In Java Wie liest man eine Datei und konvertiert eine Datei in eine Zeichenfolge? (5 verschiedene Möglichkeiten)
Veröffentlicht: 2021-11-21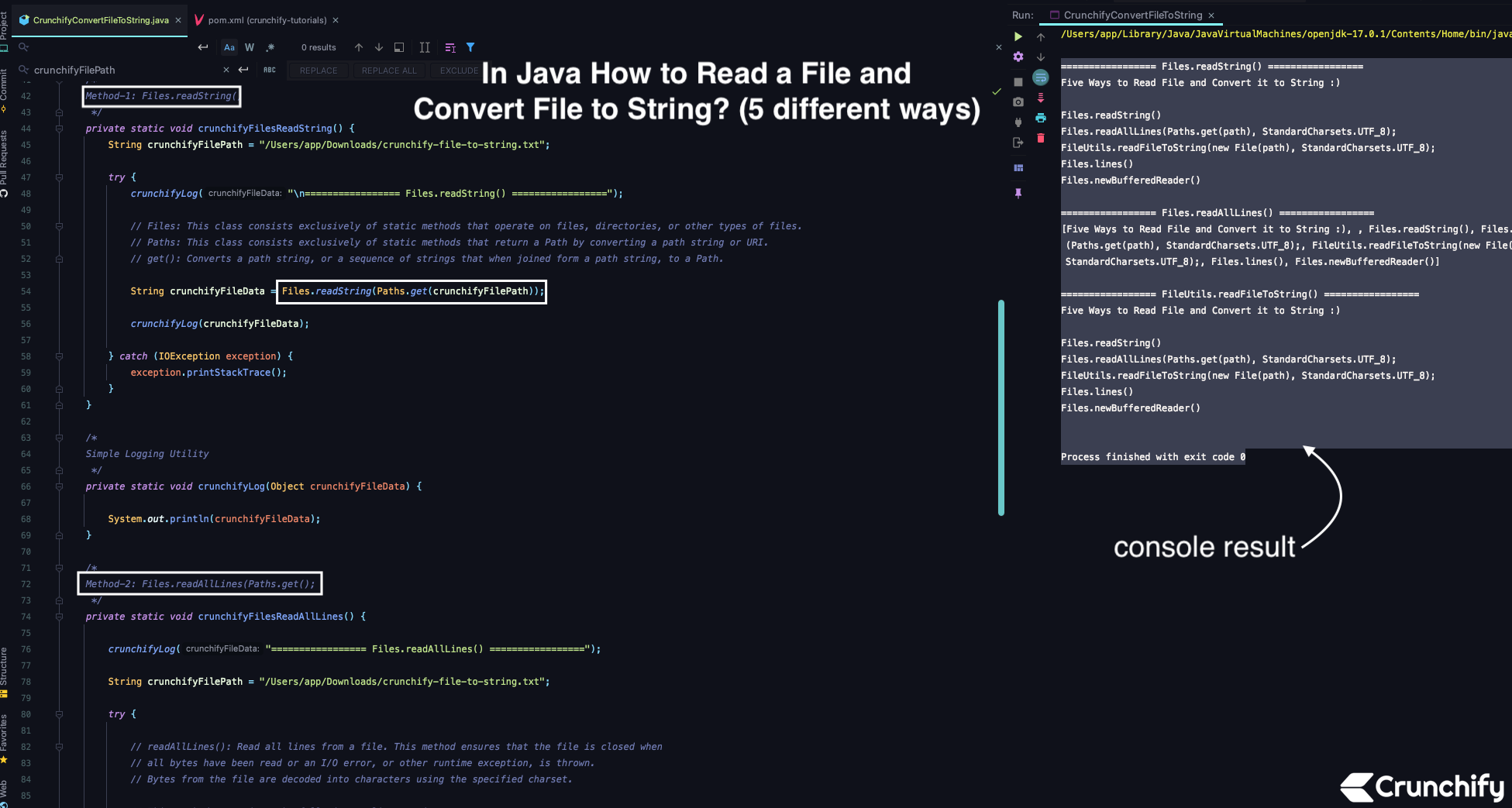
Was ist der einfachste Weg, eine Datei in String einzulesen? Möchten Sie eine reine Textdatei in Java lesen? Wie möchten Sie ein File-Objekt in ein String-Objekt konvertieren? Es gibt mehrere Möglichkeiten, wie wir eine Datei lesen und in String umwandeln können.
Es gibt insgesamt 5 Möglichkeiten, eine ganze Textdatei in Java in einen String zu konvertieren.
- Dateien.readString()
- Files.readAllLines (Paths.get (Pfad), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
- FileUtils.readFileToString (neue Datei (Pfad), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); – Apache Commons IO-Abhängigkeit
- Dateien.lines()
- Files.newBufferedReader()
Lass uns anfangen:
- Stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie unten die Apache Commons IO-Abhängigkeit hinzufügen.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
< dependency > < groupId > commons - io < / groupId > < artifactId > commons - io < / artifactId > < version > 2.11.0 < / version > < / dependency > |
- Erstellen Sie die Klasse CrunchifyConvertFileToString.java.
- Kopieren Sie den folgenden Code und fügen Sie ihn ein.
CrunchifyConvertFileToString.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 |
package crunchify . com . java . tutorials ; import org . apache . commons . io . FileUtils ; import java . io . File ; import java . io . IOException ; import java . nio . charset . StandardCharsets ; import java . nio . file . Files ; import java . nio . file . Paths ; import java . util . List ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * Program: In Java How to Read a File and Convert File to String? (5 different ways) */ public class CrunchifyConvertFileToString { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { // Files.readString() crunchifyFilesReadString ( ) ; // Files.readAllLines(Paths.get(); crunchifyFilesReadAllLines ( ) ; // FileUtils.readFileToString(new File(); // Apache Commons IO method crunchifyFileUtilsReadFileToString ( ) ; // Files.lines() // Please visit: https://crunchify.me/3CDrP7N crunchifyFilesLines ( ) ; // Files.newBufferedReader() // Please visit: https://crunchify.me/3CDrP7N crunchifyFilesNewBufferedReader ( ) ; } /* Method-1: Files.readString() */ private static void crunchifyFilesReadString ( ) { String crunchifyFilePath = "/Users/app/Downloads/crunchify-file-to-string.txt" ; try { crunchifyLog ( "\n================= Files.readString() =================" ) ; // Files: This class consists exclusively of static methods that operate on files, directories, or other types of files. // Paths: This class consists exclusively of static methods that return a Path by converting a path string or URI. // get(): Converts a path string, or a sequence of strings that when joined form a path string, to a Path. String crunchifyFileData = Files . readString ( Paths . get ( crunchifyFilePath ) ) ; crunchifyLog ( crunchifyFileData ) ; } catch ( IOException exception ) { exception . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } /* Simple Logging Utility */ private static void crunchifyLog ( Object crunchifyFileData ) { System . out . println ( crunchifyFileData ) ; } /* Method-2: Files.readAllLines(Paths.get(); */ private static void crunchifyFilesReadAllLines ( ) { crunchifyLog ( "================= Files.readAllLines() =================" ) ; String crunchifyFilePath = "/Users/app/Downloads/crunchify-file-to-string.txt" ; try { // readAllLines(): Read all lines from a file. This method ensures that the file is closed when // all bytes have been read or an I/O error, or other runtime exception, is thrown. // Bytes from the file are decoded into characters using the specified charset. // This method recognizes the following as line terminators: /* \u000D followed by \u000A, CARRIAGE RETURN followed by LINE FEED \u000A, LINE FEED \u000D, CARRIAGE RETURN */ List < String > crunchifyFileData = Files . readAllLines ( Paths . get ( crunchifyFilePath ) , StandardCharsets . UTF_8 ) ; crunchifyLog ( crunchifyFileData ) ; } catch ( IOException exception ) { exception . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } /* Method-3: FileUtils.readFileToString(new File(); Apache Commons IO: <dependency><groupId>commons-io</groupId><artifactId>commons-io</artifactId><version>2.6</version></dependency> */ private static void crunchifyFileUtilsReadFileToString ( ) { crunchifyLog ( "\n================= FileUtils.readFileToString() =================" ) ; String crunchifyFilePath = "/Users/app/Downloads/crunchify-file-to-string.txt" ; try { // readFileToString: Reads the contents of a file into a String. The file is always closed. String crunchifyFileData = FileUtils . readFileToString ( new File ( crunchifyFilePath ) , StandardCharsets . UTF_8 ) ; // UTF_8: Eight-bit UCS Transformation Format. crunchifyLog ( crunchifyFileData ) ; } catch ( IOException exception ) { exception . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } /* Method-4: Files.lines() */ private static void crunchifyFilesLines ( ) { // Please visit: https://crunchify.me/3CDrP7N } /* Method-5: Files.newBufferedReader() */ private static void crunchifyFilesNewBufferedReader ( ) { // Please visit: https://crunchify.me/3CDrP7N } } |
Ergebnis der IntelliJ IDEA-Konsole:
Führen Sie einfach das obige Programm als Java-Anwendung aus, Sie werden das Ergebnis wie unten sehen.

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
================= Files . readString ( ) ================= Five Ways to Read File and Convert it to String : ) Files . readString ( ) Files . readAllLines ( Paths . get ( path ) , StandardCharsets . UTF_8 ) ; FileUtils . readFileToString ( new File ( path ) , StandardCharsets . UTF_8 ) ; Files . lines ( ) Files . newBufferedReader ( ) ================= Files . readAllLines ( ) ================= [ Five Ways to Read File and Convert it to String : ) , , Files . readString ( ) , Files . readAllLines ( Paths . get ( path ) , StandardCharsets . UTF_8 ) ; , FileUtils . readFileToString ( new File ( path ) , StandardCharsets . UTF_8 ) ; , Files . lines ( ) , Files . newBufferedReader ( ) ] ================= FileUtils . readFileToString ( ) ================= Five Ways to Read File and Convert it to String : ) Files . readString ( ) Files . readAllLines ( Paths . get ( path ) , StandardCharsets . UTF_8 ) ; FileUtils . readFileToString ( new File ( path ) , StandardCharsets . UTF_8 ) ; Files . lines ( ) Files . newBufferedReader ( ) Process finished with exit code 0 |
Lassen Sie mich wissen, wenn Sie auf ein Problem stoßen, das den obigen Code ausführt.
Hier ein Tutorial, das Methode4 und Methode-5 erklärt:
