Java 다중 스레딩 동시성 예제에서 경쟁 조건을 발견했습니까? 그것을 처리하는 방법?
게시 됨: 2019-12-11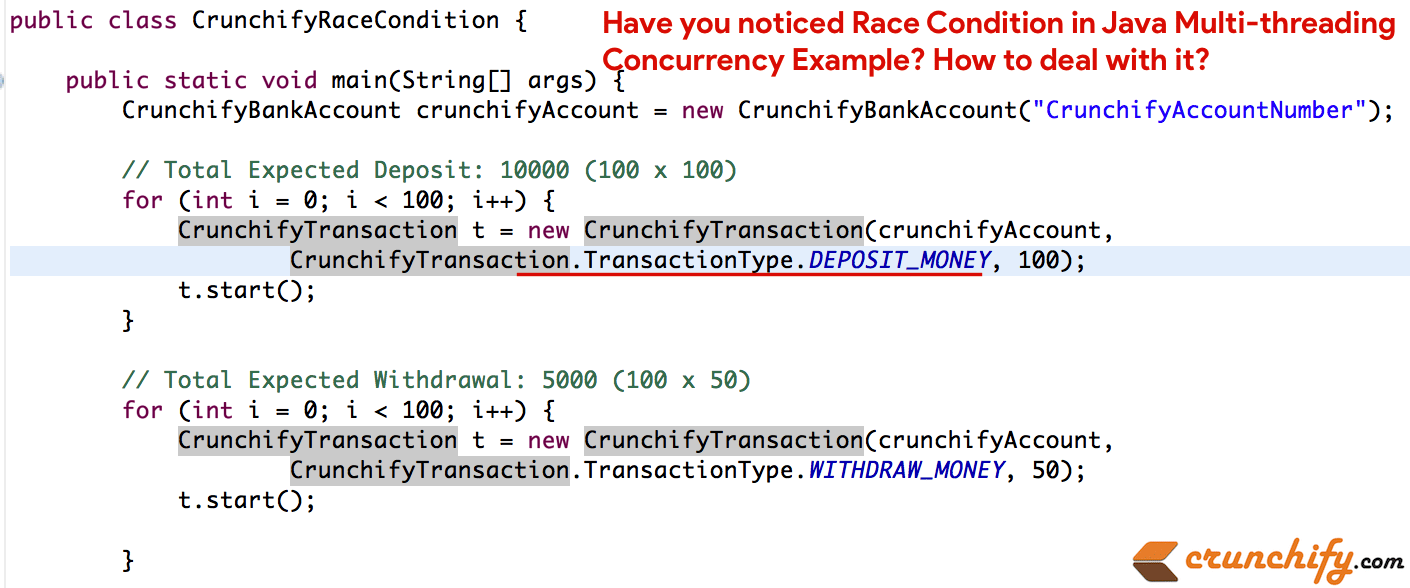
언젠가 나는 생산자 소비자 예제와 Java에서 읽기/쓰기 작업을 더 잘 처리하는 방법에 대한 기사를 작성했습니다. 비슷한 참고로 이 튜토리얼에서는 Race Condition 과 Thread locking 에 대해 논의할 것입니다.
아래 질문 중 하나라도 있으면 올바른 위치에 있습니다.
- 자바 경쟁 조건 예
- 뮤텍스 자바 예제
- 멀티스레딩 – 경쟁 조건이란 무엇입니까?
- 경쟁 조건 및 크리티컬 섹션
- 레이스 컨디션이란?
- 예제를 사용하여 Java에서 경쟁 조건을 처리하는 방법
Java에서 경쟁 조건이 발생하는 이유는 무엇입니까?
Java의 경쟁 조건은 two or more threads 가 same time 공유 데이터를 수정/업데이트하려고 할 때 발생합니다.
아래 프로그램 로직을 살펴보겠습니다.
이것은
withdraw을100 timesdeposit하는 매우 간단한 은행 업무의 예입니다. $100 총 100번 입금 = $100 x 100 = $10,000, $50 총 100번 출금 = $50 x 100 = $5,000 프로그램이 끝나면 은행에 $5000가 있어야 합니다.
단계는 다음과 같습니다.
- CrunchifyRaceCondition.java 클래스 생성
- CrunchifyTransaction.java 클래스 생성
- CrunchifyBankAccount.java 클래스 생성
- CrunchifyRaceCondition 클래스를 실행하고 루프를 100회 입출금을 시작합니다.
- 결과를 확인하기 위해
with Synchronized block으로 실행합니다. - 결과를 확인하기 위해
without Synchronized block실행합니다.
CrunchifyRaceCondition.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
package com . crunchify . tutorial ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyRaceCondition { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { CrunchifyBankAccount crunchifyAccount = new CrunchifyBankAccount ( "CrunchifyAccountNumber" ) ; // Total Expected Deposit: 10000 (100 x 100) for ( int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i ++ ) { CrunchifyTransaction t = new CrunchifyTransaction ( crunchifyAccount , CrunchifyTransaction . TransactionType . DEPOSIT_MONEY , 100 ) ; t . start ( ) ; } // Total Expected Withdrawal: 5000 (100 x 50) for ( int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i ++ ) { CrunchifyTransaction t = new CrunchifyTransaction ( crunchifyAccount , CrunchifyTransaction . TransactionType . WITHDRAW_MONEY , 50 ) ; t . start ( ) ; } // Let's just wait for a second to make sure all thread execution completes. try { Thread . sleep ( 1000 ) ; } catch ( InterruptedException e ) { System . out . println ( e ) ; } // Expected account balance is 5000 System . out . println ( "Final Account Balance: " + crunchifyAccount . getAccountBalance ( ) ) ; } } |
CrunchifyTransaction.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 |
package com . crunchify . tutorial ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ class CrunchifyTransaction extends Thread { public static enum TransactionType { DEPOSIT_MONEY ( 1 ) , WITHDRAW_MONEY ( 2 ) ; private TransactionType ( int value ) { } } ; private TransactionType transactionType ; private CrunchifyBankAccount crunchifyAccount ; private double crunchifyAmount ; /* * If transactionType == 1, depositAmount() else if transactionType == 2 withdrawAmount() */ public CrunchifyTransaction ( CrunchifyBankAccount crunchifyAccount , TransactionType transactionType , double crunchifyAmount ) { this . transactionType = transactionType ; this . crunchifyAccount = crunchifyAccount ; this . crunchifyAmount = crunchifyAmount ; } public void run ( ) { switch ( this . transactionType ) { case DEPOSIT_MONEY : depositAmount ( ) ; printBalance ( ) ; break ; case WITHDRAW_MONEY : withdrawAmount ( ) ; printBalance ( ) ; break ; default : System . out . println ( "NOT A VALID TRANSACTION" ) ; } } public void depositAmount ( ) { this . crunchifyAccount . depositAmount ( this . crunchifyAmount ) ; } public void withdrawAmount ( ) { this . crunchifyAccount . withdrawAmount ( crunchifyAmount ) ; } public void printBalance ( ) { System . out . println ( Thread . currentThread ( ) . getName ( ) + " : TransactionType: " + this . transactionType + ", Amount: " + this . crunchifyAmount ) ; System . out . println ( "New Account Balance: " + this . crunchifyAccount . getAccountBalance ( ) ) ; } } |

CrunchifyBankAccount.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
package com . crunchify . tutorial ; /** * @author Crunchify.com */ class CrunchifyBankAccount { private String crunchifyAccountNumber ; private double crunchifyAccountBalance ; public String getAccountNumber ( ) { return crunchifyAccountNumber ; } public double getAccountBalance ( ) { return crunchifyAccountBalance ; } public CrunchifyBankAccount ( String crunchifyAccountNumber ) { this . crunchifyAccountNumber = crunchifyAccountNumber ; } // Make a note of this line -- synchronized keyword added public synchronized boolean depositAmount ( double amount ) { if ( amount < 0 ) { return false ; } else { crunchifyAccountBalance = crunchifyAccountBalance + amount ; return true ; } } // Make a note of this line -- synchronized keyword added public synchronized boolean withdrawAmount ( double amount ) { if ( amount > crunchifyAccountBalance ) { return false ; } else { crunchifyAccountBalance = crunchifyAccountBalance - amount ; return true ; } } } |
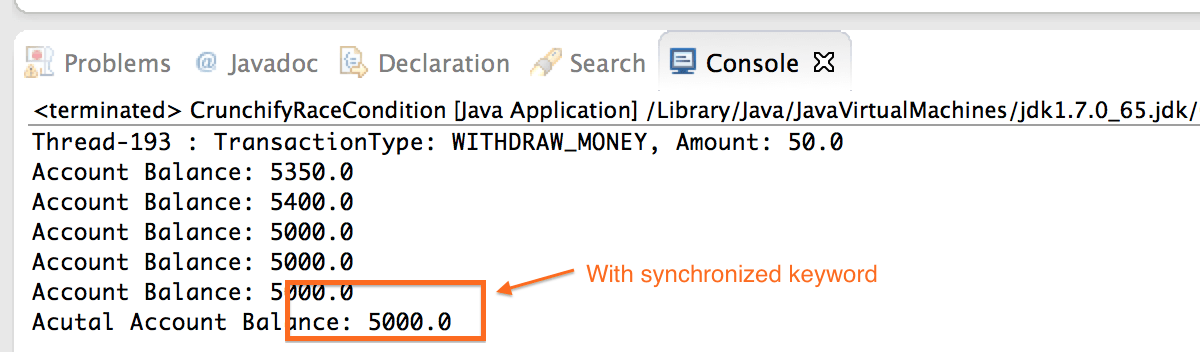
위의 24행과 34행을 확인하십시오. 해당 Synchronized 키워드를 유지하고 프로그램을 실행하십시오. 아래 이미지와 같이 올바른 결과를 확인해야 합니다.
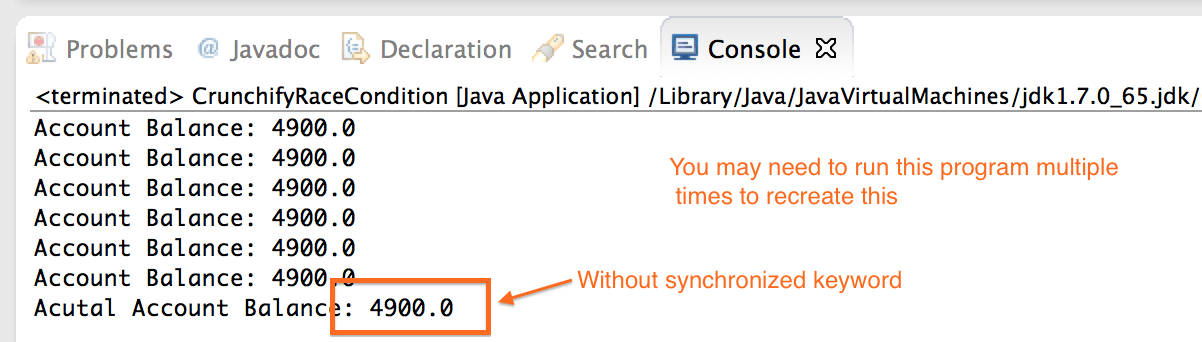
이제 24행과 34행에서 동기화된 키워드를 제거하고 동일한 프로그램을 실행하십시오.
문제를 확인하려면 이 프로그램을 여러 번 실행해야 할 수도 있습니다. Java에서는 항상 Race condition이 표시된다는 보장이 없습니다.
엔터프라이즈 수준의 응용 프로그램이 있고 초당 수백만 건의 트랜잭션에 대해 이야기하는 경우 경쟁 조건으로 인해 회사에 재앙이 발생할 수 있습니다.
이제 질문은 Java 애플리케이션에서 경쟁 조건을 피하는 방법입니다.
- 경쟁 조건이 일부 공유 메모리 내 데이터 구조에 대한 업데이트에 있는 경우 적절한 방식으로 데이터 구조에 대한 액세스 및 업데이트를 동기화해야 합니다.
- 경합 조건이 데이터베이스 업데이트에 있는 경우 적절한 세분성 수준에서 트랜잭션을 사용하도록 SQL을 재구성해야 합니다.
- 프로덕션 환경에 들어가기 전에 부하 테스트를 수행하는 것은 나쁜 생각이 아닙니다. 더 많은 로드는 희귀한 경쟁 조건을 유발할 수 있습니다. 나중에 고치는 것보다 먼저 고치는 것이 좋습니다.
- 작성하는 전역 변수가 없는지 확인하십시오.
- Java에서 모든 개체에는 하나의 모니터와 연결된 뮤텍스가 있습니다. 단일 모니터에는 여러 개의 문이 있지만 각각은
synchronized키워드로 표시됩니다. 스레드가synchronized키워드를 통과하면 모든 문을 효과적으로 잠급니다. - 물론 쓰레드가
synchronized키워드를 통과하지 못한다면 문이 잠긴 것이 아니며 다른 쓰레드는 언제든지 자유롭게 끼어들 수 있습니다.
