In Java Come convertire Map / HashMap in JSONObject? [4 modi diversi]
Pubblicato: 2019-01-13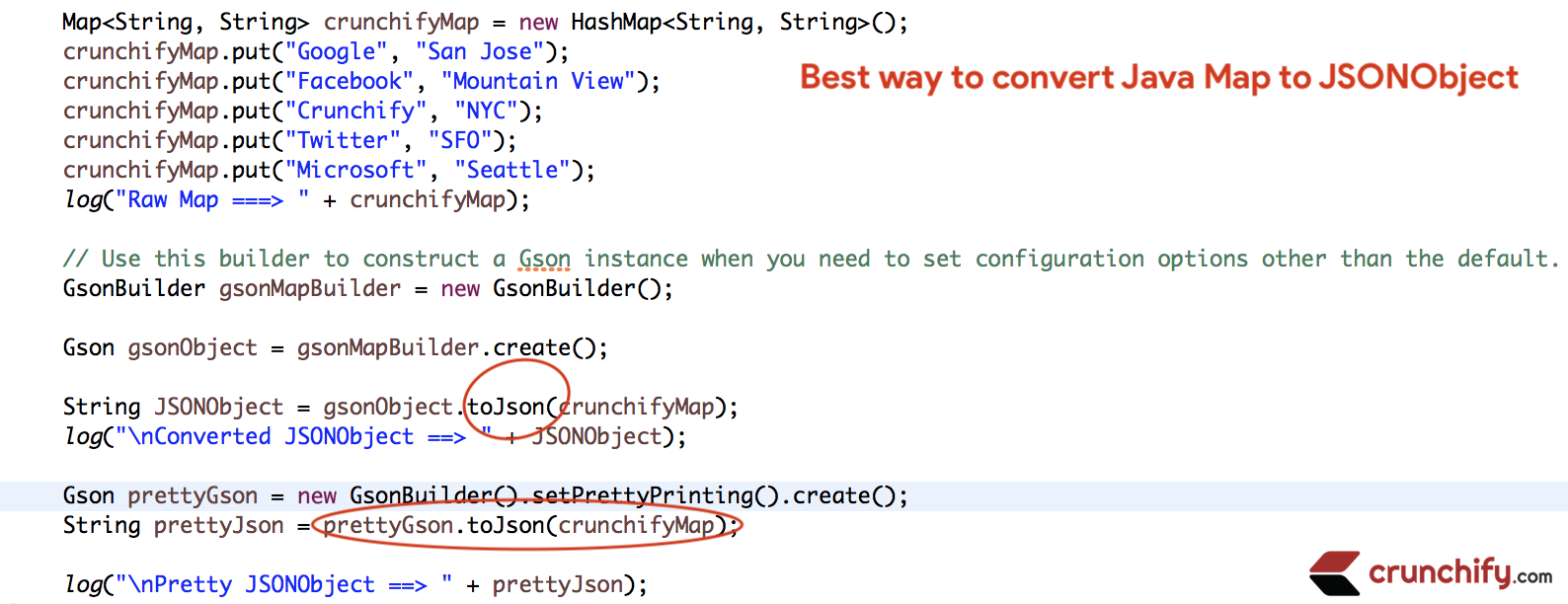
La conversione di oggetti da un modulo all'altro è una richiesta comune. There are 4 different ways per convertire Java Map/HashMap in JSONObject.
Esamineremo i dettagli su come convertire HashMap in JSONObject in questo tutorial.
Iniziamo:
Crea classe CrunchifyMapToJsonObject.java.
Metodo-1
Innanzitutto utilizziamo Google GSON dependency per convertire HashMap in JSONObject. Hai bisogno di una dipendenza da Maven nel tuo progetto.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
< dependency > < groupId > com . google . code . gson < / groupId > < artifactId > gson < / artifactId > < version > 2.8.0 < / version > < / dependency > |
Metodo-2
Successivamente useremo la org.json dependency usando new JSONObject().
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
< dependency > < groupId > org . json < / groupId > < artifactId > json < / artifactId > < version > 20180130 < / version > < / dependency > |
Metodo-3
Utilizzo jackson-core dependency con l'operazione ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString().
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
< dependency > < groupId > com . fasterxml . jackson . core < / groupId > < artifactId > jackson - core < / artifactId > < version > 2.9.5 < / version > < scope > compile < / scope > < / dependency > < dependency > < groupId > com . fasterxml . jackson . core < / groupId > < artifactId > jackson - databind < / artifactId > < version > 2.9.5 < / version > < scope > compile < / scope > < / dependency > |
Metodo-4
Utilizzo json-simple dependency con la libreria JSONValue.toJSONString().
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
< dependency > < groupId > com . googlecode . json - simple < / groupId > < artifactId > json - simple < / artifactId > < version > 1.1.1 < / version > < / dependency > |
Assicurati di aggiungere tutte le dipendenze Maven di cui sopra al tuo progetto Java J2EE. Se non hai un progetto Maven, segui questi passaggi.
Ecco un esempio completo:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 |
package crunchify . com . tutorial ; import java . util . HashMap ; import java . util . Map ; import org . json . JSONObject ; import org . json . simple . JSONValue ; import com . fasterxml . jackson . core . JsonProcessingException ; import com . fasterxml . jackson . databind . ObjectMapper ; import com . google . gson . Gson ; import com . google . gson . GsonBuilder ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * Program: 4 Best ways to convert Java Map to JSONObject. * Version: 1.0.0 * */ public class CrunchifyMapToJsonObject { public static void main ( String a [ ] ) { Map < String , String > crunchifyMap = new HashMap < String , String > ( ) ; crunchifyMap . put ( "Google" , "San Jose" ) ; crunchifyMap . put ( "Facebook" , "Mountain View" ) ; crunchifyMap . put ( "Crunchify" , "NYC" ) ; crunchifyMap . put ( "Twitter" , "SFO" ) ; crunchifyMap . put ( "Microsoft" , "Seattle" ) ; log ( "Raw Map ===> " + crunchifyMap ) ; // Use this builder to construct a Gson instance when you need to set configuration options other than the default. GsonBuilder gsonMapBuilder = new GsonBuilder ( ) ; Gson gsonObject = gsonMapBuilder . create ( ) ; String JSONObject = gsonObject . toJson ( crunchifyMap ) ; log ( "\nMethod-1: Using Google GSON ==> " + JSONObject ) ; Gson prettyGson = new GsonBuilder ( ) . setPrettyPrinting ( ) . create ( ) ; String prettyJson = prettyGson . toJson ( crunchifyMap ) ; log ( "\nPretty JSONObject ==> " + prettyJson ) ; // Construct a JSONObject from a Map. JSONObject crunchifyObject = new JSONObject ( crunchifyMap ) ; log ( "\nMethod-2: Using new JSONObject() ==> " + crunchifyObject ) ; try { // Default constructor, which will construct the default JsonFactory as necessary, use SerializerProvider as its // SerializerProvider, and BeanSerializerFactory as its SerializerFactory. String objectMapper = new ObjectMapper ( ) . writeValueAsString ( crunchifyMap ) ; log ( "\nMethod-3: Using ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString() ==> " + objectMapper ) ; } catch ( JsonProcessingException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } // Convert an object to JSON text. If this object is a Map or a List, and it's also a JSONAware, JSONAware will be considered firstly. String jsonValue = JSONValue . toJSONString ( crunchifyMap ) ; log ( "\nMethod-4: Using JSONValue.toJSONString() ==> " + jsonValue ) ; } private static void log ( Object print ) { System . out . println ( print ) ; } } |
Basta eseguire sopra Programma come applicazione Java e dovresti vedere sotto l'output.

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
Raw Map === > { Google = San Jose , Twitter = SFO , Microsoft = Seattle , Facebook = Mountain View , Crunchify = NYC } Method - 1 : Using Google GSON == > { "Google" : "San Jose" , "Twitter" : "SFO" , "Microsoft" : "Seattle" , "Facebook" : "Mountain View" , "Crunchify" : "NYC" } Pretty JSONObject == > { "Google" : "San Jose" , "Twitter" : "SFO" , "Microsoft" : "Seattle" , "Facebook" : "Mountain View" , "Crunchify" : "NYC" } Method - 2 : Using new JSONObject ( ) == > { "Google" : "San Jose" , "Twitter" : "SFO" , "Microsoft" : "Seattle" , "Facebook" : "Mountain View" , "Crunchify" : "NYC" } Method - 3 : Using ObjectMapper ( ) . writeValueAsString ( ) == > { "Google" : "San Jose" , "Twitter" : "SFO" , "Microsoft" : "Seattle" , "Facebook" : "Mountain View" , "Crunchify" : "NYC" } Method - 4 : Using JSONValue . toJSONString ( ) == > { "Google" : "San Jose" , "Twitter" : "SFO" , "Microsoft" : "Seattle" , "Facebook" : "Mountain View" , "Crunchify" : "NYC" } |
Se conosci un altro modo per convertire Java Map in JSONObject, faccelo sapere a noi e a tutti i lettori tramite un commento di seguito.
Buona codifica.
