อินเทอร์เฟซใน Java คืออะไร? คู่มือเริ่มต้นสำหรับอินเทอร์เฟซ Java วิธีการใช้งาน? ตัวอย่างที่แนบมา
เผยแพร่แล้ว: 2020-10-31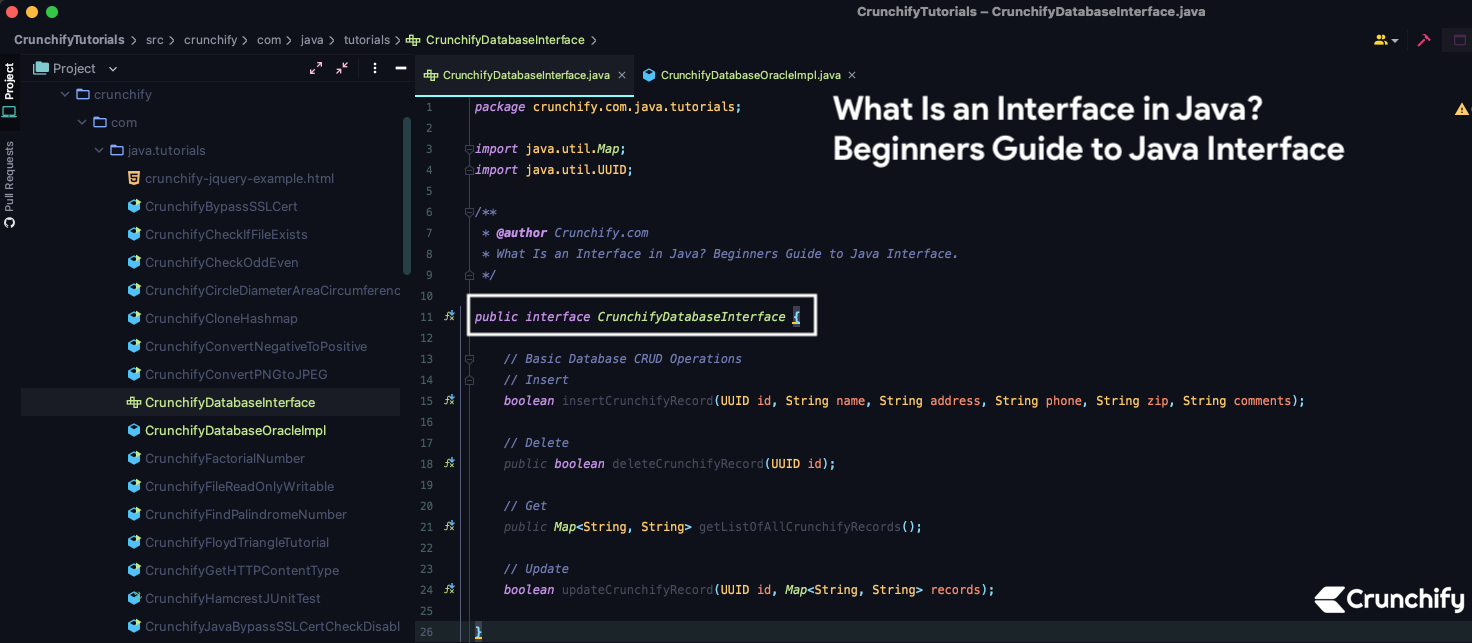
ทำไมและเมื่อใดจึงควรใช้อินเทอร์เฟซ
- อินเทอร์เฟซเป็นประเภทอ้างอิงใน Java
- มันคล้ายกับชั้นเรียน
- เป็นการรวบรวมวิธีการเชิงนามธรรม
- ใช้เพื่อให้บรรลุนามธรรมทั้งหมด
ฉันเชื่อว่านี่เป็นคำถามแรกที่คุณคาดหวังใน Java Interview คำถามพื้นๆ แต่ใช้กันอย่างแพร่หลายในการสัมภาษณ์
ไม่มีคำตอบที่สมบูรณ์แบบสำหรับเรื่องนี้ และมีหลายวิธีในการตอบคำถามนี้ อาจเป็นผู้สัมภาษณ์ของคุณที่กำลังมองหาแนวทางปฏิบัติสำหรับคำถามนี้หรือไม่? เป็นไปได้.
มาเริ่มกันที่คำจำกัดความพื้นฐานของ Java Interface
เราจะพูดถึงเรื่องเดียวกันด้วยตัวอย่างหลายตัวอย่าง
- อินเทอร์เฟซใน Java คืออะไร?
- อินเทอร์เฟซใน java พร้อมตัวอย่างเรียลไทม์คืออะไร?
- เหตุใดจึงต้องใช้อินเทอร์เฟซใน java
- การออกแบบส่วนต่อประสาน Java
- คำถามสัมภาษณ์ที่พบบ่อยที่สุดใน Interface
พื้นฐานของอินเทอร์เฟซ:

-
interfaceเป็นเพียงสัญญา คำอธิบายเกี่ยวกับพฤติกรรมที่คลาสการนำไปใช้งานจะมี คลาสการดำเนินการทำให้แน่ใจว่าจะมีวิธีการเหล่านี้ที่สามารถใช้ได้ โดยพื้นฐานแล้วมันเป็นสัญญาหรือสัญญาที่ชั้นเรียนต้องทำ - จะเกิดอะไรขึ้นถ้าในโปรเจ็กต์ของคุณ การใช้งานต่างๆ ทั้งหมดใช้ลายเซ็นเมธอดเดียวกัน อินเทอร์เฟซทำงานได้ดีที่สุดในกรณีนั้น
- ในระยะหลังหลังจากดำเนินโครงการหลักแล้ว มาดูกันว่าคุณได้ใช้ข้อกำหนดอินเทอร์เฟซเป็น ~50 แห่งแล้วจะเกิดอะไรขึ้นถ้าคุณเปลี่ยนอินเทอร์เฟซ คุณต้องทำการปรับเปลี่ยนทั้ง 50 แห่งในโครงการของคุณ
- ขอแนะนำให้ใช้เวลามากขึ้นในการกำหนดอินเทอร์เฟซระหว่างขั้นตอนการออกแบบ แทนที่จะเปลี่ยนในขั้นตอนภายหลัง
- อินเทอร์เฟซประกอบด้วยตัวแปร
singleton(public static final) และวิธีpublic abstractปกติเราชอบอินเทอร์เฟซแบบเรียลไทม์มากกว่าเมื่อเรารู้ว่าต้องทำอะไรแต่ไม่รู้ว่าต้องทำอย่างไร อินเทอร์เฟซไม่สามารถมีฟิลด์อินสแตนซ์ - คลาสที่ใช้อินเทอร์เฟซต้องมีข้อกำหนดของเมธอดสำหรับเมธอดทั้งหมดที่มีอยู่
- คลาสอาจใช้อินเทอร์เฟซหลายแบบ
- การใช้งานส่วนต่อประสานอาจถูกเพิ่มในคลาสบุคคลที่สามที่มีอยู่
- อินเทอร์เฟซสามารถมีได้หลายวิธี
- ใน Java คุณไม่สามารถสร้างอินสแตนซ์อินเทอร์เฟซได้
- อินเทอร์เฟซไม่มีตัวสร้างใด ๆ
- อินเตอร์เฟสไม่ได้ถูกขยายโดยคลาส มันถูกนำไปใช้โดยชั้นเรียน
- อินเทอร์เฟซสามารถขยายได้หลายอินเทอร์เฟซ
ตัวอย่างอินเทอร์เฟซ:
เคล็ดลับที่ 1
สร้างอินเทอร์เฟซ CrunchifyDatabaseInterface.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
package crunchify . com . java . tutorials ; import java . util . Map ; import java . util . UUID ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * What Is an Interface in Java? Beginners Guide to Java Interface. */ public interface CrunchifyDatabaseInterface { // Basic Database CRUD Operations // Insert boolean insertCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id , String name , String address , String phone , String zip , String comments ) ; // Delete public boolean deleteCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id ) ; // Get public Map < String , String > getListOfAllCrunchifyRecords ( ) ; // Update boolean updateCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id , Map < String , String > records ) ; } |
เคล็ดลับที่ 2
ใช้อินเทอร์เฟซ CrunchifyDatabaseOracleImpl.java
เมื่อคุณใช้อินเทอร์เฟซครั้งแรก Eclipse จะแสดงให้คุณเห็นว่าเพิ่มวิธีการที่ยังไม่ได้ใช้งาน
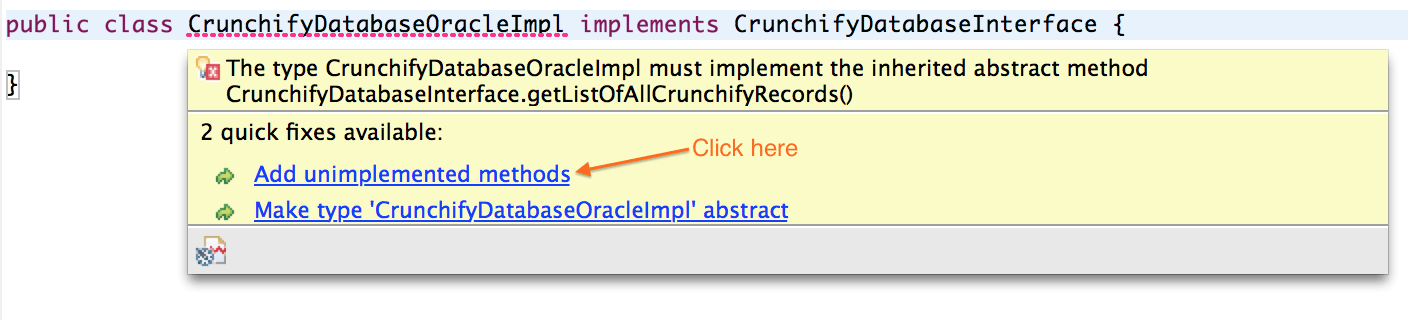
เพียงคลิกที่ " Add unimplemented methods ที่ไม่ได้ใช้งาน" และคลาส IMPL ของคุณควรพร้อมด้วย Auto-generated method stub อัตโนมัติ
เคล็ดลับ 3 วิธีการ Impl จริง
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 |
package crunchify . com . java . tutorials ; import java . util . Map ; import java . util . UUID ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * What Is an Interface in Java? Beginners Guide to Java Interface. */ public class CrunchifyDatabaseOracleImpl implements CrunchifyDatabaseInterface { // Override: Indicates that a method declaration is intended to override a method declaration in a supertype. // If a method is annotated with this annotation type compilers are required to generate an error message unless at least one of the following conditions hold: // The method does override or implement a method declared in a supertype. // The method has a signature that is override-equivalent to that of any public method declared in Object. @Override public boolean insertCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id , String name , String address , String phone , String zip , String comments ) { // TODO Provide your actual implementation here based on your need specific to Oracle return false ; } // UUID(): A class that represents an immutable universally unique identifier (UUID). // A UUID represents a 128-bit value. // There exist different variants of these global identifiers. // The methods of this class are for manipulating the Leach-Salz variant, although the constructors allow the creation of any variant of UUID @Override public boolean deleteCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id ) { // TODO Provide your actual implementation here based on your need specific to Oracle return false ; } // Map(): An object that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value. // This interface takes the place of the Dictionary class, which was a totally abstract class rather than an interface. @Override public Map < String , String > getListOfAllCrunchifyRecords ( ) { // TODO Provide your actual implementation here based on your need specific to Oracle return null ; } @Override public boolean updateCrunchifyRecord ( UUID id , Map < String , String > records ) { // TODO Provide your actual implementation here based on your need specific to Oracle return false ; } } |
เคล็ดลับที่ 4
ในทำนองเดียวกันคุณสามารถใช้อินเทอร์เฟซเดียวกันเพื่อใช้การดำเนินการเฉพาะของฐานข้อมูลที่แตกต่างกัน เช่นเดียวกับ DB2, MySQL, MongoDB, Cassandra DB เป็นต้น

อะไรต่อไป?
อยู่ระหว่างการเขียน Tutorial on Abstract Class และบทช่วยสอนอื่นที่แสดงความแตกต่างระหว่าง Abstract Class และ Interface อย่างชัดเจน
