Une implémentation simple de liste chaînée simple en Java
Publié: 2013-11-27Dans ce didacticiel, je vais montrer une implémentation simple de la liste chaînée en Java.
Une liste chaînée est une série de nœuds en mémoire tels que :
- Il y a un nœud de départ.
- Chaque nœud contient un pointeur qui pointe vers le nœud suivant ou enfant.
- Si un nœud n'a pas de nœud enfant, son pointeur est défini sur NULL.
- Chaque nœud contient des données, peut-être beaucoup.
- La liste liée a également des fonctions qui gèrent la liste en effectuant des ajouts, des suppressions, en modifiant les données d'un nœud, en retournant le nombre de nœuds, etc., etc.
Si vous avez l'une des questions ci-dessous, vous êtes au bon article de blog :
- Comment supprimer un nœud donné dans la liste liée
- Supprimer un nœud au milieu d'une liste liée individuellement
- LISTE LIÉE UNIQUE :: SUPPRESSION (SUPPRESSION)
- Suppression de nœuds d'une liste chaînée individuellement
Une liste chaînée est utilisée aux mêmes fins qu'un tableau. Cependant, la liste chaînée présente certains avantages : un tableau est de taille fixe (sauf s'il est alloué dynamiquement), une liste chaînée peut s'agrandir en récupérant de la nouvelle mémoire sur le tas selon les besoins. Si vous stockez une liste dans un tableau, puis supprimez un élément au milieu, vous devez déplacer de nombreux éléments vers le bas pour combler l'écart. Mais dans une liste chaînée, vous redirigez simplement les pointeurs autour du nœud à supprimer, puis vous le supprimez.
Voici une implémentation simple de la liste Singly Linked :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyNode <V> { // instance variables private V element ; private CrunchifyNode <V> next ; // constructor first public CrunchifyNode ( ) { this ( null , null ) ; } public CrunchifyNode ( V element , CrunchifyNode <V> next ) { this . element = element ; this . next = next ; } public V getElement ( ) { return element ; } public CrunchifyNode <V> getNext ( ) { return next ; } public void setElement ( V element ) { this . element = element ; } public void setNext ( CrunchifyNode <V> next ) { this . next = next ; } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 |
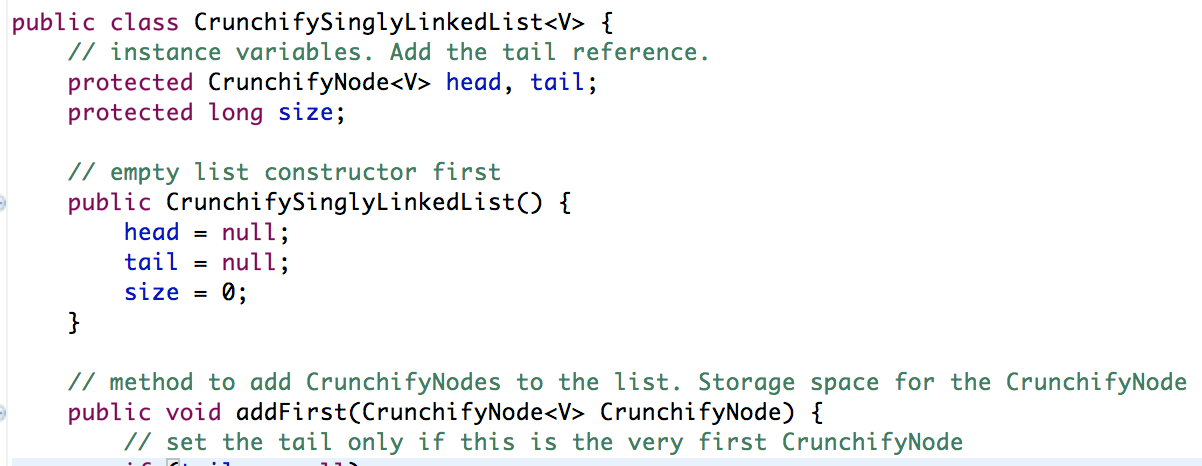
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifySinglyLinkedList <V> { // Instance Variables. Add the tail reference. protected CrunchifyNode <V> head , tail ; protected long size ; // Empty list constructor first public CrunchifySinglyLinkedList ( ) { head = null ; tail = null ; size = 0 ; } // Method to add CrunchifyNodes to the list. Storage space for the CrunchifyNode is already allocated in the calling method public void addFirst ( CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNode ) { // Set the tail only if this is the very first CrunchifyNode if ( tail == null ) tail = CrunchifyNode ; CrunchifyNode . setNext ( head ) ; // Make next of the new CrunchifyNode refer to the head head = CrunchifyNode ; // Give head a new value // change the size size ++ ; } // Add new CrunchifyNode after current CrunchifyNode, checking to see if we are at the tail public void addAfter ( CrunchifyNode <V> currentCrunchifyNode , CrunchifyNode <V> newCrunchifyNode ) { if ( currentCrunchifyNode == tail ) tail = newCrunchifyNode ; newCrunchifyNode . setNext ( currentCrunchifyNode . getNext ( ) ) ; currentCrunchifyNode . setNext ( newCrunchifyNode ) ; // change the size size ++ ; } // Add new CrunchifyNode after the tail CrunchifyNode. public void addLast ( CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNode ) { CrunchifyNode . setNext ( null ) ; tail . setNext ( CrunchifyNode ) ; tail = CrunchifyNode ; size ++ ; } // Methods to remove CrunchifyNodes from the list. (Unfortunately, with a single linked list. there is no way to remove last. Need a previous reference to do that. public CrunchifyNode <V> removeFirst ( ) { if ( head == null ) System . err . println ( "Error: Attempt to remove from an empty list" ) ; // save the one to return CrunchifyNode <V> temp = head ; // do reference manipulation head = head . getNext ( ) ; temp . setNext ( null ) ; size -- ; return temp ; } // Remove the CrunchifyNode at the end of the list. tail refers to this CrunchifyNode, but since the list is single linked, there is no way to refer to the CrunchifyNode before the tail CrunchifyNode. Need to traverse the list. public CrunchifyNode <V> removeLast ( ) { // Declare local variables/objects CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeBefore ; CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeToRemove ; // Make sure we have something to remove if ( size == 0 ) System . err . println ( "Error: Attempt to remove fron an empty list" ) ; // Traverse through the list, getting a reference to the CrunchifyNode before the trailer. Since there is no previous reference. CrunchifyNodeBefore = getFirst ( ) ; for ( int count = 0 ; count < size - 2 ; count ++ ) CrunchifyNodeBefore = CrunchifyNodeBefore . getNext ( ) ; // Save the last CrunchifyNode CrunchifyNodeToRemove = tail ; // Let's do the pointer manipulation CrunchifyNodeBefore . setNext ( null ) ; tail = CrunchifyNodeBefore ; size -- ; return CrunchifyNodeToRemove ; } // Remove a known CrunchifyNode from the list. No need to search or return a value. This method makes use of a 'before' reference in order to allow list manipulation. public void remove ( CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) { // Declare local variables/references CrunchifyNode <V> CrunchifyNodeBefore , currentCrunchifyNode ; // Make sure we have something to remove if ( size == 0 ) System . err . println ( "Error: Attempt to remove fron an empty list" ) ; // Starting at the beginning check for removal currentCrunchifyNode = getFirst ( ) ; if ( currentCrunchifyNode == CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) removeFirst ( ) ; currentCrunchifyNode = getLast ( ) ; if ( currentCrunchifyNode == CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) removeLast ( ) ; // We've already check two CrunchifyNodes, check the rest if ( size - 2 > 0 ) { CrunchifyNodeBefore = getFirst ( ) ; currentCrunchifyNode = getFirst ( ) . getNext ( ) ; for ( int count = 0 ; count < size - 2 ; count ++ ) { if ( currentCrunchifyNode == CrunchifyNodeToRemove ) { // remove current CrunchifyNode CrunchifyNodeBefore . setNext ( currentCrunchifyNode . getNext ( ) ) ; size -- ; break ; } // Change references CrunchifyNodeBefore = currentCrunchifyNode ; currentCrunchifyNode = currentCrunchifyNode . getNext ( ) ; } } } // The gets to return the head and/or tail CrunchifyNodes and size of the list public CrunchifyNode <V> getFirst ( ) { return head ; } public CrunchifyNode <V> getLast ( ) { return tail ; } public long getSize ( ) { return size ; } } |

N'hésitez pas à fournir votre commentaire si vous trouvez un bogue ou une autre condition qui n'est pas géré correctement :). Vos remarques sont très appréciées.