Jak uruchomić wiele wątków jednocześnie w Javie? Podejście Wykonawcy
Opublikowany: 2021-10-09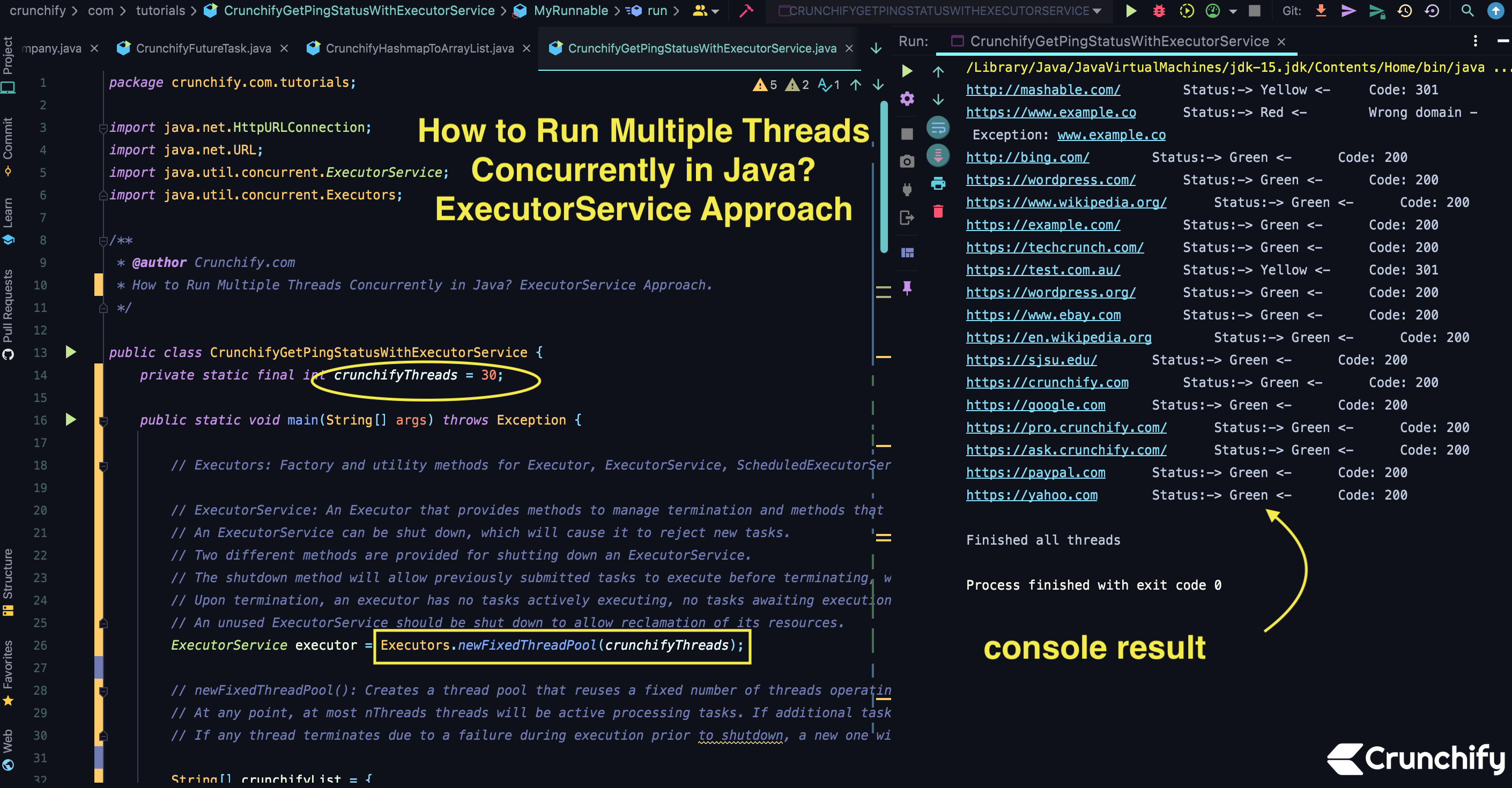
Przyjrzyjmy się jeszcze raz temu przykładowi: Jak uzyskać status ping dowolnego punktu końcowego HTTP w Javie?
Czy zauważyłeś wykonanie wątku dla tego przykładu? Jest sekwencyjny. What if you have 500 endpoints? Założę się, że musisz poczekać co najmniej 5 minut, aby uzyskać wynik. Co z pewnością nie jest najlepszym rozwiązaniem.
Co teraz? Prawidłowe pytanie brzmiałoby:
- Jak uruchomić wiele wątków jednocześnie?
- Jak zaimplementować wiele wątków w Javie?
- Jak uruchomić różne wątki w Javie?
- Java – gdzie jest samouczek programowania wielowątkowego?
- Wątek: Jak korzystać z wielu wątków, aby przyspieszyć przetwarzanie?
ExecutorService Approach to Twoja odpowiedź.
Executor, który zapewnia metody zarządzania zakończeniem i metody, które mogą generować Future do śledzenia postępu jednego lub więcej zadań asynchronicznych.
Usługa ExecutorService może zostać zamknięta, co spowoduje odrzucenie nowych zadań. Dostępne są dwie różne metody zamykania usługi ExecutorService. Metoda shutdown() pozwoli na wykonanie wcześniej przesłanych zadań przed zakończeniem, natomiast metoda shutdownNow() zapobiega uruchamianiu oczekujących zadań i próbom zatrzymania aktualnie wykonywanych zadań.
Po rozwiązaniu executor nie ma żadnych aktywnych zadań, nie ma zadań oczekujących na wykonanie i nie można przesyłać nowych zadań. Nieużywaną usługę ExecutorService należy zamknąć, aby umożliwić odzyskanie jej zasobów.
Metoda submit rozszerza podstawową metodę Executor.execute ( java.lang.Runnable ) poprzez utworzenie i zwrócenie Future, która może być użyta do anulowania wykonania i/lub oczekiwania na zakończenie. Metody invokeAny i invokeAll wykonują najczęściej przydatne formy wykonywania zbiorczego, wykonując kolekcję zadań, a następnie czekają na ukończenie co najmniej jednego lub wszystkich. (Class ExecutorCompletionService może służyć do pisania niestandardowych wariantów tych metod).
Klasa Executors udostępnia metody fabryczne dla usług executorów dostarczanych w tym pakiecie.
- java – ExecutorService, jak czekać na zakończenie wszystkich zadań?
- Przewodnik po usłudze Java Executor
- Java Thread Pool – wyjaśnienie usługi ExecutorService
Poniżej znajduje się prosty przykład Java, który wyjaśnia usage of ExecutorService .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . net . HttpURLConnection ; import java . net . URL ; import java . util . concurrent . ExecutorService ; import java . util . concurrent . Executors ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * How to Run Multiple Threads Concurrently in Java? ExecutorService Approach. */ public class CrunchifyGetPingStatusWithExecutorService { private static final int crunchifyThreads = 30 ; public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws Exception { // Executors: Factory and utility methods for Executor, ExecutorService, ScheduledExecutorService, ThreadFactory, and Callable classes defined in this package. // ExecutorService: An Executor that provides methods to manage termination and methods that can produce a Future for tracking progress of one or more asynchronous tasks. // An ExecutorService can be shut down, which will cause it to reject new tasks. // Two different methods are provided for shutting down an ExecutorService. // The shutdown method will allow previously submitted tasks to execute before terminating, while the shutdownNow method prevents waiting tasks from starting and attempts to stop currently executing tasks. // Upon termination, an executor has no tasks actively executing, no tasks awaiting execution, and no new tasks can be submitted. // An unused ExecutorService should be shut down to allow reclamation of its resources. ExecutorService executor = Executors . newFixedThreadPool ( crunchifyThreads ) ; // newFixedThreadPool(): Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads operating off a shared unbounded queue. // At any point, at most nThreads threads will be active processing tasks. If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active, they will wait in the queue until a thread is available. // If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to execute subsequent tasks String [ ] crunchifyList = { "https://crunchify.com" , "https://yahoo.com" , "https://www.ebay.com" , "https://google.com" , "https://www.example.co" , "https://paypal.com" , "http://bing.com/" , "https://techcrunch.com/" , "http://mashable.com/" , "https://pro.crunchify.com/" , "https://wordpress.com/" , "https://wordpress.org/" , "https://example.com/" , "https://sjsu.edu/" , "https://ask.crunchify.com/" , "https://test.com.au/" , "https://www.wikipedia.org/" , "https://en.wikipedia.org" } ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyList . length ; i ++ ) { String url = crunchifyList [ i ] ; Runnable worker = new MyRunnable ( url ) ; // execute(): Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, // or in the calling thread, at the discretion of the Executor implementation. executor . execute ( worker ) ; } // shutdown(): Initiates an orderly shutdown in which previously submitted tasks are executed, but no new tasks will be accepted. // Invocation has no additional effect if already shut down. // This method does not wait for previously submitted tasks to complete execution. Use awaitTermination to do that. executor . shutdown ( ) ; // Wait until all threads are finish // Returns true if all tasks have completed following shut down. // Note that isTerminated is never true unless either shutdown or shutdownNow was called first. while ( ! executor . isTerminated ( ) ) { // empty body } System . out . println ( "\nFinished all threads" ) ; } // Runnable: The Runnable interface should be implemented by any class whose instances are intended to be executed by a thread. // The class must define a method of no arguments called run. public static class MyRunnable implements Runnable { private final String url ; MyRunnable ( String url ) { this . url = url ; } @Override public void run ( ) { String result = "" ; int code = 200 ; try { URL siteURL = new URL ( url ) ; // HttpURLConnection: A URLConnection with support for HTTP-specific features. See the spec for details. // openConnection(): Returns a URLConnection instance that represents a connection to the remote object referred to by the URL. HttpURLConnection connection = ( HttpURLConnection ) siteURL . openConnection ( ) ; // setRequestMethod: Set the method for the URL request, one of: //GET //POST //HEAD //OPTIONS //PUT //DELETE //TRACE connection . setRequestMethod ( "GET" ) ; // setConnectTimeout(): Sets a specified timeout value, in milliseconds, to be used when opening a communications link to the resource referenced by this URLConnection. // If the timeout expires before the connection can be established, a java.net connection . setConnectTimeout ( 3000 ) ; // connect(): Opens a communications link to the resource referenced by this URL, if such a connection has not already been established. connection . connect ( ) ; // getResponseCode(): Gets the status code from an HTTP response message. For example, in the case of the following status lines: // HTTP/1.0 200 OK // HTTP/1.0 401 Unauthorized code = connection . getResponseCode ( ) ; if ( code == 200 ) { result = "-> Green <-\t\t" + "Code: " + code ; ; } else { result = "-> Yellow <-\t\t" + "Code: " + code ; } } catch ( Exception e ) { result = "-> Red <-\t\t" + "Wrong domain - Exception: " + e . getMessage ( ) ; } System . out . println ( url + "\t\t\t\tStatus:" + result ) ; } } } |
Wyjście:

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
/ Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / slf4j - api / 1.7.31 / slf4j - api - 1.7.31.jar : / Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / jul - to - slf4j / 1.7.31 / jul - to - slf4j - 1.7.31.jar : / Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / jcl - over - slf4j / 1.7.31 / jcl - over - slf4j - 1.7.31.jar : / Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / log4j - over - slf4j / 1.7.31 / log4j - over - slf4j - 1.7.31.jar crunchify . com . tutorials . CrunchifyGetPingStatusWithExecutorService http : //mashable.com/ Status:-> Yellow <- Code: 301 http : //bing.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //www.example.co Status:-> Red <- Wrong domain - Exception: www.example.co https : //example.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //wordpress.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //www.wikipedia.org/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //test.com.au/ Status:-> Yellow <- Code: 301 https : //wordpress.org/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //techcrunch.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //www.ebay.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //ask.crunchify.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //en.wikipedia.org Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //crunchify.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //sjsu.edu/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //pro.crunchify.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //google.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //paypal.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //yahoo.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 Finished all threads Process finished with exit code 0 |
Teraz sprawdź wynik.
Powinno to nastąpić w ciągu kilku sekund. Mam nadzieję, że okaże się to pomocne. Spróbuj uruchomić to więcej niż jeden raz, a możesz zobaczyć różne wyniki, ponieważ wszystkie wątki działają równolegle, a kto kiedykolwiek uzyska szybki wynik, zobaczysz wynik opublikowany w konsoli Eclipse.
Daj mi znać na każde zapytanie.
