Una semplice implementazione di elenchi collegati singolarmente in Java
Pubblicato: 2013-11-27In questo tutorial mostrerò la semplice implementazione dell'elenco con collegamenti singoli in Java.
Un elenco collegato è una serie di nodi in memoria tali che:
- C'è un nodo di partenza.
- Ogni nodo contiene un puntatore che punta al nodo successivo o figlio.
- Se un nodo non ha un nodo figlio, il suo puntatore è impostato su NULL.
- Ogni nodo contiene dati, forse molti.
- L'elenco collegato ha anche funzioni che gestiscono l'elenco eseguendo aggiunte, cancellazioni, modifica dei dati di un nodo, restituzione del numero di nodi, ecc., ecc.
Se hai una delle seguenti domande, sei nel post giusto del blog:
- Come eliminare un determinato nodo nell'elenco collegato
- Elimina un nodo nel mezzo di un elenco collegato singolarmente
- ELENCO COLLEGATI SINGOLAMENTE :: RIMOZIONE (CANCELLA)
- Rimozione di nodi da un elenco collegato singolarmente
Un elenco collegato viene utilizzato per gli stessi scopi di un array. Tuttavia, l'elenco collegato presenta alcuni vantaggi: un array ha una dimensione fissa (a meno che non sia allocato dinamicamente), un elenco collegato può crescere prelevando nuova memoria dall'heap secondo necessità. Se memorizzi un elenco in un array e poi elimini un elemento nel mezzo, devi spostare molti elementi in basso di uno per colmare il divario. Ma in un elenco collegato, devi semplicemente reindirizzare i puntatori attorno al nodo per eliminarlo, quindi lo elimini.
Ecco una semplice implementazione dell'elenco con collegamenti singoli:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyNode <V> { // instance variables private V element ; private CrunchifyNode <V> next ; // constructor first public CrunchifyNode ( ) { this ( null , null ) ; } public CrunchifyNode ( V element , CrunchifyNode <V> next ) { this . element = element ; this . next = next ; } public V getElement ( ) { return element ; } public CrunchifyNode <V> getNext ( ) { return next ; } public void setElement ( V element ) { this . element = element ; } public void setNext ( CrunchifyNode <V> next ) { this . next = next ; } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 |
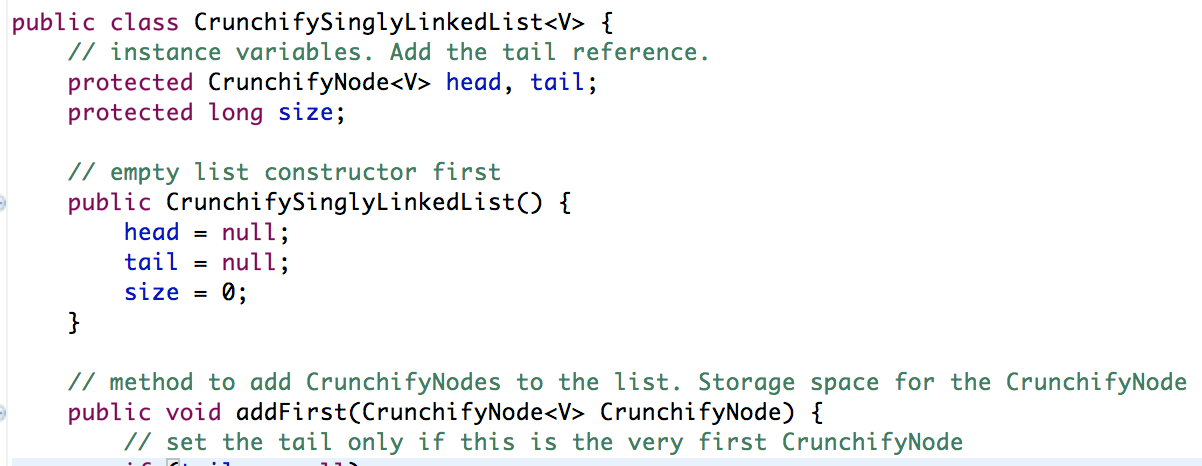
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifySinglyLinkedList <V> { // Instance Variables. Add the tail reference. protected CrunchifyNode <V> head , tail ; protected long size ; // Empty list constructor first public CrunchifySinglyLinkedList ( ) { head = null ; tail = null ; size = 0 ; } // Method to add CrunchifyNodes to the list. Storage space for the CrunchifyNode is already allocated in the calling method public void addFirst ( CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNode ) { // Set the tail only if this is the very first CrunchifyNode if ( tail == null ) tail = CrunchifyNode ; CrunchifyNode . setNext ( head ) ; // Make next of the new CrunchifyNode refer to the head head = CrunchifyNode ; // Give head a new value // change the size size ++ ; } // Add new CrunchifyNode after current CrunchifyNode, checking to see if we are at the tail public void addAfter ( CrunchifyNode <V> currentCrunchifyNode , CrunchifyNode <V> newCrunchifyNode ) { if ( currentCrunchifyNode == tail ) tail = newCrunchifyNode ; newCrunchifyNode . setNext ( currentCrunchifyNode . getNext ( ) ) ; currentCrunchifyNode . setNext ( newCrunchifyNode ) ; // change the size size ++ ; } // Add new CrunchifyNode after the tail CrunchifyNode. public void addLast ( CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNode ) { CrunchifyNode . setNext ( null ) ; tail . setNext ( CrunchifyNode ) ; tail = CrunchifyNode ; size ++ ; } // Methods to remove CrunchifyNodes from the list. (Unfortunately, with a single linked list. there is no way to remove last. Need a previous reference to do that. public CrunchifyNode <V> removeFirst ( ) { if ( head == null ) System . err . println ( "Error: Attempt to remove from an empty list" ) ; // save the one to return CrunchifyNode <V> temp = head ; // do reference manipulation head = head . getNext ( ) ; temp . setNext ( null ) ; size -- ; return temp ; } // Remove the CrunchifyNode at the end of the list. tail refers to this CrunchifyNode, but since the list is single linked, there is no way to refer to the CrunchifyNode before the tail CrunchifyNode. Need to traverse the list. public CrunchifyNode <V> removeLast ( ) { // Declare local variables/objects CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeBefore ; CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeToRemove ; // Make sure we have something to remove if ( size == 0 ) System . err . println ( "Error: Attempt to remove fron an empty list" ) ; // Traverse through the list, getting a reference to the CrunchifyNode before the trailer. Since there is no previous reference. CrunchifyNodeBefore = getFirst ( ) ; for ( int count = 0 ; count < size - 2 ; count ++ ) CrunchifyNodeBefore = CrunchifyNodeBefore . getNext ( ) ; // Save the last CrunchifyNode CrunchifyNodeToRemove = tail ; // Let's do the pointer manipulation CrunchifyNodeBefore . setNext ( null ) ; tail = CrunchifyNodeBefore ; size -- ; return CrunchifyNodeToRemove ; } // Remove a known CrunchifyNode from the list. No need to search or return a value. This method makes use of a 'before' reference in order to allow list manipulation. public void remove ( CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) { // Declare local variables/references CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeBefore , currentCrunchifyNode ; // Make sure we have something to remove if ( size == 0 ) System . err . println ( "Error: Attempt to remove fron an empty list" ) ; // Starting at the beginning check for removal currentCrunchifyNode = getFirst ( ) ; if ( currentCrunchifyNode == CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) removeFirst ( ) ; currentCrunchifyNode = getLast ( ) ; if ( currentCrunchifyNode == CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) removeLast ( ) ; // We've already check two CrunchifyNodes, check the rest if ( size - 2 > 0 ) { CrunchifyNodeBefore = getFirst ( ) ; currentCrunchifyNode = getFirst ( ) . getNext ( ) ; for ( int count = 0 ; count < size - 2 ; count ++ ) { if ( currentCrunchifyNode == CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) { // remove current CrunchifyNode CrunchifyNodeBefore . setNext ( currentCrunchifyNode . getNext ( ) ) ; size -- ; break ; } // Change references CrunchifyNodeBefore = currentCrunchifyNode ; currentCrunchifyNode = currentCrunchifyNode . getNext ( ) ; } } } // The gets to return the head and/or tail CrunchifyNodes and size of the list public CrunchifyNode <V> getFirst ( ) { return head ; } public CrunchifyNode <V> getLast ( ) { return tail ; } public long getSize ( ) { return size ; } } |

Sentiti libero di fornire il tuo commento se trovi bug o altre condizioni che non vengono gestite correttamente :). Il tuo feedback è molto apprezzato.