Podstawy statycznej metody Java, klasy, zmiennej i bloku
Opublikowany: 2019-12-13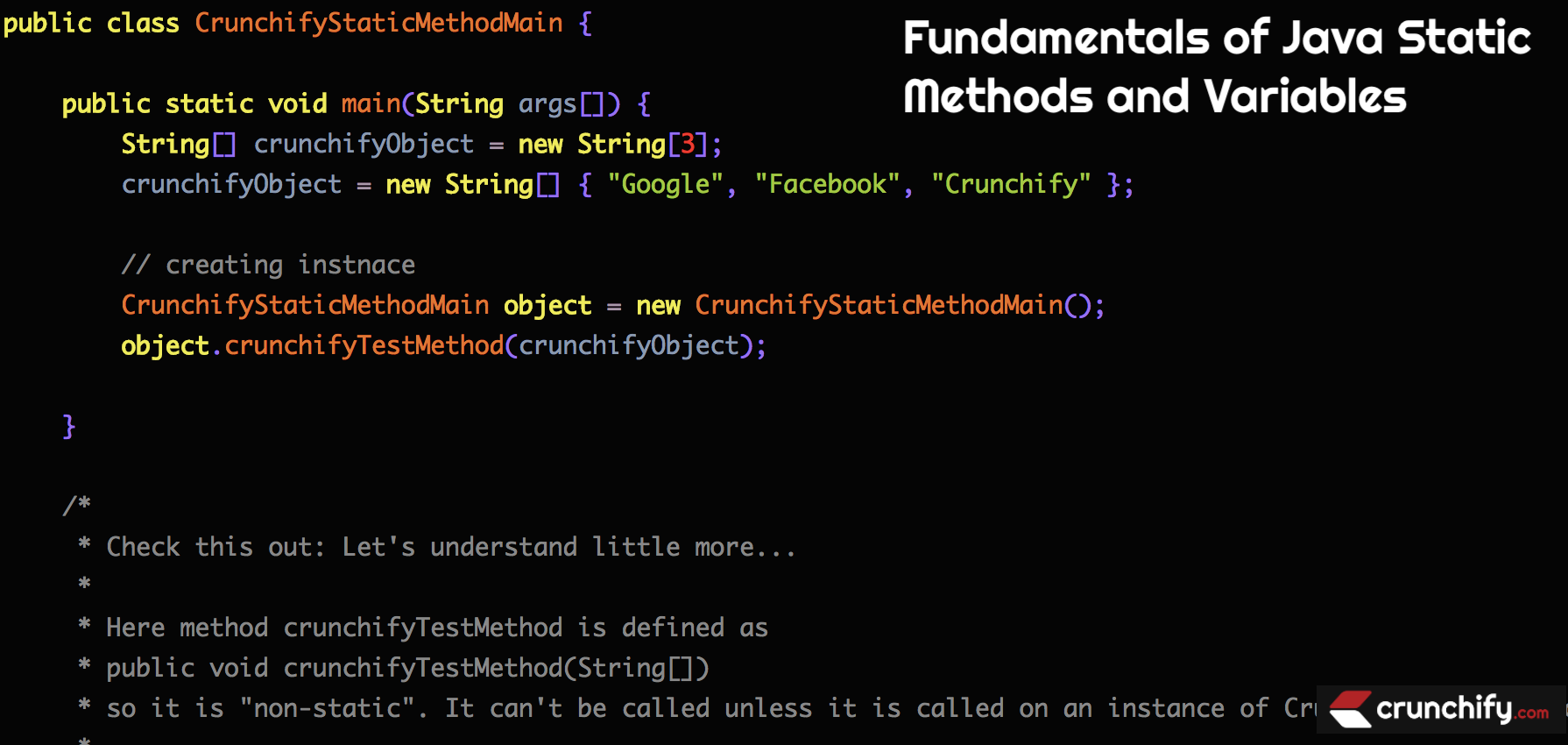
Co jest statyczne w Javie?
- Słowo kluczowe Static może być używane z klasą, zmienną, metodą i blokiem.
- Statyczne elementy członkowskie nie należą do żadnej konkretnej instancji.
- Elementy statyczne należą tylko do klasy.
- Gdy ustawisz element członkowski jako statyczny, możesz uzyskać do niego dostęp bez żadnego obiektu.
Czy masz któreś z poniższych pytań?
- Czy mógłbyś spisać najlepsze praktyki dotyczące statycznych metod Java?
- Co to są statyczne metody Java w interfejsie?
- Masz pytanie dotyczące metod statycznych Java vs singleton?
- Metody statyczne Java a wydajność metod instancji
- Statyczne metody i zmienne Java
- Metody statyczne Java vs niestatyczne
- Metody statyczne Java w klasie abstrakcyjnej
Słowo kluczowe static może być użyte w 3 scenariuszach:
- Zmienne statyczne
- Metody statyczne
- Statyczne bloki kodu.
zmienna statyczna („statyczne” słowo kluczowe = zmienne klasowe)
W Javie Zmienne można deklarować za pomocą słowa kluczowego „ static ”.
Przykład: static int y = 0;
Kiedy zmienna jest zadeklarowana za pomocą słowa kluczowego static , nazywana jest class variable . Wszystkie instancje mają tę samą kopię zmiennej. Dostęp do zmiennej klasy można uzyskać bezpośrednio z klasą, bez konieczności tworzenia instancji.
Brak „statycznego” słowa kluczowego = zmienne instancji
Bez static keyword nosi ona nazwę instance variable , a każda instancja klasy ma swoją własną kopię zmiennej.
Przykład: static int crunchify_variable_name ;
- Zmienne statyczne są wspólne dla wszystkich instancji klasy.
- Jeden z głównych powodów, dla których jest to potrzebne, gdy chcesz dużo zarządzać pamięcią.
- Dla wszystkich zmiennych statycznych – dostępna będzie tylko jedna kopia.
- Absolutnie nie potrzebujesz obiektu klasy, aby uzyskać dostęp do zmiennej statycznej.
- Po prostu użyj go bezpośrednio. Nie potrzebujesz
object.StaticVariable
- Po prostu użyj go bezpośrednio. Nie potrzebujesz
Co to jest blok statyczny?
Blok statyczny to blok instrukcji wewnątrz Java class , który zostanie wykonany, gdy klasa zostanie po raz pierwszy załadowana do JVM.
Czy możesz zmienić metodę prywatną w Javie?
- Więc nie. Nie można nadpisać metod prywatnych, ponieważ nie można ich używać poza klasą.
Dlaczego nie możemy nadpisać metod statycznych w Javie?
- Metody statyczne również nie mogą być nadpisane, ponieważ są one częścią klasy, a nie obiektu
Czy możemy uzyskać dostęp do zmiennej niestatycznej w kontekście statycznym?
- Aby móc uzyskać dostęp do niestatycznych zmiennych z metod statycznych, muszą one być statycznymi zmiennymi składowymi.
Szczegóły dotyczące metody statycznej
- Jak rozpoznać? Po prostu to najpierw sprawdź. Czy potrzebujesz obiektu klasy, aby uzyskać dostęp do metody statycznej? Jeśli nie potrzebujesz obiektu, to jest to metoda statyczna.
- Aby określić metodę statyczną, musisz użyć słowa kluczowego static
- Lepiej użyj słowa kluczowego static, jeśli ta metoda nie zmieni się w całym projekcie w czasie wykonywania.
- Nie możesz zmienić metody statycznej.
Rzućmy okiem na poniższe przykłady:
Przykład 1:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyStaticMethodMain { public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { String [ ] crunchifyObject = new String [ 3 ] ; crunchifyObject = new String [ ] { "Google" , "Facebook" , "Crunchify" } ; // creating instnace CrunchifyStaticMethodMain object = new CrunchifyStaticMethodMain ( ) ; object . crunchifyTestMethod ( crunchifyObject ) ; } /* * Check this out: Let's understand little more... * * Here method crunchifyTestMethod is defined as * public void crunchifyTestMethod(String[]) * so it is "non-static". It can't be called unless it is called on an instance of CrunchifyStaticMethodMain. * * If you declared your method as * public static void crunchifyTestMethod(int[]) * then you could call: CrunchifyStaticMethodMain.crunchifyTestMethod(arr); within main without having created an instance for it. */ public void crunchifyTestMethod ( String [ ] crunchifyObject ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyObject . length ; i ++ ) System . out . println ( crunchifyObject [ i ] ) ; } } |
Sprawdź wyjaśnienie w above code block . Musimy stworzyć instancję Class, aby uzyskać dostęp do metody niestatycznej.
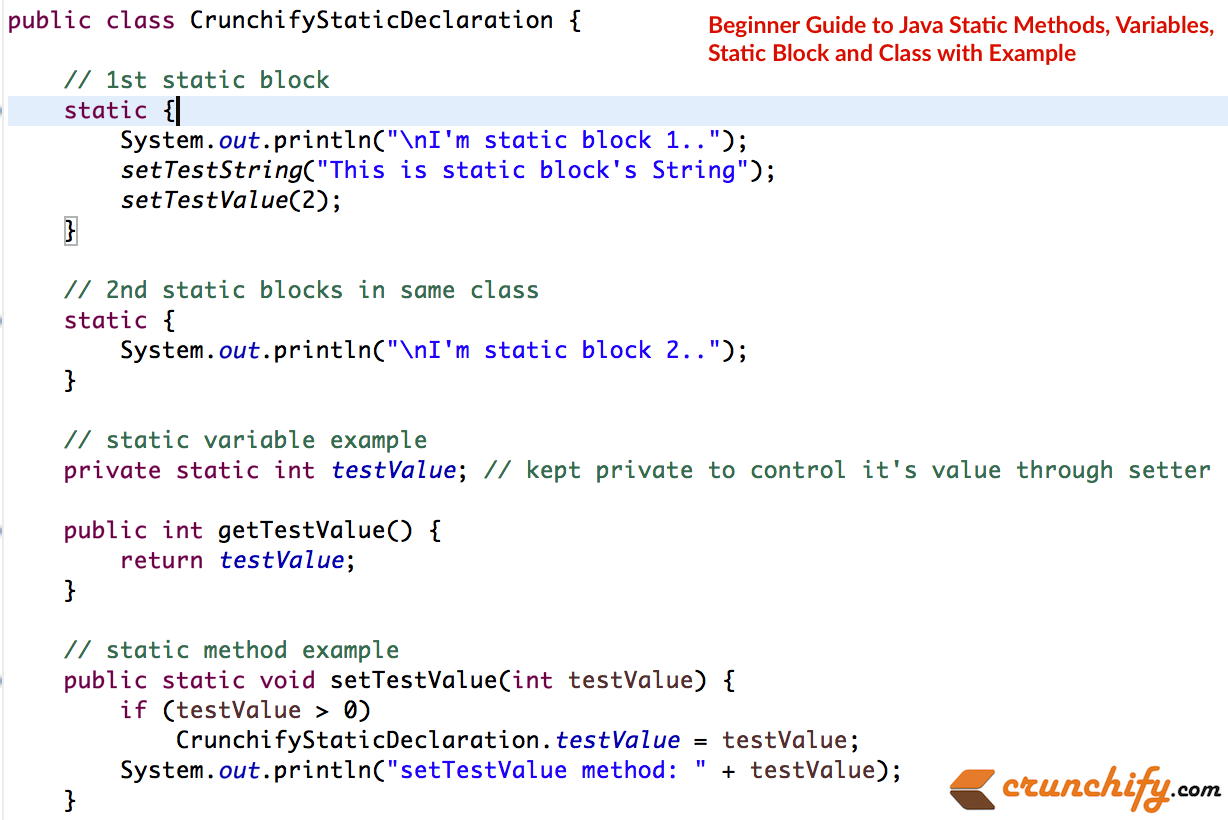
Przykład-2:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyStaticDeclaration { // 1st static block static { System . out . println ( "\nI'm static block 1.." ) ; setTestString ( "This is static block's String" ) ; setTestValue ( 2 ) ; } // 2nd static blocks in same class static { System . out . println ( "\nI'm static block 2.." ) ; } // static variable example private static int testValue ; // kept private to control it's value through setter public int getTestValue ( ) { return testValue ; } // static method example public static void setTestValue ( int testValue ) { if ( testValue > 0 ) CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testValue = testValue ; System . out . println ( "setTestValue method: " + testValue ) ; } public static String testString ; /** * @return the testString */ public static String getTestString ( ) { return testString ; } /** * @param testString the testString to set */ public static void setTestString ( String testString ) { CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString = testString ; System . out . println ( "setTestString method: " + testString ) ; } // static util method public static int subValue ( int i , int . . . js ) { int sum = i ; for ( int x : js ) sum -= x ; return sum ; } } |
Teraz przetestujmy:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyStaticExample { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . setTestValue ( 5 ) ; // non-private static variables can be accessed with class name CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString = "\nAssigning testString a value" ; CrunchifyStaticDeclaration csd = new CrunchifyStaticDeclaration ( ) ; System . out . println ( csd . getTestString ( ) ) ; // class and instance static variables are same System . out . print ( "\nCheck if Class and Instance Static Variables are same: " ) ; System . out . println ( CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString == csd . testString ) ; System . out . println ( "Why? Because: CrunchifyStaticDeclaration.testString == csd.testString" ) ; } } |
Wyjście:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
I 'm static block 1.. setTestString method: This is static block' s String setTestValue method : 2 I ' m static block 2.. setTestValue method : 5 Assigning testString a value Check if Class and Instance Static Variables are same : true Why ? Because : CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString == csd . testString |
Mam nadzieję, że naprawdę uzyskasz dobre informacje o metodzie statycznej, zmiennych i blokach.

Daj nam znać, jeśli napotkasz problem z działaniem powyższego programu lub masz problem ze zrozumieniem słowa kluczowego Static w Javie.
