Java Merge Sort Algoritmo Implementazione? Spiegazione dettagliata e tutorial completo
Pubblicato: 2021-01-20
Su Crunchify, abbiamo scritto finora 500+ Java and Spring MVC . Imparare cose nuove non mi ha mai annoiato. Mi piace imparare cose nuove ogni giorno e credo che sia lo stesso per i miei lettori :).
Come potresti aver visto prima, l'algoritmo di ordinamento a bolle, l'algoritmo di ordinamento di selezione e l'algoritmo di ordinamento di inserimento sono molto popolari tra le varie interviste.
In questo tutorial, esamineremo Merge Sort Algorithm .
L'algoritmo di ordinamento di unione è molto semplice. Dividi un array a metà quando raggiunge un solo livello, quindi ordinalo. Il prossimo passo è unirlo in sequenza. Fondamentalmente è l'approccio divide and conquer .
Ecco una semplice spiegazione sull'ordinamento per unione su come dividere e unire gli elementi.
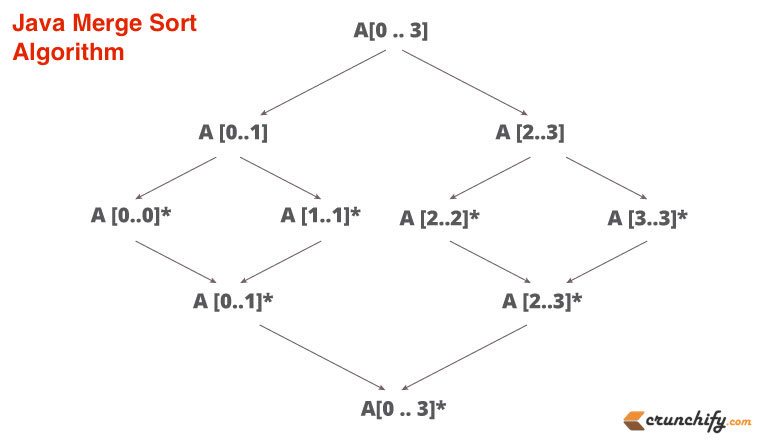
Rispondiamo a tutte le seguenti domande oggi in questo tutorial:
- Qual è l'algoritmo di ordinamento di unione?
- Qual è l'implementazione della fusione?
- Mergesort in Java – Tutorial
- unisci il codice java di ordinamento
Eseguiamo i seguenti passaggi:
- Crea
crunchifyArraycon dimensione 10 - Riempi 10 numeri interi casuali nell'array
- Stampa matrice iniziale
- Esegui ordinamento per unione
- Stampa l'array finale dopo l'ordinamento di unione
Ecco un codice Java:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 |
package crunchify . com . tutorial ; import java . util . * ; /** * @author Crunchify.com Merge Sort Algorithm in Java * */ public class CrunchifyMergeSortAlgorithm { public static Integer [ ] crunchifyArray = new Integer [ 10 ] ; ; public static int iteration = 1 ; // Divide and Merge public static void crunchifyMergeSort ( Integer [ ] crunchifyArray ) { Integer [ ] tempArray = new Integer [ crunchifyArray . length ] ; // recursively perform merge sort crunchifyMergeSort ( crunchifyArray , tempArray , 0 , crunchifyArray . length - 1 ) ; } // Idea is simple: // First divide whole array into 2 part // Divide each array into another 2 part // Once it reaches to only 1 elements in each side tree, just sort it // Merge backward the same way to get complete sorted array private static void crunchifyMergeSort ( Integer [ ] crunchifyArray , Integer [ ] tempArray , int myLeft , int myRight ) { if ( myLeft < myRight ) { int center = ( myLeft + myRight ) / 2 ; crunchifyMergeSort ( crunchifyArray , tempArray , myLeft , center ) ; crunchifyMergeSort ( crunchifyArray , tempArray , center + 1 , myRight ) ; crunchifyMerge ( crunchifyArray , tempArray , myLeft , center + 1 , myRight ) ; } } // Merge Sort Algorithm private static void crunchifyMerge ( Integer [ ] crunchifyArray , Integer [ ] tempArray , int left , int myRight , int rightMost ) { int leftEnd = myRight - 1 ; int k = left ; int num = rightMost - left + 1 ; while ( left < = leftEnd && myRight <= rightMost) if (crunchifyArray[left].compareTo(crunchifyArray[myRight]) <= 0) tempArray[k++] = crunchifyArray[left++]; else tempArray [ k ++ ] = crunchifyArray [ myRight ++ ] ; while ( left < = leftEnd ) tempArray [ k ++ ] = crunchifyArray [ left ++ ] ; while ( myRight < = rightMost ) tempArray [ k ++ ] = crunchifyArray [ myRight ++ ] ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < num ; i ++ , rightMost -- ) crunchifyArray [ rightMost ] = tempArray [ rightMost ] ; System . out . print ( "Iteration # " + iteration + " ===> " ) ; crunchifyPrint ( ) ; iteration ++ ; } // Get Random Integer in Java public static Integer getRandomIntegers ( ) { Random crunchifyRandom = new Random ( ) ; int myNumber = crunchifyRandom . nextInt ( 150 ) ; return myNumber ; } // Simply Print Arrays public static void crunchifyPrint ( ) { for ( int n : crunchifyArray ) { System . out . print ( " " + n + " " ) ; } System . out . print ( "\n" ) ; } // Main Method public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyArray . length ; i ++ ) { crunchifyArray [ i ] = getRandomIntegers ( ) ; } System . out . print ( "Here is our initial array: " ) ; crunchifyPrint ( ) ; System . out . println ( ) ; // Perform actual sorting crunchifyMergeSort ( crunchifyArray ) ; System . out . println ( ) ; System . out . print ( "Here is an array after Merge Sort: " ) ; crunchifyPrint ( ) ; } } |
Uscita console Eclipse:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
Here is our initial array : 45 53 10 50 48 8 106 77 44 108 Iteration # 1 ===> 45 53 10 50 48 8 106 77 44 108 Iteration # 2 ===> 10 45 53 50 48 8 106 77 44 108 Iteration # 3 ===> 10 45 53 48 50 8 106 77 44 108 Iteration # 4 ===> 10 45 48 50 53 8 106 77 44 108 Iteration # 5 ===> 10 45 48 50 53 8 106 77 44 108 Iteration # 6 ===> 10 45 48 50 53 8 77 106 44 108 Iteration # 7 ===> 10 45 48 50 53 8 77 106 44 108 Iteration # 8 ===> 10 45 48 50 53 8 44 77 106 108 Iteration # 9 ===> 8 10 44 45 48 50 53 77 106 108 Here is an array after Merge Sort : 8 10 44 45 48 50 53 77 106 108 |
Prova a eseguire il debug del programma con attenzione per comprendere due metodi crunchifyMergeSort e crunchifyMerge . Fammi sapere se hai domande o problemi con l'esecuzione del codice sopra.

Notazione O grande / Che cos'è una complessità dell'algoritmo di ordinamento unione?
-
n*log(n)
Unisci Ordina la complessità dello scenario del caso migliore?
-
O(n)in caso di input già ordinato
