Java中的接口是什么? Java 接口初学者指南。 如何使用它? 附上示例。
已发表: 2020-10-31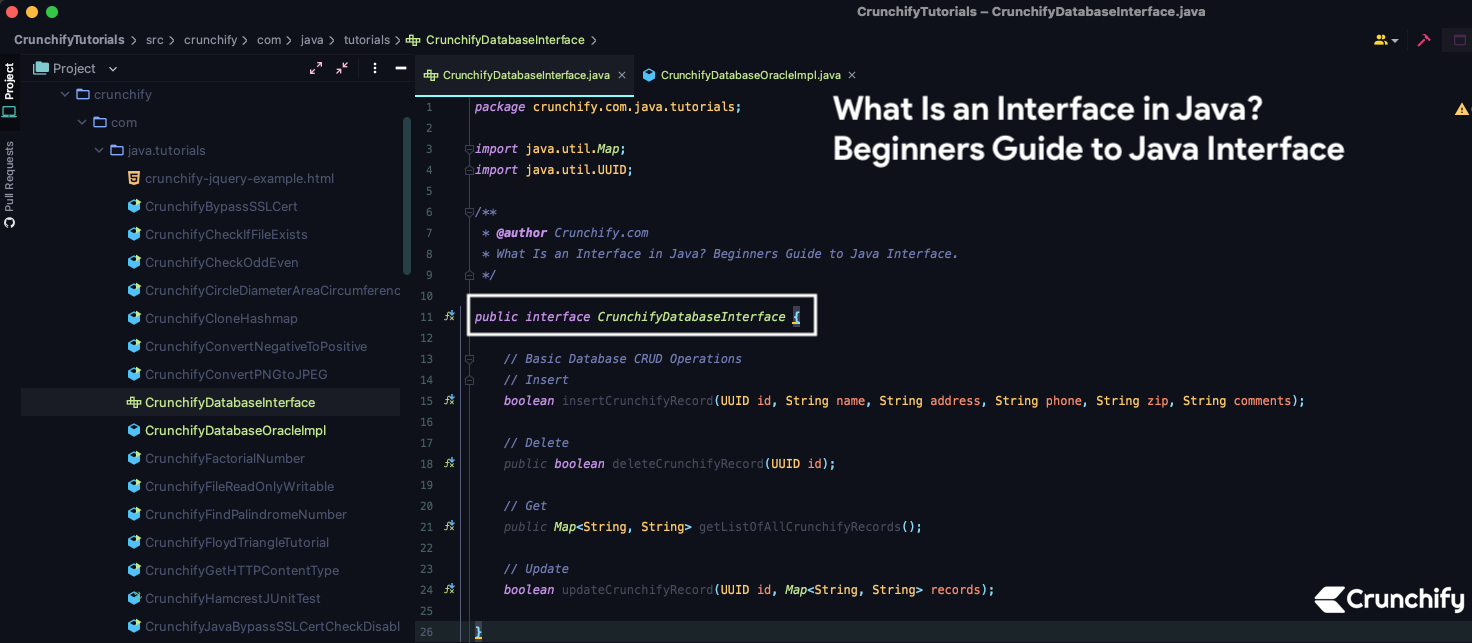
为什么以及何时使用接口?
- 接口是 Java 中的引用类型。
- 它类似于类。
- 它是抽象方法的集合。
- 它用于实现完全抽象。
我相信这是您在 Java 面试中可能会想到的第一个问题。 非常基本的问题,但在面试中被广泛使用
这个问题没有完美的答案,有很多方法可以回答这个问题。 可能是你的面试官正在寻找这个问题的实用方法? 可能的。
那么让我们从Java接口的基本定义开始吧
我们将通过多个示例进行相同的处理。
- Java中的接口是什么?
- 带有实时示例的java中的接口是什么?
- 为什么在java中使用接口
- 界面设计Java
- Interface上最常见的面试问题
接口基础:

-
interface只是一个契约,是对实现类将具有的行为的描述。 实现类确保它将具有可以在其上使用的这些方法。 它基本上是班级必须做出的合同或承诺。 - 如果在您的项目中所有不同的实现共享相同的方法签名怎么办? 在这种情况下,界面效果最好。
- 大项目实施后的后期,看看你有没有把接口定义实现到~50个地方,如果换接口怎么办? 您必须对项目中的所有 50 个位置进行修改。
- 建议在设计阶段花更多时间定义接口,而不是在后期更改它
- 接口由
singleton变量(public static final)和public abstract方法组成。 当我们知道该做什么但不知道该怎么做时,我们通常更喜欢实时界面。 接口不能包含实例字段。 - 实现接口的类必须为所有存在的方法提供方法定义。
- 一个类可以实现多个接口。
- 可以将接口实现添加到任何现有的第三方类。
- 一个接口可以包含任意数量的方法。
- 在 Java 中,您不能实例化接口。
- 接口不包含任何构造函数。
- 接口不被类扩展; 它由一个类实现。
- 一个接口可以扩展多个接口。
接口示例:
提示 1。
创建接口CrunchifyDatabaseInterface.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
package crunchify . com . java . tutorials ; import java . util . Map ; import java . util . UUID ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * What Is an Interface in Java? Beginners Guide to Java Interface. */ public interface CrunchifyDatabaseInterface { // Basic Database CRUD Operations // Insert boolean insertCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id , String name , String address , String phone , String zip , String comments ) ; // Delete public boolean deleteCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id ) ; // Get public Map < String , String > getListOfAllCrunchifyRecords ( ) ; // Update boolean updateCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id , Map < String , String > records ) ; } |
提示 2。
实现接口CrunchifyDatabaseOracleImpl.java
当您第一次实现接口时,Eclipse 将向您显示添加未实现的方法。
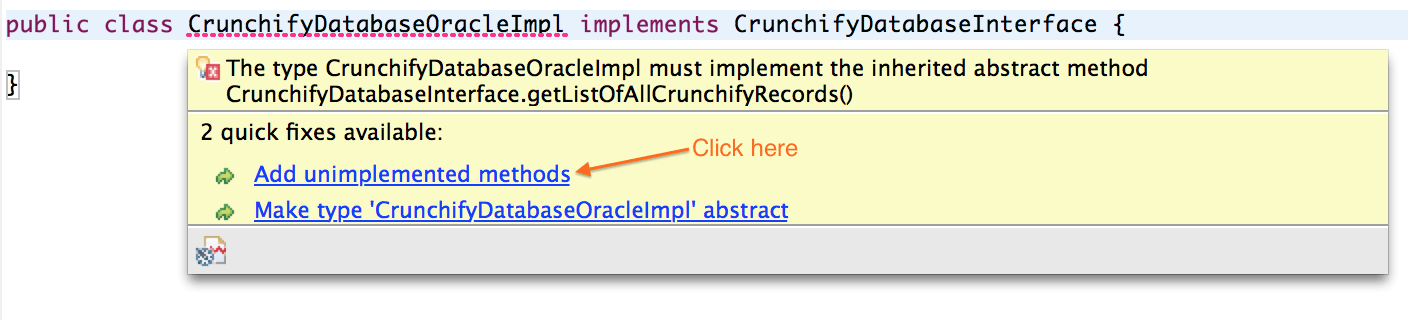
只需单击“ Add unimplemented methods ”,您的 IMPL 类就应该准备好使用Auto-generated method stub 。
提示 3. 实际 Impl 方法。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 |
package crunchify . com . java . tutorials ; import java . util . Map ; import java . util . UUID ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * What Is an Interface in Java? Beginners Guide to Java Interface. */ public class CrunchifyDatabaseOracleImpl implements CrunchifyDatabaseInterface { // Override: Indicates that a method declaration is intended to override a method declaration in a supertype. // If a method is annotated with this annotation type compilers are required to generate an error message unless at least one of the following conditions hold: // The method does override or implement a method declared in a supertype. // The method has a signature that is override-equivalent to that of any public method declared in Object. @Override public boolean insertCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id , String name , String address , String phone , String zip , String comments ) { // TODO Provide your actual implementation here based on your need specific to Oracle return false ; } // UUID(): A class that represents an immutable universally unique identifier (UUID). // A UUID represents a 128-bit value. // There exist different variants of these global identifiers. // The methods of this class are for manipulating the Leach-Salz variant, although the constructors allow the creation of any variant of UUID @Override public boolean deleteCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id ) { // TODO Provide your actual implementation here based on your need specific to Oracle return false ; } // Map(): An object that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value. // This interface takes the place of the Dictionary class, which was a totally abstract class rather than an interface. @Override public Map < String , String > getListOfAllCrunchifyRecords ( ) { // TODO Provide your actual implementation here based on your need specific to Oracle return null ; } @Override public boolean updateCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id , Map < String , String > records ) { // TODO Provide your actual implementation here based on your need specific to Oracle return false ; } } |
提示 4。
类似的方式,您可以使用相同的接口来实现不同的数据库特定操作。 比如,对于 DB2、MySQL、MongoDB、Cassandra DB 等。

下一步是什么?
在编写抽象类教程的过程中,然后另一个教程清楚地显示了抽象类和接口之间的区别。
