Como executar vários threads simultaneamente em Java? Abordagem de serviço executor
Publicados: 2021-10-09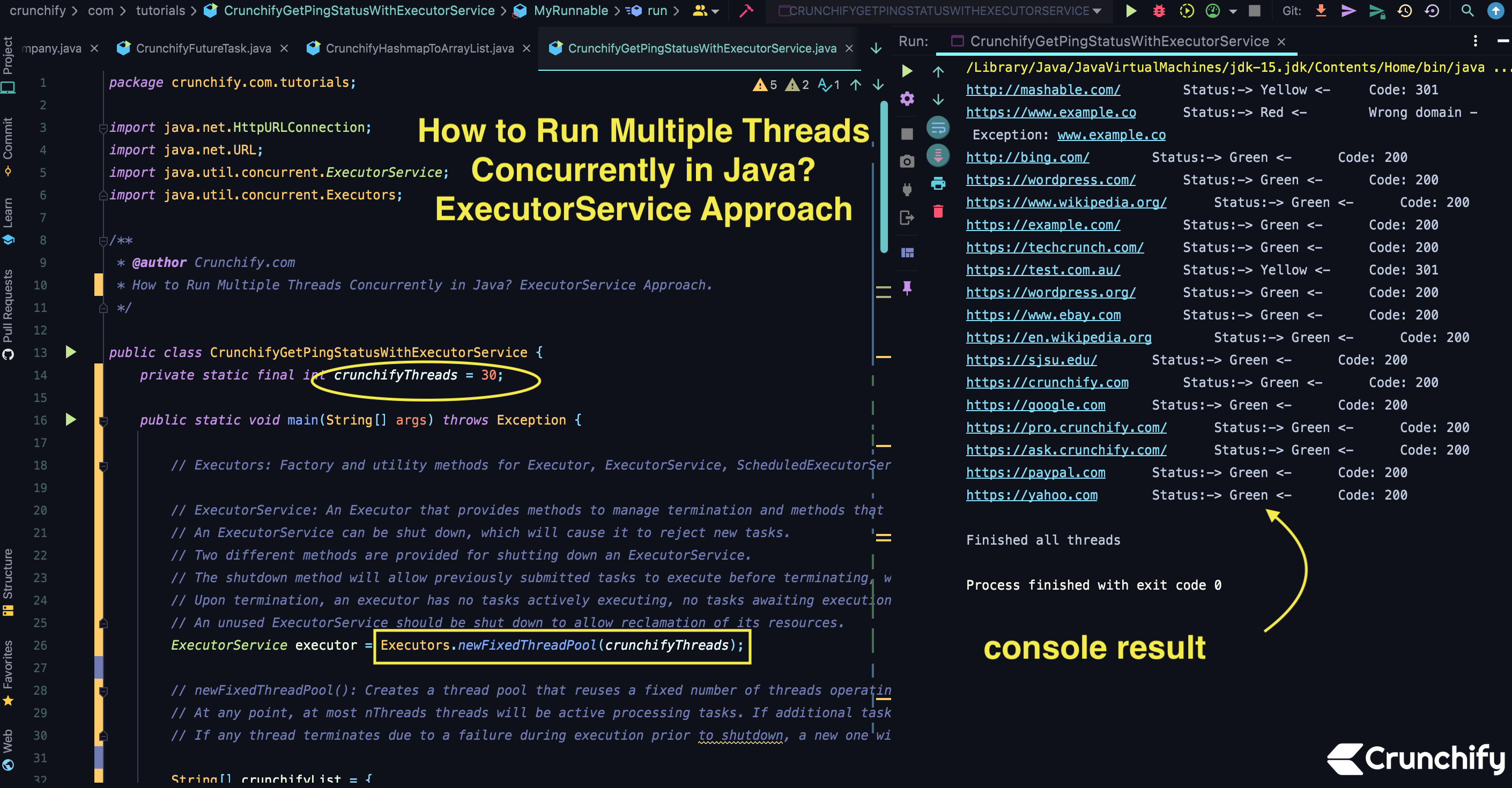
Vamos dar uma olhada neste exemplo novamente: Como obter o status de ping de qualquer ponto final HTTP em Java?
Você notou a execução do thread para esse exemplo? É sequencial. What if you have 500 endpoints? Aposto que você tem que esperar pelo menos 5 minutos para obter resultado. O que tenho certeza que não é a melhor solução.
O que agora? A pergunta correta seria:
- Como executar vários threads simultaneamente?
- Como implementar vários threads em Java?
- Como executo diferentes threads em Java?
- Java – Onde está o Tutorial de Programação Multithreading?
- Thread: Como usar vários threads para acelerar o processamento?
ExecutorService Approach é a sua resposta.
Um Executor que fornece métodos para gerenciar o encerramento e métodos que podem produzir um Future para rastrear o progresso de uma ou mais tarefas assíncronas.
Um ExecutorService pode ser encerrado, o que fará com que ele rejeite novas tarefas. Dois métodos diferentes são fornecidos para encerrar um ExecutorService. O método shutdown() permitirá que as tarefas enviadas anteriormente sejam executadas antes de serem encerradas, enquanto o método shutdownNow() impede que as tarefas em espera sejam iniciadas e tenta interromper as tarefas em execução no momento.
Após o término, um executor não tem tarefas em execução ativa, nenhuma tarefa aguardando execução e nenhuma nova tarefa pode ser enviada. Um ExecutorService não utilizado deve ser encerrado para permitir a recuperação de seus recursos.
O método submit estende o método base Executor.execute ( java.lang.Runnable ) criando e retornando um Future que pode ser usado para cancelar a execução e/ou aguardar a conclusão. Os métodos invokeAny e invokeAll executam as formas mais úteis de execução em massa, executando uma coleção de tarefas e, em seguida, aguardando a conclusão de pelo menos uma, ou todas. (A classe ExecutorCompletionService pode ser usada para escrever variantes personalizadas desses métodos.)
A classe Executors fornece métodos de fábrica para os serviços de executor fornecidos neste pacote.
- java – ExecutorService, como esperar que todas as tarefas terminem?
- Um guia para o Java ExecutorService
- Java Thread Pool – explicação do ExecutorService
Abaixo está um exemplo simples de Java que explica o usage of ExecutorService .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . net . HttpURLConnection ; import java . net . URL ; import java . util . concurrent . ExecutorService ; import java . util . concurrent . Executors ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * How to Run Multiple Threads Concurrently in Java? ExecutorService Approach. */ public class CrunchifyGetPingStatusWithExecutorService { private static final int crunchifyThreads = 30 ; public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws Exception { // Executors: Factory and utility methods for Executor, ExecutorService, ScheduledExecutorService, ThreadFactory, and Callable classes defined in this package. // ExecutorService: An Executor that provides methods to manage termination and methods that can produce a Future for tracking progress of one or more asynchronous tasks. // An ExecutorService can be shut down, which will cause it to reject new tasks. // Two different methods are provided for shutting down an ExecutorService. // The shutdown method will allow previously submitted tasks to execute before terminating, while the shutdownNow method prevents waiting tasks from starting and attempts to stop currently executing tasks. // Upon termination, an executor has no tasks actively executing, no tasks awaiting execution, and no new tasks can be submitted. // An unused ExecutorService should be shut down to allow reclamation of its resources. ExecutorService executor = Executors . newFixedThreadPool ( crunchifyThreads ) ; // newFixedThreadPool(): Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads operating off a shared unbounded queue. // At any point, at most nThreads threads will be active processing tasks. If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active, they will wait in the queue until a thread is available. // If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to execute subsequent tasks String [ ] crunchifyList = { "https://crunchify.com" , "https://yahoo.com" , "https://www.ebay.com" , "https://google.com" , "https://www.example.co" , "https://paypal.com" , "http://bing.com/" , "https://techcrunch.com/" , "http://mashable.com/" , "https://pro.crunchify.com/" , "https://wordpress.com/" , "https://wordpress.org/" , "https://example.com/" , "https://sjsu.edu/" , "https://ask.crunchify.com/" , "https://test.com.au/" , "https://www.wikipedia.org/" , "https://en.wikipedia.org" } ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyList . length ; i ++ ) { String url = crunchifyList [ i ] ; Runnable worker = new MyRunnable ( url ) ; // execute(): Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, // or in the calling thread, at the discretion of the Executor implementation. executor . execute ( worker ) ; } // shutdown(): Initiates an orderly shutdown in which previously submitted tasks are executed, but no new tasks will be accepted. // Invocation has no additional effect if already shut down. // This method does not wait for previously submitted tasks to complete execution. Use awaitTermination to do that. executor . shutdown ( ) ; // Wait until all threads are finish // Returns true if all tasks have completed following shut down. // Note that isTerminated is never true unless either shutdown or shutdownNow was called first. while ( ! executor . isTerminated ( ) ) { // empty body } System . out . println ( "\nFinished all threads" ) ; } // Runnable: The Runnable interface should be implemented by any class whose instances are intended to be executed by a thread. // The class must define a method of no arguments called run. public static class MyRunnable implements Runnable { private final String url ; MyRunnable ( String url ) { this . url = url ; } @Override public void run ( ) { String result = "" ; int code = 200 ; try { URL siteURL = new URL ( url ) ; // HttpURLConnection: A URLConnection with support for HTTP-specific features. See the spec for details. // openConnection(): Returns a URLConnection instance that represents a connection to the remote object referred to by the URL. HttpURLConnection connection = ( HttpURLConnection ) siteURL . openConnection ( ) ; // setRequestMethod: Set the method for the URL request, one of: //GET //POST //HEAD //OPTIONS //PUT //DELETE //TRACE connection . setRequestMethod ( "GET" ) ; // setConnectTimeout(): Sets a specified timeout value, in milliseconds, to be used when opening a communications link to the resource referenced by this URLConnection. // If the timeout expires before the connection can be established, a java.net connection . setConnectTimeout ( 3000 ) ; // connect(): Opens a communications link to the resource referenced by this URL, if such a connection has not already been established. connection . connect ( ) ; // getResponseCode(): Gets the status code from an HTTP response message. For example, in the case of the following status lines: // HTTP/1.0 200 OK // HTTP/1.0 401 Unauthorized code = connection . getResponseCode ( ) ; if ( code == 200 ) { result = "-> Green <-\t\t" + "Code: " + code ; ; } else { result = "-> Yellow <-\t\t" + "Code: " + code ; } } catch ( Exception e ) { result = "-> Red <-\t\t" + "Wrong domain - Exception: " + e . getMessage ( ) ; } System . out . println ( url + "\t\t\t\tStatus:" + result ) ; } } } |
Saída:

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
/ Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / slf4j - api / 1.7.31 / slf4j - api - 1.7.31.jar : / Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / jul - to - slf4j / 1.7.31 / jul - to - slf4j - 1.7.31.jar : / Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / jcl - over - slf4j / 1.7.31 / jcl - over - slf4j - 1.7.31.jar : / Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / log4j - over - slf4j / 1.7.31 / log4j - over - slf4j - 1.7.31.jar crunchify . com . tutorials . CrunchifyGetPingStatusWithExecutorService http : //mashable.com/ Status:-> Yellow <- Code: 301 http : //bing.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //www.example.co Status:-> Red <- Wrong domain - Exception: www.example.co https : //example.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //wordpress.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //www.wikipedia.org/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //test.com.au/ Status:-> Yellow <- Code: 301 https : //wordpress.org/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //techcrunch.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //www.ebay.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //ask.crunchify.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //en.wikipedia.org Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //crunchify.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //sjsu.edu/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //pro.crunchify.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //google.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //paypal.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //yahoo.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 Finished all threads Process finished with exit code 0 |
Agora confira o resultado.
Deve ser em apenas alguns segundos. Eu espero que você ache isto útil. Tente executar isso mais de uma vez e você poderá ver resultados diferentes, pois todos os threads estão sendo executados em paralelo e quem obtiver resultado rápido, você verá o resultado postado no console do Eclipse.
Deixe-me saber para qualquer consulta.
