Comment exécuter plusieurs threads simultanément en Java ? Approche ExecutorService
Publié: 2021-10-09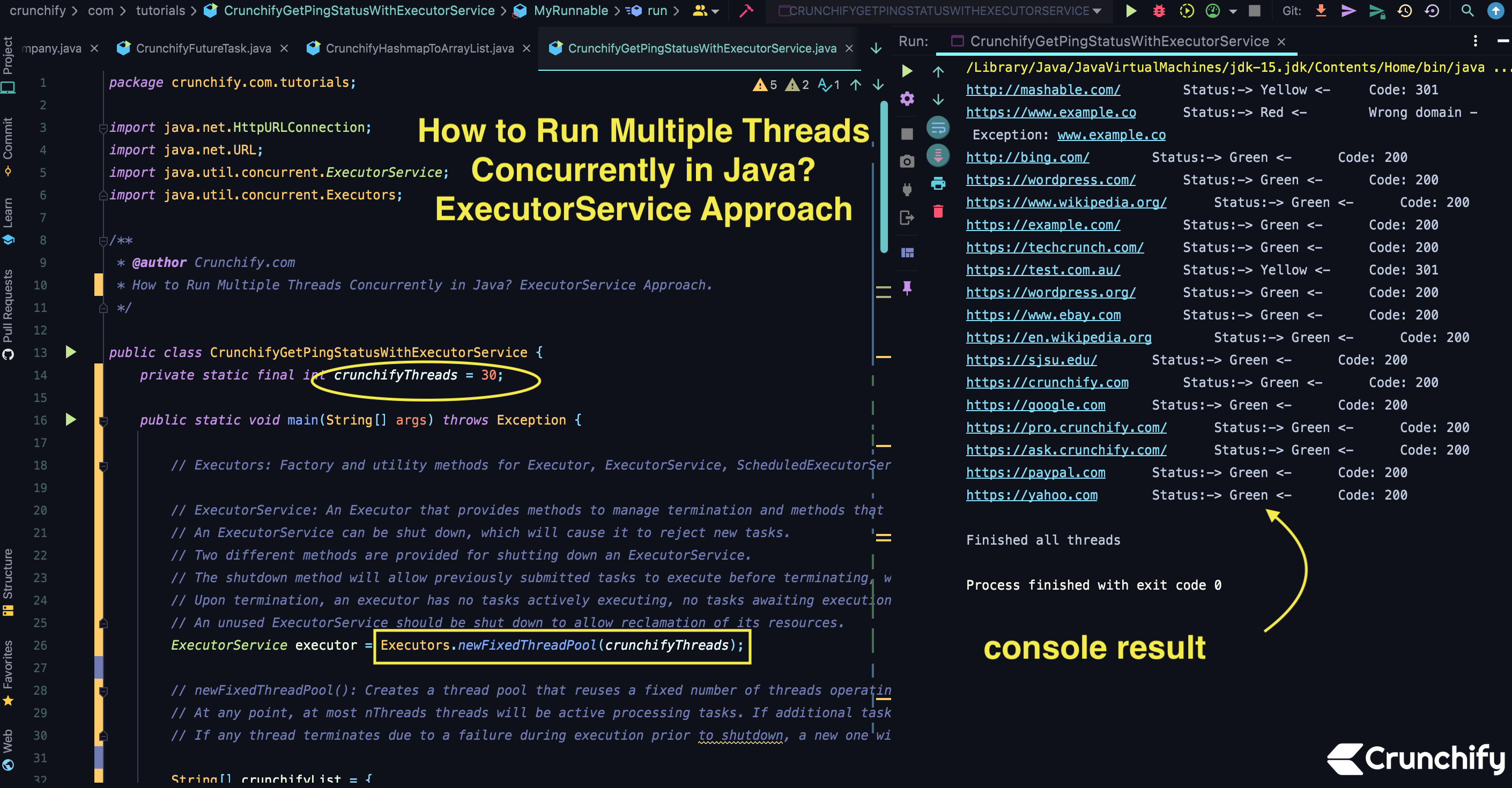
Reprenons cet exemple : Comment obtenir le statut Ping de n'importe quel point de terminaison HTTP en Java ?
Avez-vous remarqué l'exécution du thread pour cet exemple ? C'est séquentiel. What if you have 500 endpoints? Je parie que vous devez attendre au moins 5 minutes pour obtenir un résultat. Ce qui, j'en suis sûr, n'est pas la meilleure solution.
Maintenant quoi? La bonne question serait :
- Comment exécuter plusieurs threads simultanément ?
- Comment implémenter plusieurs threads en Java ?
- Comment exécuter différents threads en Java ?
- Java - Où est le didacticiel de programmation multithreading ?
- Thread : Comment utiliser plusieurs threads pour accélérer le traitement ?
ExecutorService Approach est votre réponse.
Un exécuteur qui fournit des méthodes pour gérer la terminaison et des méthodes qui peuvent produire un futur pour suivre la progression d'une ou plusieurs tâches asynchrones.
Un ExecutorService peut être arrêté, ce qui entraînera le rejet de nouvelles tâches. Deux méthodes différentes sont fournies pour arrêter un ExecutorService. La méthode shutdown() permettra aux tâches précédemment soumises de s'exécuter avant de se terminer, tandis que la méthode shutdownNow() empêche le démarrage des tâches en attente et tente d'arrêter les tâches en cours d'exécution.
À la fin, un exécuteur n'a aucune tâche en cours d'exécution, aucune tâche en attente d'exécution et aucune nouvelle tâche ne peut être soumise. Un ExecutorService inutilisé doit être arrêté pour permettre la récupération de ses ressources.
La méthode submit étend la méthode de base Executor.execute ( java.lang.Runnable ) en créant et en renvoyant un Future qui peut être utilisé pour annuler l'exécution et/ou attendre la fin. Les méthodes invokeAny et invokeAll exécutent les formes d'exécution en bloc les plus couramment utilisées, exécutant une collection de tâches, puis attendant qu'au moins une, ou toutes, se terminent. (La classe ExecutorCompletionService peut être utilisée pour écrire des variantes personnalisées de ces méthodes.)
La classe Executors fournit des méthodes de fabrique pour les services d'exécution fournis dans ce package.
- java – ExecutorService, comment attendre que toutes les tâches se terminent ?
- Un guide du Java ExecutorService
- Pool de threads Java - Explication ExecutorService
Vous trouverez ci-dessous un exemple Java simple qui explique l' usage of ExecutorService .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . net . HttpURLConnection ; import java . net . URL ; import java . util . concurrent . ExecutorService ; import java . util . concurrent . Executors ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * How to Run Multiple Threads Concurrently in Java? ExecutorService Approach. */ public class CrunchifyGetPingStatusWithExecutorService { private static final int crunchifyThreads = 30 ; public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws Exception { // Executors: Factory and utility methods for Executor, ExecutorService, ScheduledExecutorService, ThreadFactory, and Callable classes defined in this package. // ExecutorService: An Executor that provides methods to manage termination and methods that can produce a Future for tracking progress of one or more asynchronous tasks. // An ExecutorService can be shut down, which will cause it to reject new tasks. // Two different methods are provided for shutting down an ExecutorService. // The shutdown method will allow previously submitted tasks to execute before terminating, while the shutdownNow method prevents waiting tasks from starting and attempts to stop currently executing tasks. // Upon termination, an executor has no tasks actively executing, no tasks awaiting execution, and no new tasks can be submitted. // An unused ExecutorService should be shut down to allow reclamation of its resources. ExecutorService executor = Executors . newFixedThreadPool ( crunchifyThreads ) ; // newFixedThreadPool(): Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads operating off a shared unbounded queue. // At any point, at most nThreads threads will be active processing tasks. If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active, they will wait in the queue until a thread is available. // If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to execute subsequent tasks String [ ] crunchifyList = { "https://crunchify.com" , "https://yahoo.com" , "https://www.ebay.com" , "https://google.com" , "https://www.example.co" , "https://paypal.com" , "http://bing.com/" , "https://techcrunch.com/" , "http://mashable.com/" , "https://pro.crunchify.com/" , "https://wordpress.com/" , "https://wordpress.org/" , "https://example.com/" , "https://sjsu.edu/" , "https://ask.crunchify.com/" , "https://test.com.au/" , "https://www.wikipedia.org/" , "https://en.wikipedia.org" } ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyList . length ; i ++ ) { String url = crunchifyList [ i ] ; Runnable worker = new MyRunnable ( url ) ; // execute(): Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, // or in the calling thread, at the discretion of the Executor implementation. executor . execute ( worker ) ; } // shutdown(): Initiates an orderly shutdown in which previously submitted tasks are executed, but no new tasks will be accepted. // Invocation has no additional effect if already shut down. // This method does not wait for previously submitted tasks to complete execution. Use awaitTermination to do that. executor . shutdown ( ) ; // Wait until all threads are finish // Returns true if all tasks have completed following shut down. // Note that isTerminated is never true unless either shutdown or shutdownNow was called first. while ( ! executor . isTerminated ( ) ) { // empty body } System . out . println ( "\nFinished all threads" ) ; } // Runnable: The Runnable interface should be implemented by any class whose instances are intended to be executed by a thread. // The class must define a method of no arguments called run. public static class MyRunnable implements Runnable { private final String url ; MyRunnable ( String url ) { this . url = url ; } @Override public void run ( ) { String result = "" ; int code = 200 ; try { URL siteURL = new URL ( url ) ; // HttpURLConnection: A URLConnection with support for HTTP-specific features. See the spec for details. // openConnection(): Returns a URLConnection instance that represents a connection to the remote object referred to by the URL. HttpURLConnection connection = ( HttpURLConnection ) siteURL . openConnection ( ) ; // setRequestMethod: Set the method for the URL request, one of: //GET //POST //HEAD //OPTIONS //PUT //DELETE //TRACE connection . setRequestMethod ( "GET" ) ; // setConnectTimeout(): Sets a specified timeout value, in milliseconds, to be used when opening a communications link to the resource referenced by this URLConnection. // If the timeout expires before the connection can be established, a java.net connection . setConnectTimeout ( 3000 ) ; // connect(): Opens a communications link to the resource referenced by this URL, if such a connection has not already been established. connection . connect ( ) ; // getResponseCode(): Gets the status code from an HTTP response message. For example, in the case of the following status lines: // HTTP/1.0 200 OK // HTTP/1.0 401 Unauthorized code = connection . getResponseCode ( ) ; if ( code == 200 ) { result = "-> Green <-\t\t" + "Code: " + code ; ; } else { result = "-> Yellow <-\t\t" + "Code: " + code ; } } catch ( Exception e ) { result = "-> Red <-\t\t" + "Wrong domain - Exception: " + e . getMessage ( ) ; } System . out . println ( url + "\t\t\t\tStatus:" + result ) ; } } } |
Sortir:

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
/ Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / slf4j - api / 1.7.31 / slf4j - api - 1.7.31.jar : / Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / jul - to - slf4j / 1.7.31 / jul - to - slf4j - 1.7.31.jar : / Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / jcl - over - slf4j / 1.7.31 / jcl - over - slf4j - 1.7.31.jar : / Users / app / . m2 / repository / org / slf4j / log4j - over - slf4j / 1.7.31 / log4j - over - slf4j - 1.7.31.jar crunchify . com . tutorials . CrunchifyGetPingStatusWithExecutorService http : //mashable.com/ Status:-> Yellow <- Code: 301 http : //bing.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //www.example.co Status:-> Red <- Wrong domain - Exception: www.example.co https : //example.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //wordpress.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //www.wikipedia.org/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //test.com.au/ Status:-> Yellow <- Code: 301 https : //wordpress.org/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //techcrunch.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //www.ebay.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //ask.crunchify.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //en.wikipedia.org Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //crunchify.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //sjsu.edu/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //pro.crunchify.com/ Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //google.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //paypal.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 https : //yahoo.com Status:-> Green <- Code: 200 Finished all threads Process finished with exit code 0 |
Vérifiez maintenant le résultat.
Cela devrait être en quelques secondes. J'espère que ça t'as aidé. Essayez de l'exécuter plusieurs fois et vous verrez peut-être un résultat différent car tous les threads s'exécutent en parallèle et quiconque obtient un résultat rapide, vous verrez le résultat affiché dans la console Eclipse.
Faites-le moi savoir pour toute question.
