y = 0;
変数がキーワードstaticで宣言されている場合、それはclass variableと呼ばれます。 すべてのインスタンスは、変数の同じコピーを共有します。 クラス変数には、インスタンスを作成しなくても、クラスから直接アクセスできます。
「静的」キーワードなし=インスタンス変数
static keywordがない場合、これはinstance variableと呼ばれ、クラスの各インスタンスには変数の独自のコピーがあります。
例:static int crunchify_variable_name ;
- 静的変数は、クラスのすべてのインスタンス間で共有されます。
- 大量のメモリ管理を行う場合に必要になる主な理由の1つ。
- すべての静的変数について–使用できるコピーは1つだけです。
- 静的変数にアクセスするためにクラスオブジェクトは絶対に必要ありません。
- 直接使用してください。
object.StaticVariableは必要ありません
- 直接使用してください。
静的ブロックとは何ですか?
静的ブロックは、クラスが最初にJVMにロードされるときに実行されるJava class内のステートメントのブロックです。
Javaでプライベートメソッドをオーバーライドできますか?
- うーん、ダメ。 プライベートメソッドはクラス外で使用できないため、オーバーライドできません。
Javaで静的メソッドをオーバーライドできないのはなぜですか?
- 静的メソッドは、オブジェクトではなくクラスの一部であるため、オーバーライドすることもできません。
静的コンテキストで非静的変数にアクセスできますか?
- 静的メソッドから非静的変数にアクセスできるようにするには、静的メンバー変数である必要があります。
静的メソッドの詳細
- 識別する方法は? 最初にこれを確認してください。 静的メソッドにアクセスするためにクラスオブジェクトが必要ですか? オブジェクトが必要ない場合は、Staticメソッドです。
- staticメソッドを指定するには、staticキーワードを使用する必要があります
- 実行時にプロジェクト全体でそのメソッドが変更されない場合は、キーワードstaticを使用することをお勧めします。
- 静的メソッドをオーバーライドすることはできません。
以下の例を見てみましょう。
例-1:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyStaticMethodMain { public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { String [ ] crunchifyObject = new String [ 3 ] ; crunchifyObject = new String [ ] { "Google" , "Facebook" , "Crunchify" } ; // creating instnace CrunchifyStaticMethodMain object = new CrunchifyStaticMethodMain ( ) ; object . crunchifyTestMethod ( crunchifyObject ) ; } /* * Check this out: Let's understand little more... * * Here method crunchifyTestMethod is defined as * public void crunchifyTestMethod(String[]) * so it is "non-static". It can't be called unless it is called on an instance of CrunchifyStaticMethodMain. * * If you declared your method as * public static void crunchifyTestMethod(int[]) * then you could call: CrunchifyStaticMethodMain.crunchifyTestMethod(arr); within main without having created an instance for it. */ public void crunchifyTestMethod ( String [ ] crunchifyObject ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyObject . length ; i ++ ) System . out . println ( crunchifyObject [ i ] ) ; } } |
above code blockの説明を確認してください。 非静的メソッドにアクセスするには、Classのインスタンスを作成する必要があります。
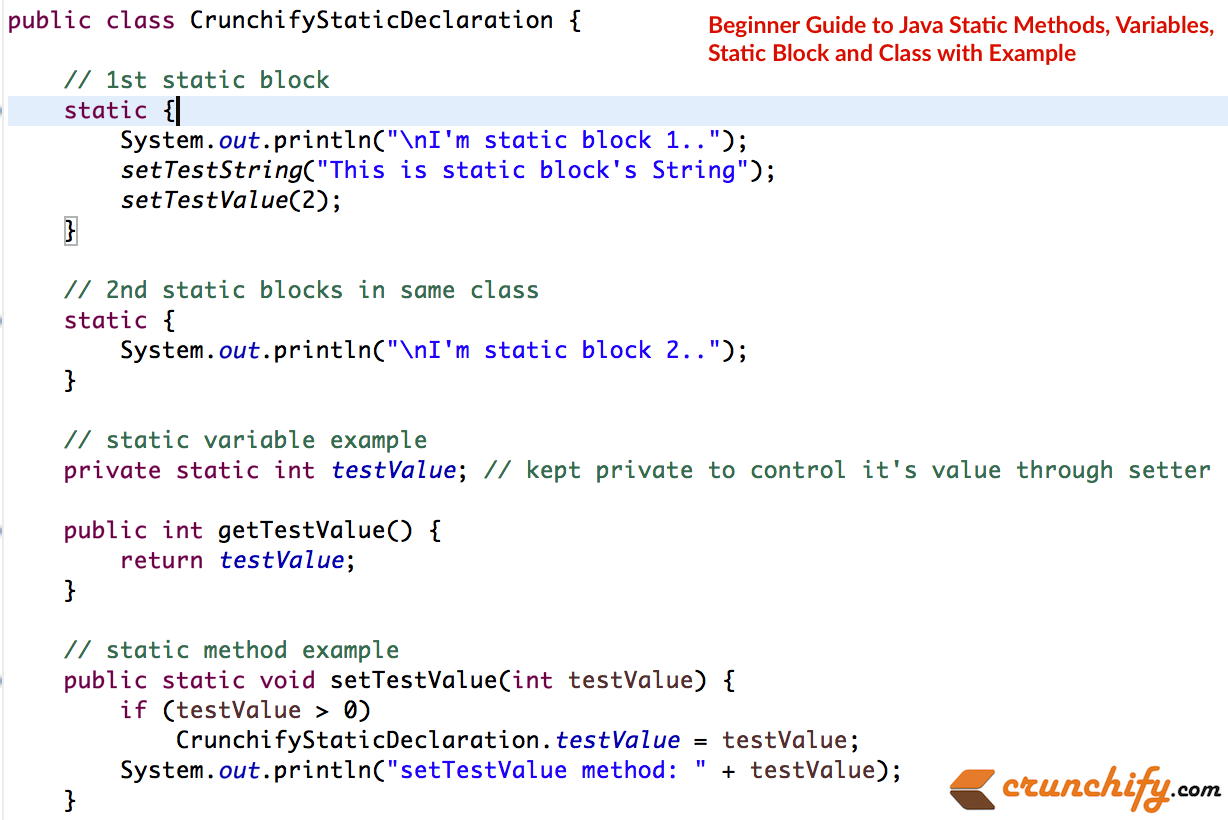
例-2:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyStaticDeclaration { // 1st static block static { System . out . println ( "\nI'm static block 1.." ) ; setTestString ( "This is static block's String" ) ; setTestValue ( 2 ) ; } // 2nd static blocks in same class static { System . out . println ( "\nI'm static block 2.." ) ; } // static variable example private static int testValue ; // kept private to control it's value through setter public int getTestValue ( ) { return testValue ; } // static method example public static void setTestValue ( int testValue ) { if ( testValue > 0 ) CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testValue = testValue ; System . out . println ( "setTestValue method: " + testValue ) ; } public static String testString ; /** * @return the testString */ public static String getTestString ( ) { return testString ; } /** * @param testString the testString to set */ public static void setTestString ( String testString ) { CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString = testString ; System . out . println ( "setTestString method: " + testString ) ; } // static util method public static int subValue ( int i , int . . . js ) { int sum = i ; for ( int x : js ) sum -= x ; return sum ; } } |
それでは、テストを行いましょう。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyStaticExample { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . setTestValue ( 5 ) ; // non-private static variables can be accessed with class name CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString = "\nAssigning testString a value" ; CrunchifyStaticDeclaration csd = new CrunchifyStaticDeclaration ( ) ; System . out . println ( csd . getTestString ( ) ) ; // class and instance static variables are same System . out . print ( "\nCheck if Class and Instance Static Variables are same: " ) ; System . out . println ( CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString == csd . testString ) ; System . out . println ( "Why? Because: CrunchifyStaticDeclaration.testString == csd.testString" ) ; } } |
出力:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
I 'm static block 1.. setTestString method: This is static block' s String setTestValue method : 2 I ' m static block 2.. setTestValue method : 5 Assigning testString a value Check if Class and Instance Static Variables are same : true Why ? Because : CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString == csd . testString |
静的メソッド、変数、ブロックについての良い情報が得られることを願っています。

上記のプログラムの実行中に問題が発生した場合、またはJavaの静的キーワードの理解に問題がある場合はお知らせください。
