你注意到 Java 多线程并发示例中的 Race Condition 了吗? 如何处理?
已发表: 2019-12-11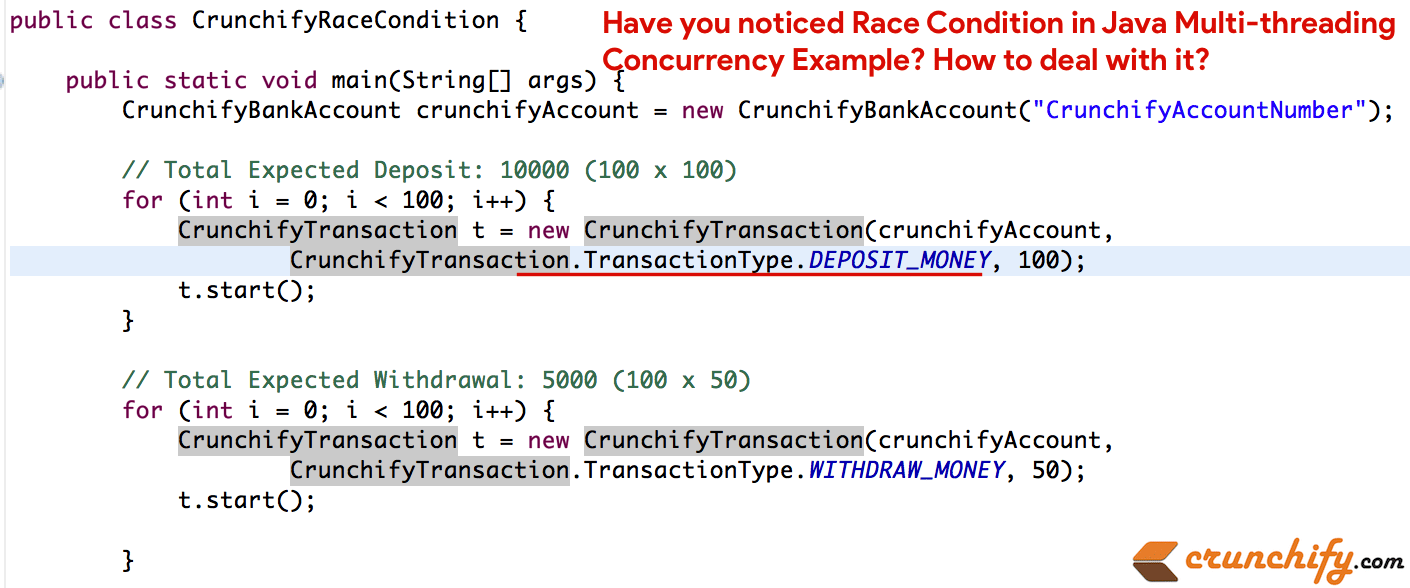
前段时间我写了一篇关于生产者消费者示例以及如何在 Java 中更好地处理读/写操作的文章。 同样,在本教程中,我们将讨论Race Condition和Thread locking 。
如果您有以下任何问题,那么您来对地方了:
- Java 竞争条件示例
- 互斥量 java 示例
- 多线程——什么是竞争条件?
- 比赛条件和关键部分
- 什么是比赛条件?
- 如何通过示例处理 Java 中的竞争条件
为什么会出现 Java 中的竞争条件?
Java 中的竞态条件发生在two or more threads尝试修改/更新共享数据same time 。
让我们看一下下面的程序逻辑:
这是一个非常简单的银行示例,您将在其中
deposit和withdraw100 times。 您将总共存入 $100 100 次 = $100 x 100 = $10,000 并且您将总共提取 $50 100 次 = $50 x 100 = $5,000。 计划完成时,您的银行中应该有 5000 美元。
以下是步骤:
- 创建类 CrunchifyRaceCondition.java
- 创建类 CrunchifyTransaction.java
- 创建类 CrunchifyBankAccount.java
- 我们将运行 CrunchifyRaceCondition 类,它将启动存款和取款循环 100 次。
- 我们将
with Synchronized block运行它以检查结果 - 我们将在
without Synchronized block的情况下运行它来检查结果
CrunchifyRaceCondition.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
package com . crunchify . tutorial ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyRaceCondition { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { CrunchifyBankAccount crunchifyAccount = new CrunchifyBankAccount ( "CrunchifyAccountNumber" ) ; // Total Expected Deposit: 10000 (100 x 100) for ( int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i ++ ) { CrunchifyTransaction t = new CrunchifyTransaction ( crunchifyAccount , CrunchifyTransaction . TransactionType . DEPOSIT_MONEY , 100 ) ; t . start ( ) ; } // Total Expected Withdrawal: 5000 (100 x 50) for ( int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i ++ ) { CrunchifyTransaction t = new CrunchifyTransaction ( crunchifyAccount , CrunchifyTransaction . TransactionType . WITHDRAW_MONEY , 50 ) ; t . start ( ) ; } // Let's just wait for a second to make sure all thread execution completes. try { Thread . sleep ( 1000 ) ; } catch ( InterruptedException e ) { System . out . println ( e ) ; } // Expected account balance is 5000 System . out . println ( "Final Account Balance: " + crunchifyAccount . getAccountBalance ( ) ) ; } } |
CrunchifyTransaction.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 |
package com . crunchify . tutorial ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ class CrunchifyTransaction extends Thread { public static enum TransactionType { DEPOSIT_MONEY ( 1 ) , WITHDRAW_MONEY ( 2 ) ; private TransactionType ( int value ) { } } ; private TransactionType transactionType ; private CrunchifyBankAccount crunchifyAccount ; private double crunchifyAmount ; /* * If transactionType == 1, depositAmount() else if transactionType == 2 withdrawAmount() */ public CrunchifyTransaction ( CrunchifyBankAccount crunchifyAccount , TransactionType transactionType , double crunchifyAmount ) { this . transactionType = transactionType ; this . crunchifyAccount = crunchifyAccount ; this . crunchifyAmount = crunchifyAmount ; } public void run ( ) { switch ( this . transactionType ) { case DEPOSIT_MONEY : depositAmount ( ) ; printBalance ( ) ; break ; case WITHDRAW_MONEY : withdrawAmount ( ) ; printBalance ( ) ; break ; default : System . out . println ( "NOT A VALID TRANSACTION" ) ; } } public void depositAmount ( ) { this . crunchifyAccount . depositAmount ( this . crunchifyAmount ) ; } public void withdrawAmount ( ) { this . crunchifyAccount . withdrawAmount ( crunchifyAmount ) ; } public void printBalance ( ) { System . out . println ( Thread . currentThread ( ) . getName ( ) + " : TransactionType: " + this . transactionType + ", Amount: " + this . crunchifyAmount ) ; System . out . println ( "New Account Balance: " + this . crunchifyAccount . getAccountBalance ( ) ) ; } } |

CrunchifyBankAccount.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
package com . crunchify . tutorial ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ class CrunchifyBankAccount { private String crunchifyAccountNumber ; private double crunchifyAccountBalance ; public String getAccountNumber ( ) { return crunchifyAccountNumber ; } public double getAccountBalance ( ) { return crunchifyAccountBalance ; } public CrunchifyBankAccount ( String crunchifyAccountNumber ) { this . crunchifyAccountNumber = crunchifyAccountNumber ; } // Make a note of this line -- synchronized keyword added public synchronized boolean depositAmount ( double amount ) { if ( amount < 0 ) { return false ; } else { crunchifyAccountBalance = crunchifyAccountBalance + amount ; return true ; } } // Make a note of this line -- synchronized keyword added public synchronized boolean withdrawAmount ( double amount ) { if ( amount > crunchifyAccountBalance ) { return false ; } else { crunchifyAccountBalance = crunchifyAccountBalance - amount ; return true ; } } } |
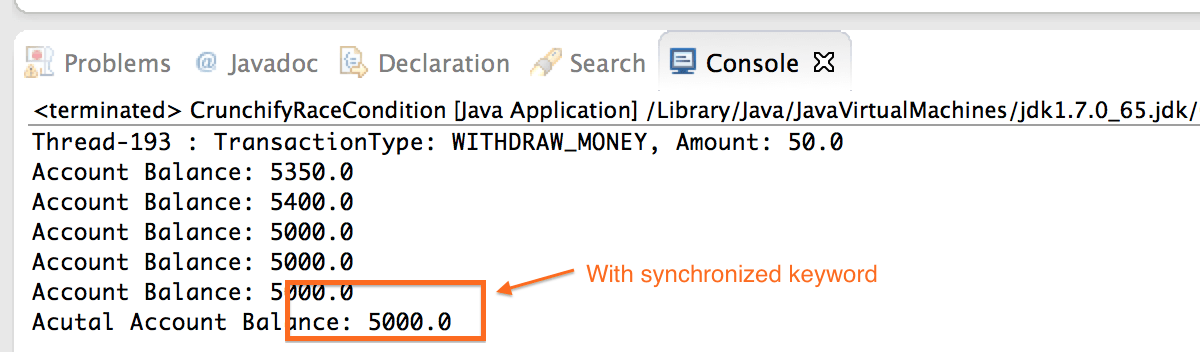
请检查上面的第 24 和 34 行。 保留Synchronized关键字并运行您的程序。 您应该看到正确的结果,如下图所示。
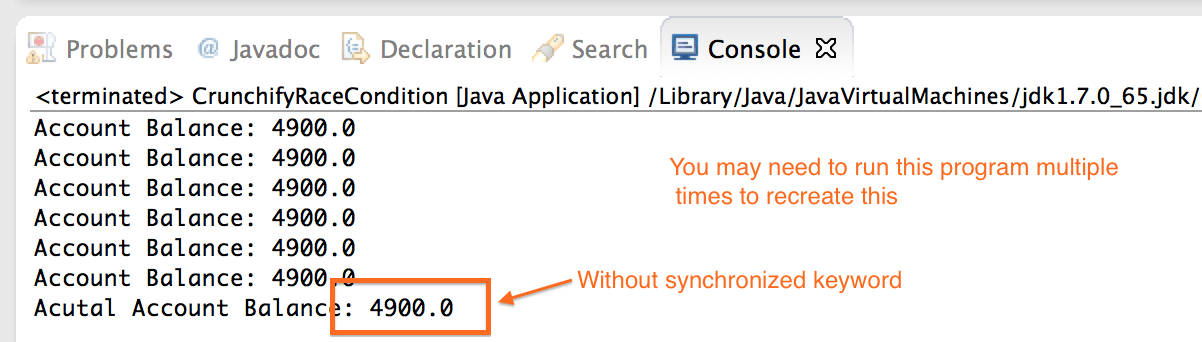
现在从第 24 行和第 34 行删除同步关键字并运行相同的程序。
您可能需要多次运行此程序才能看到问题。 在 java 中,不能保证你会一直看到 Race 条件。
如果您有企业级应用程序并且您正在谈论每秒数百万笔交易,那么竞争条件可能会给您的公司带来灾难。
现在的问题是如何避免 Java 应用程序中的竞争条件?
- 如果竞态条件是对某些共享内存数据结构的更新,则需要以适当的方式同步对数据结构的访问和更新。
- 如果竞争条件是更新数据库,则需要重组 SQL 以使用适当粒度级别的事务。
- 在投入生产之前进行负载测试并不是一个坏主意。 更多的负载可能会导致罕见的竞争条件。 最好先修复它,然后再修复它。
- 确保没有要写入的全局变量。
- 在 Java 中,每个对象都有一个且只有一个与之关联的监视器和互斥锁。 然而,单个监视器有几个门,每个都由
synchronized关键字指示。 当一个线程通过synchronized关键字时,它有效地锁定了所有的门。 - 当然,如果一个线程没有通过
synchronized关键字,它还没有锁门,其他线程随时可以自由插入。
