HashMap 对比ConcurrentHashMap 对比SynchronizedMap – 如何在 Java 中同步 HashMap
已发表: 2015-01-29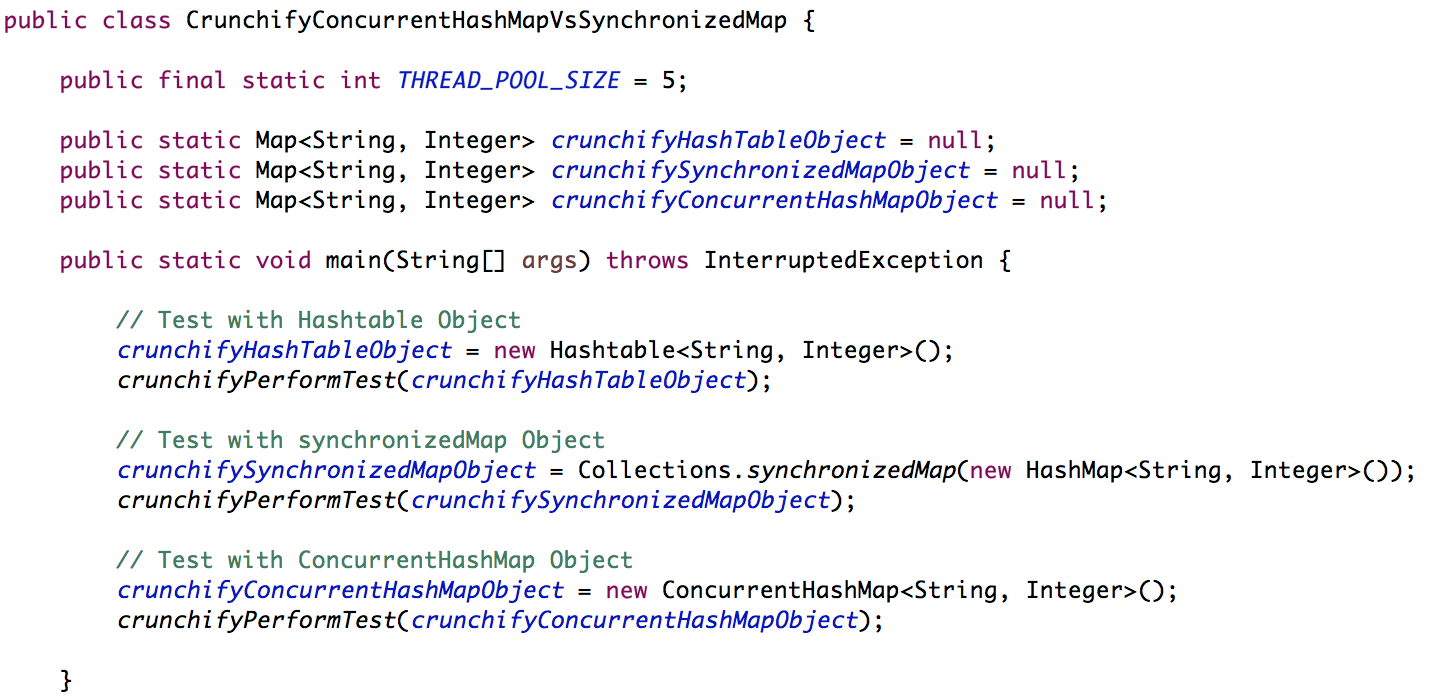
HashMap是 Java 中非常强大的数据结构。 我们每天都在使用它,几乎在所有应用程序中都使用它。 我之前写过很多例子,关于如何实现线程安全缓存,如何将 Hashmap 转换为 Arraylist?
我们在上面的两个示例中都使用了 Hashmap,但这些都是非常简单的 Hashmap 用例。 HashMap is a non-synchronized集合类。
您有以下任何问题吗?
- ConcurrentHashMap 和 Collections.synchronizedMap(Map) 有什么区别?
- ConcurrentHashMap 和 Collections.synchronizedMap(Map) 在性能方面有什么区别?
- ConcurrentHashMap 与 Collections.synchronizedMap()
- 热门 HashMap 和 ConcurrentHashMap 面试题
在本教程中,我们将介绍所有上述查询以及why and how同步 Hashmap?
为什么?
Map 对象是存储元素的关联容器,由唯一标识的key和映射的value组合而成。 如果您有非常高并发的应用程序,您可能希望在不同的线程中修改或读取键值,那么使用 Concurrent Hashmap 是理想的选择。 最好的例子是处理并发读/写的生产者消费者。
那么线程安全的 Map 是什么意思呢? 如果multiple threads同时访问一个哈希映射,并且至少有一个线程在结构上修改了映射,则must be synchronized externally以避免内容视图不一致。
如何?
有两种方法可以同步 HashMap
- Java 集合 synchronizedMap() 方法
- 使用 ConcurrentHashMap
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
//Hashtable Map < String , String > normalMap = new Hashtable < String , String > ( ) ; //synchronizedMap synchronizedHashMap = Collections . synchronizedMap ( new HashMap < String , String > ( ) ) ; //ConcurrentHashMap concurrentHashMap = new ConcurrentHashMap < String , String > ( ) ; |
并发哈希映射
- 当您的项目需要非常高的并发性时,您应该使用 ConcurrentHashMap。
- 它是线程安全的,无需同步
whole map。 - 使用锁完成写入时,读取可能会非常快。
- 在对象级别没有锁定。
- 锁定在哈希图存储桶级别的粒度要细得多。
- 如果一个线程尝试修改它而另一个线程正在对其进行迭代,则 ConcurrentHashMap 不会引发
ConcurrentModificationException。 - ConcurrentHashMap 使用大量锁。
同步HashMap
- 对象级别的同步。
- 每个读/写操作都需要获取锁。
- 锁定整个集合是一种性能开销。
- 这实质上只允许访问整个映射的一个线程并阻止所有其他线程。
- 它可能会引起争用。
- SynchronizedHashMap 返回
Iterator,它在并发修改时快速失败。
现在让我们看一下代码
- 创建类
CrunchifyConcurrentHashMapVsSynchronizedHashMap.java - 为每个 HashTable、SynchronizedMap 和 CrunchifyConcurrentHashMap 创建对象
- 从 Map 添加和检索 500k 条目
- 测量开始和结束时间并以毫秒为单位显示时间
- 我们将使用 ExecutorService 并行运行
5 threads
这是一个Java代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . util . Collections ; import java . util . HashMap ; import java . util . Hashtable ; import java . util . Map ; import java . util . concurrent . ConcurrentHashMap ; import java . util . concurrent . ExecutorService ; import java . util . concurrent . Executors ; import java . util . concurrent . TimeUnit ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyConcurrentHashMapVsSynchronizedMap { public final static int THREAD_POOL_SIZE = 5 ; public static Map < String , Integer > crunchifyHashTableObject = null ; public static Map < String , Integer > crunchifySynchronizedMapObject = null ; public static Map < String , Integer > crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject = null ; public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws InterruptedException { // Test with Hashtable Object crunchifyHashTableObject = new Hashtable < String , Integer > ( ) ; crunchifyPerformTest ( crunchifyHashTableObject ) ; // Test with synchronizedMap Object crunchifySynchronizedMapObject = Collections . synchronizedMap ( new HashMap < String , Integer > ( ) ) ; crunchifyPerformTest ( crunchifySynchronizedMapObject ) ; // Test with ConcurrentHashMap Object crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject = new ConcurrentHashMap < String , Integer > ( ) ; crunchifyPerformTest ( crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject ) ; } public static void crunchifyPerformTest ( final Map < String , Integer > crunchifyThreads ) throws InterruptedException { System . out . println ( "Test started for: " + crunchifyThreads . getClass ( ) ) ; long averageTime = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++ ) { long startTime = System . nanoTime ( ) ; ExecutorService crunchifyExServer = Executors . newFixedThreadPool ( THREAD_POOL_SIZE ) ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < THREAD_POOL_SIZE ; j ++ ) { crunchifyExServer . execute ( new Runnable ( ) { @SuppressWarnings ( "unused" ) @Override public void run ( ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < 500000 ; i ++ ) { Integer crunchifyRandomNumber = ( int ) Math . ceil ( Math . random ( ) * 550000 ) ; // Retrieve value. We are not using it anywhere Integer crunchifyValue = crunchifyThreads . get ( String . valueOf ( crunchifyRandomNumber ) ) ; // Put value crunchifyThreads . put ( String . valueOf ( crunchifyRandomNumber ) , crunchifyRandomNumber ) ; } } } ) ; } // Initiates an orderly shutdown in which previously submitted tasks are executed, but no new tasks will be accepted. Invocation // has no additional effect if already shut down. // This method does not wait for previously submitted tasks to complete execution. Use awaitTermination to do that. crunchifyExServer . shutdown ( ) ; // Blocks until all tasks have completed execution after a shutdown request, or the timeout occurs, or the current thread is // interrupted, whichever happens first. crunchifyExServer . awaitTermination ( Long . MAX_VALUE , TimeUnit . DAYS ) ; long entTime = System . nanoTime ( ) ; long totalTime = ( entTime - startTime ) / 1000000L ; averageTime += totalTime ; System . out . println ( "500K entried added/retrieved in " + totalTime + " ms" ) ; } System . out . println ( "For " + crunchifyThreads . getClass ( ) + " the average time is " + averageTime / 5 + " ms\n" ) ; } } |

shutdown()表示执行器服务不再接受传入任务。-
awaitTermination()在关闭请求后调用。
因此,您需要先关闭 serviceExecutor,然后阻塞并等待线程完成。
Eclipse 控制台结果:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
Test started for: class java.util.Hashtable 500K entried added/retrieved in 1832 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1723 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1782 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1607 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1851 ms For class java.util.Hashtable the average time is 1759 ms Test started for: class java.util.Collections$SynchronizedMap 500K entried added/retrieved in 1923 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 2032 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1621 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1833 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 2048 ms For class java.util.Collections$SynchronizedMap the average time is 1891 ms Test started for: class java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap 500K entried added/retrieved in 1068 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1029 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1165 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 840 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1017 ms For class java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap the average time is 1023 ms |
