Eine einfache Single-Linked-List-Implementierung in Java
Veröffentlicht: 2013-11-27In diesem Tutorial zeige ich die einfache Implementierung einer einfach verketteten Liste in Java.
Eine verknüpfte Liste ist eine Reihe von Knoten im Speicher, so dass:
- Es gibt einen Startknoten.
- Jeder Knoten enthält einen Zeiger, der auf den nächsten oder untergeordneten Knoten zeigt.
- Wenn ein Knoten keinen untergeordneten Knoten hat, wird sein Zeiger auf NULL gesetzt.
- Jeder Knoten enthält Daten, vielleicht viele davon.
- Die verknüpfte Liste hat auch Funktionen, die die Liste verwalten, indem sie Hinzufügungen, Löschungen, Änderung der Daten eines Knotens, Rückgabe der Anzahl von Knoten usw. usw. durchführen.
Wenn Sie eine der folgenden Fragen haben, sind Sie im richtigen Blog-Beitrag:
- So löschen Sie einen bestimmten Knoten in der verknüpften Liste
- Löschen Sie einen Knoten in der Mitte einer einfach verknüpften Liste
- EINZELVERKNÜPFTE LISTE :: ENTFERNUNG (LÖSCHUNG)
- Entfernen von Knoten aus einer einfach verknüpften Liste
Eine verknüpfte Liste wird für die gleichen Zwecke wie ein Array verwendet. Die verknüpfte Liste hat jedoch einige Vorteile: Ein Array hat eine feste Größe (es sei denn, es wird dynamisch zugewiesen), eine verknüpfte Liste kann wachsen, indem sie bei Bedarf neuen Speicher vom Heap holt. Wenn Sie eine Liste in einem Array speichern und dann ein Element in der Mitte löschen, müssen Sie viele Elemente um eins nach unten verschieben, um die Lücke zu schließen. Aber in einer verknüpften Liste leiten Sie einfach die Zeiger um den zu löschenden Knoten herum und löschen ihn dann.
Hier ist eine einfache Implementierung der einfach verknüpften Liste:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyNode <V> { // instance variables private V element ; private CrunchifyNode <V> next ; // constructor first public CrunchifyNode ( ) { this ( null , null ) ; } public CrunchifyNode ( V element , CrunchifyNode <V> next ) { this . element = element ; this . next = next ; } public V getElement ( ) { return element ; } public CrunchifyNode <V> getNext ( ) { return next ; } public void setElement ( V element ) { this . element = element ; } public void setNext ( CrunchifyNode <V> next ) { this . next = next ; } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 |
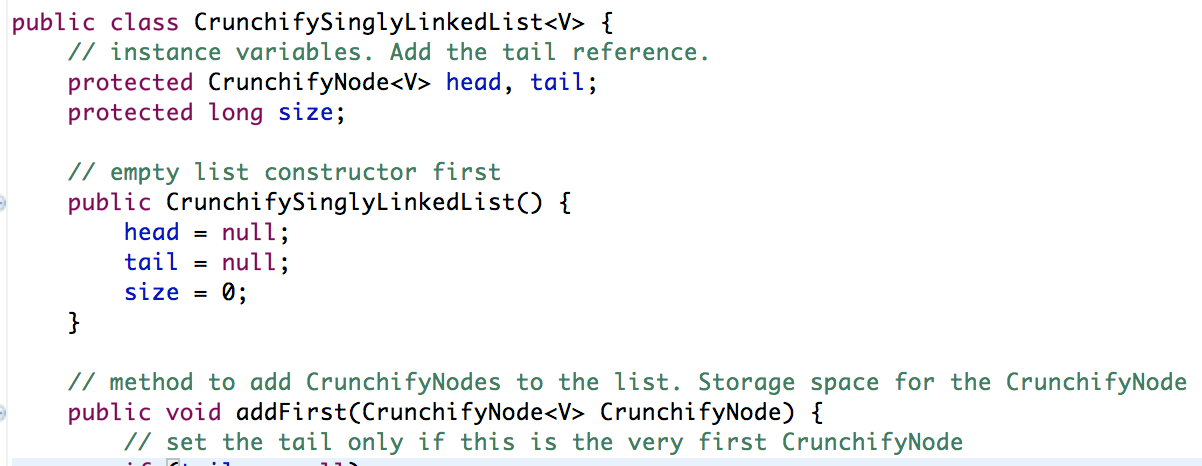
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifySinglyLinkedList <V> { // Instance Variables. Add the tail reference. protected CrunchifyNode <V> head , tail ; protected long size ; // Empty list constructor first public CrunchifySinglyLinkedList ( ) { head = null ; tail = null ; size = 0 ; } // Method to add CrunchifyNodes to the list. Storage space for the CrunchifyNode is already allocated in the calling method public void addFirst ( CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNode ) { // Set the tail only if this is the very first CrunchifyNode if ( tail == null ) tail = CrunchifyNode ; CrunchifyNode . setNext ( head ) ; // Make next of the new CrunchifyNode refer to the head head = CrunchifyNode ; // Give head a new value // change the size size ++ ; } // Add new CrunchifyNode after current CrunchifyNode, checking to see if we are at the tail public void addAfter ( CrunchifyNode <V> currentCrunchifyNode , CrunchifyNode <V> newCrunchifyNode ) { if ( currentCrunchifyNode == tail ) tail = newCrunchifyNode ; newCrunchifyNode . setNext ( currentCrunchifyNode . getNext ( ) ) ; currentCrunchifyNode . setNext ( newCrunchifyNode ) ; // change the size size ++ ; } // Add new CrunchifyNode after the tail CrunchifyNode. public void addLast ( CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNode ) { CrunchifyNode . setNext ( null ) ; tail . setNext ( CrunchifyNode ) ; tail = CrunchifyNode ; size ++ ; } // Methods to remove CrunchifyNodes from the list. (Unfortunately, with a single linked list. there is no way to remove last. Need a previous reference to do that. public CrunchifyNode <V> removeFirst ( ) { if ( head == null ) System . err . println ( "Error: Attempt to remove from an empty list" ) ; // save the one to return CrunchifyNode <V> temp = head ; // do reference manipulation head = head . getNext ( ) ; temp . setNext ( null ) ; size -- ; return temp ; } // Remove the CrunchifyNode at the end of the list. tail refers to this CrunchifyNode, but since the list is single linked, there is no way to refer to the CrunchifyNode before the tail CrunchifyNode. Need to traverse the list. public CrunchifyNode <V> removeLast ( ) { // Declare local variables/objects CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeBefore ; CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeToRemove ; // Make sure we have something to remove if ( size == 0 ) System . err . println ( "Error: Attempt to remove fron an empty list" ) ; // Traverse through the list, getting a reference to the CrunchifyNode before the trailer. Since there is no previous reference. CrunchifyNodeBefore = getFirst ( ) ; for ( int count = 0 ; count < size - 2 ; count ++ ) CrunchifyNodeBefore = CrunchifyNodeBefore . getNext ( ) ; // Save the last CrunchifyNode CrunchifyNodeToRemove = tail ; // Let's do the pointer manipulation CrunchifyNodeBefore . setNext ( null ) ; tail = CrunchifyNodeBefore ; size -- ; return CrunchifyNodeToRemove ; } // Remove a known CrunchifyNode from the list. No need to search or return a value. This method makes use of a 'before' reference in order to allow list manipulation. public void remove ( CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) { // Declare local variables/references CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeBefore , currentCrunchifyNode ; // Make sure we have something to remove if ( size == 0 ) System . err . println ( "Error: Attempt to remove fron an empty list" ) ; // Starting at the beginning check for removal currentCrunchifyNode = getFirst ( ) ; if ( currentCrunchifyNode == CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) removeFirst ( ) ; currentCrunchifyNode = getLast ( ) ; if ( currentCrunchifyNode == CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) removeLast ( ) ; // We've already check two CrunchifyNodes, check the rest if ( size - 2 > 0 ) { CrunchifyNodeBefore = getFirst ( ) ; currentCrunchifyNode = getFirst ( ) . getNext ( ) ; for ( int count = 0 ; count < size - 2 ; count ++ ) { if ( currentCrunchifyNode == CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) { // remove current CrunchifyNode CrunchifyNodeBefore . setNext ( currentCrunchifyNode . getNext ( ) ) ; size -- ; break ; } // Change references CrunchifyNodeBefore = currentCrunchifyNode ; currentCrunchifyNode = currentCrunchifyNode . getNext ( ) ; } } } // The gets to return the head and/or tail CrunchifyNodes and size of the list public CrunchifyNode <V> getFirst ( ) { return head ; } public CrunchifyNode <V> getLast ( ) { return tail ; } public long getSize ( ) { return size ; } } |

Fühlen Sie sich frei, Ihren Kommentar abzugeben, wenn Sie einen Fehler oder eine andere Bedingung finden, die nicht richtig gehandhabt wird :). Ihr Feedback wird sehr geschätzt.