Java 정적 메소드, 클래스, 변수 및 블록의 기초
게시 됨: 2019-12-13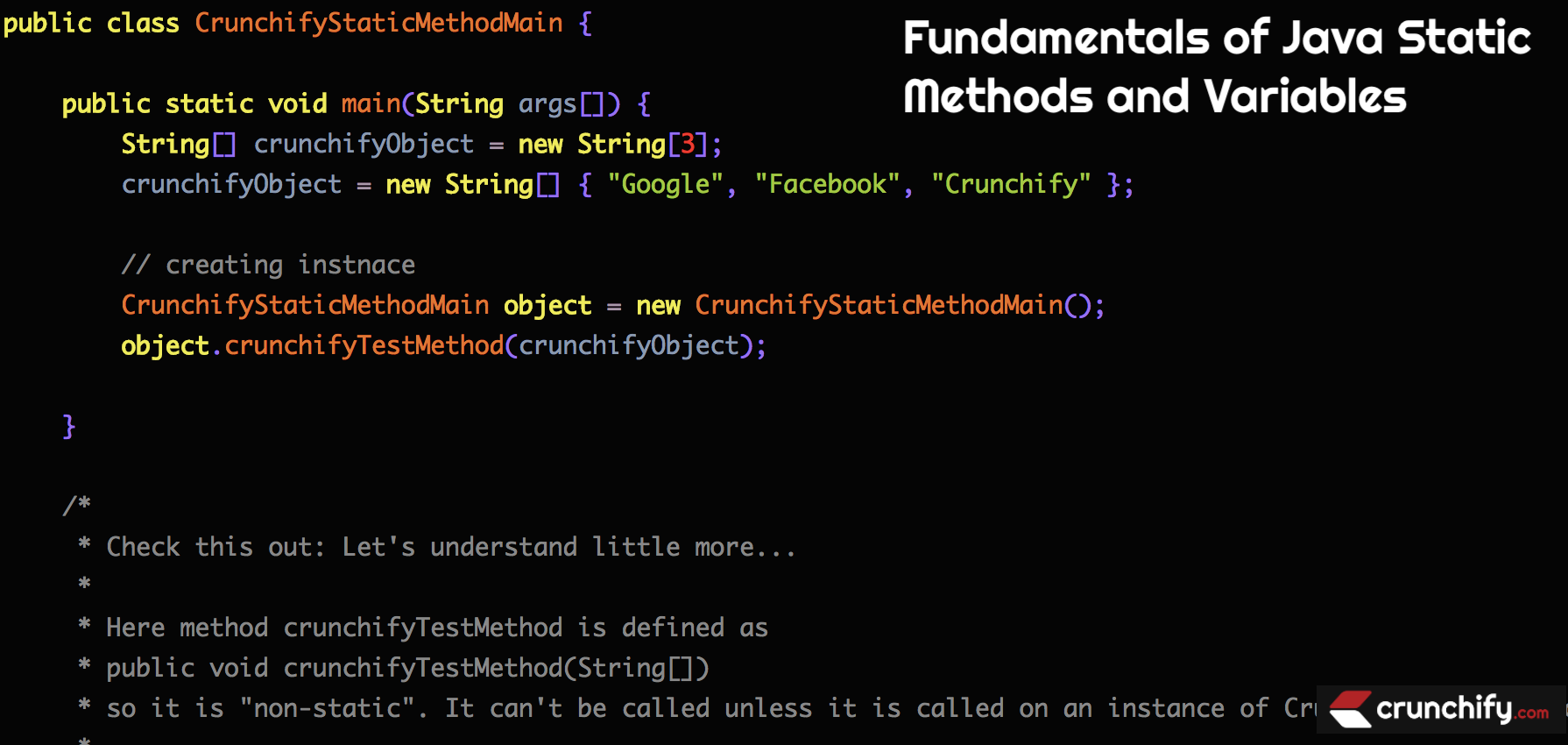
Java에서 정적이란 무엇입니까?
- Static 키워드는 클래스, 변수, 메서드 및 블록과 함께 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 정적 멤버는 특정 인스턴스에 속하지 않습니다.
- 정적 멤버는 클래스에만 속합니다.
- 멤버를 정적으로 만들면 개체 없이 액세스할 수 있습니다.
아래 질문이 있습니까?
- Java 정적 메소드 모범 사례를 기록해 주시겠습니까?
- 인터페이스의 Java 정적 메소드는 무엇입니까?
- Java 정적 메서드와 싱글톤에 대한 질문이 있습니까?
- Java 정적 메서드 대 인스턴스 메서드 성능
- Java 정적 메서드 및 변수
- Java 정적 메소드와 비 정적 메소드
- 추상 클래스의 Java 정적 메서드
static 키워드는 3가지 시나리오에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 정적 변수
- 정적 메서드
- 정적 코드 블록.
정적 변수("정적" 키워드 = 클래스 변수)
Java에서 변수는 " static " 키워드로 선언할 수 있습니다.
예: static int y = 0;
변수가 static 키워드로 선언되면 class variable 라고 합니다. 모든 인스턴스는 변수의 동일한 복사본을 공유합니다. 클래스 변수는 인스턴스를 만들 필요 없이 클래스와 함께 직접 액세스할 수 있습니다.
"정적" 키워드 없음 = 인스턴스 변수
static keyword 가 없으면 instance variable 라고 하며 클래스의 각 인스턴스에는 고유한 변수 복사본이 있습니다.
예: 정적 int crunchify_variable_name ;
- 정적 변수는 클래스의 모든 인스턴스에서 공유됩니다.
- 많은 메모리 관리를 수행하려는 경우 필요한 주요 이유 중 하나입니다.
- 모든 정적 변수에 대해 - 사용할 수 있는 복사본은 하나만 있습니다.
- 정적 변수에 액세스하기 위해 클래스 개체가 절대적으로 필요하지 않습니다.
- 직접 사용하시면 됩니다.
object.StaticVariable이 필요하지 않습니다.
- 직접 사용하시면 됩니다.
정적 블록이란 무엇입니까?
정적 블록은 클래스가 JVM에 처음 로드될 때 실행되는 Java class 내부의 명령문 블록입니다.
Java에서 개인 메서드를 재정의할 수 있습니까?
- 음 ... 아니. 비공개 메서드는 클래스 외부에서 사용할 수 없으므로 재정의할 수 없습니다.
Java에서 정적 메서드를 재정의할 수 없는 이유는 무엇입니까?
- 정적 메서드는 개체가 아닌 클래스의 일부이므로 재정의할 수도 없습니다.
정적 컨텍스트에서 비 정적 변수에 액세스할 수 있습니까?
- 정적 메서드에서 비정적 변수에 액세스하려면 정적 멤버 변수여야 합니다.
정적 메서드에 대한 세부 정보
- 식별하는 방법? 이것을 먼저 확인하십시오. 정적 메서드에 액세스하려면 클래스 개체가 필요합니까? 객체가 필요하지 않은 경우 정적 메서드입니다.
- 정적 메서드를 지정하려면 정적 키워드를 사용해야 합니다.
- 해당 메서드가 런타임에 프로젝트 전체에서 변경되지 않을 경우 키워드 static을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
- 정적 메서드를 재정의할 수 없습니다.
아래의 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
예-1:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyStaticMethodMain { public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { String [ ] crunchifyObject = new String [ 3 ] ; crunchifyObject = new String [ ] { "Google" , "Facebook" , "Crunchify" } ; // creating instnace CrunchifyStaticMethodMain object = new CrunchifyStaticMethodMain ( ) ; object . crunchifyTestMethod ( crunchifyObject ) ; } /* * Check this out: Let's understand little more... * * Here method crunchifyTestMethod is defined as * public void crunchifyTestMethod(String[]) * so it is "non-static". It can't be called unless it is called on an instance of CrunchifyStaticMethodMain. * * If you declared your method as * public static void crunchifyTestMethod(int[]) * then you could call: CrunchifyStaticMethodMain.crunchifyTestMethod(arr); within main without having created an instance for it. */ public void crunchifyTestMethod ( String [ ] crunchifyObject ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyObject . length ; i ++ ) System . out . println ( crunchifyObject [ i ] ) ; } } |
above code block 에서 설명을 확인하십시오. 비정적 메서드에 액세스하려면 Class의 인스턴스를 만들어야 합니다.
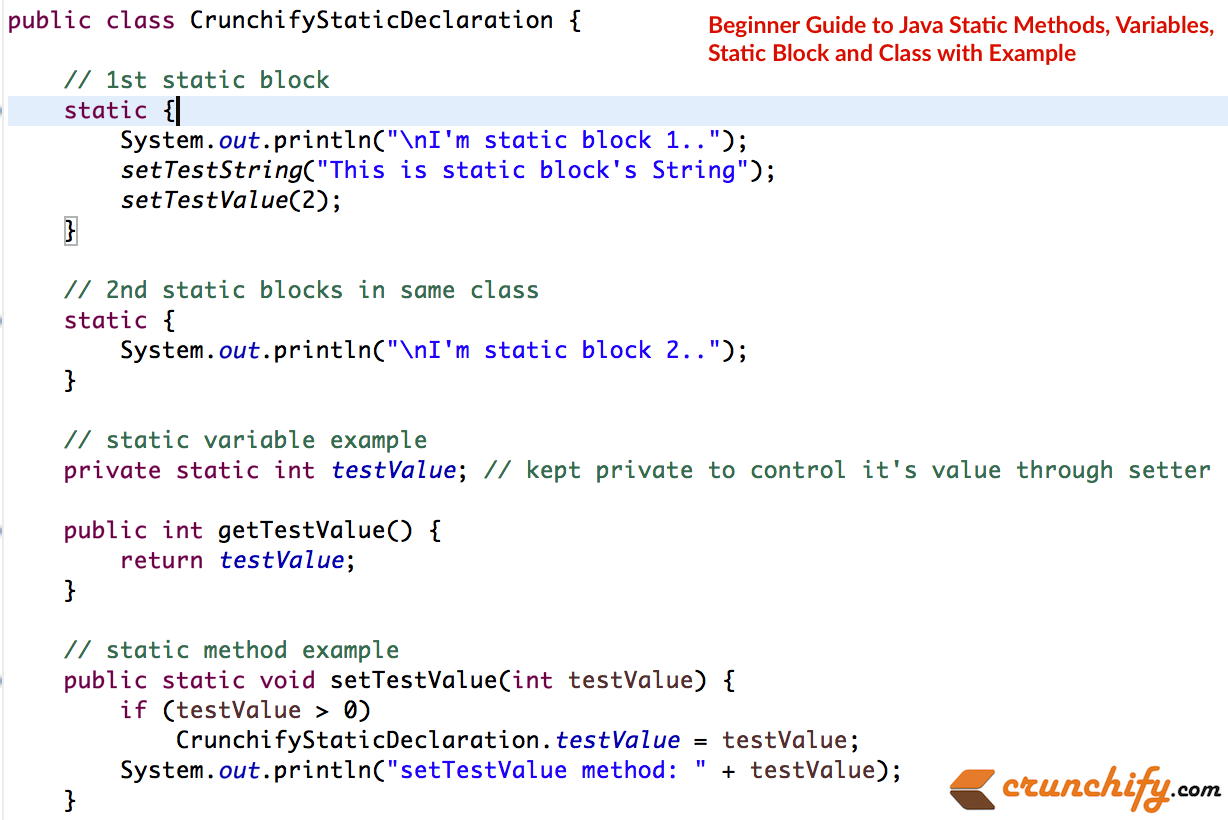
예-2:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyStaticDeclaration { // 1st static block static { System . out . println ( "\nI'm static block 1.." ) ; setTestString ( "This is static block's String" ) ; setTestValue ( 2 ) ; } // 2nd static blocks in same class static { System . out . println ( "\nI'm static block 2.." ) ; } // static variable example private static int testValue ; // kept private to control it's value through setter public int getTestValue ( ) { return testValue ; } // static method example public static void setTestValue ( int testValue ) { if ( testValue > 0 ) CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testValue = testValue ; System . out . println ( "setTestValue method: " + testValue ) ; } public static String testString ; /** * @return the testString */ public static String getTestString ( ) { return testString ; } /** * @param testString the testString to set */ public static void setTestString ( String testString ) { CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString = testString ; System . out . println ( "setTestString method: " + testString ) ; } // static util method public static int subValue ( int i , int . . . js ) { int sum = i ; for ( int x : js ) sum -= x ; return sum ; } } |
이제 테스트를 해보자:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyStaticExample { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . setTestValue ( 5 ) ; // non-private static variables can be accessed with class name CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString = "\nAssigning testString a value" ; CrunchifyStaticDeclaration csd = new CrunchifyStaticDeclaration ( ) ; System . out . println ( csd . getTestString ( ) ) ; // class and instance static variables are same System . out . print ( "\nCheck if Class and Instance Static Variables are same: " ) ; System . out . println ( CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString == csd . testString ) ; System . out . println ( "Why? Because: CrunchifyStaticDeclaration.testString == csd.testString" ) ; } } |
산출:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
I 'm static block 1.. setTestString method: This is static block' s String setTestValue method : 2 I ' m static block 2.. setTestValue method : 5 Assigning testString a value Check if Class and Instance Static Variables are same : true Why ? Because : CrunchifyStaticDeclaration . testString == csd . testString |
Static 메서드, 변수 및 블록에 대한 좋은 정보를 얻으시기 바랍니다.

위 프로그램을 실행하는 데 문제가 있거나 Java의 Static 키워드를 이해하는 데 문제가 있으면 알려주십시오.
