해시맵 대 ConcurrentHashMap 대. SynchronizedMap – Java에서 HashMap을 동기화하는 방법
게시 됨: 2015-01-29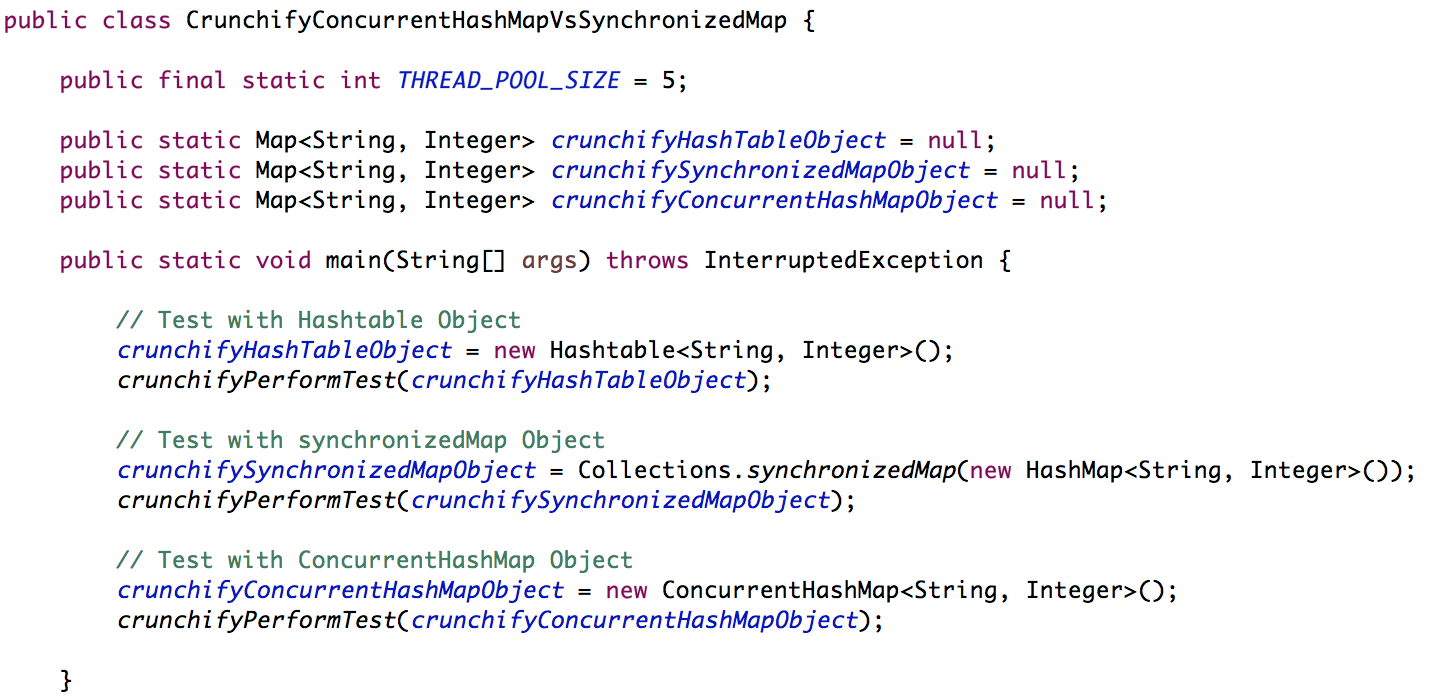
HashMap 은 Java에서 매우 강력한 데이터 구조입니다. 우리는 매일 거의 모든 응용 프로그램에서 사용합니다. Threadsafe 캐시를 구현하는 방법, Hashmap을 Arraylist로 변환하는 방법에 대해 이전에 작성한 몇 가지 예가 있습니다.
위의 두 예제에서 Hashmap을 사용했지만 Hashmap의 아주 간단한 사용 사례입니다. HashMap is a non-synchronized 컬렉션 클래스입니다.
아래 질문이 있습니까?
- ConcurrentHashMap과 Collections.synchronizedMap(Map)의 차이점은 무엇입니까?
- 성능 면에서 ConcurrentHashMap과 Collections.synchronizedMap(Map)의 차이점은 무엇입니까?
- ConcurrentHashMap 대 Collections.synchronizedMap()
- 인기있는 HashMap 및 ConcurrentHashMap 인터뷰 질문
이 튜토리얼에서는 위의 모든 쿼리와 해시맵을 동기화할 수 있는 why and how 을 살펴보겠습니다.
왜요?
Map 객체는 고유하게 식별되는 key 와 매핑된 value 의 조합으로 형성된 요소를 저장하는 연관 컨테이너입니다. 다른 스레드에서 키 값을 수정하거나 읽으려는 매우 동시성이 높은 애플리케이션이 있는 경우 Concurrent Hashmap을 사용하는 것이 이상적입니다. 가장 좋은 예는 동시 읽기/쓰기를 처리하는 생산자 소비자입니다.
그렇다면 스레드로부터 안전한 맵은 무엇을 의미합니까? multiple threads 가 해시 맵에 동시에 액세스하고 스레드 중 적어도 하나가 구조적으로 맵을 수정하는 경우 콘텐츠의 일관성 없는 보기를 피하기 위해 must be synchronized externally .
어떻게?
HashMap을 동기화할 수 있는 두 가지 방법이 있습니다.
- Java 컬렉션 synchronizedMap() 메서드
- ConcurrentHashMap 사용
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
//Hashtable Map < String , String > normalMap = new Hashtable < String , String > ( ) ; //synchronizedMap synchronizedHashMap = Collections . synchronizedMap ( new HashMap < String , String > ( ) ) ; //ConcurrentHashMap concurrentHashMap = new ConcurrentHashMap < String , String > ( ) ; |
ConcurrentHashMap
- 프로젝트에서 매우 높은 동시성이 필요할 때 ConcurrentHashMap을 사용해야 합니다.
-
whole map을 동기화하지 않고도 스레드로부터 안전합니다. - 쓰기가 잠금으로 수행되는 동안 읽기는 매우 빠르게 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 개체 수준에는 잠금이 없습니다.
- 잠금은 해시맵 버킷 수준에서 훨씬 더 세밀합니다.
- ConcurrentHashMap은 다른 스레드가 반복하는 동안 한 스레드가 수정을 시도하는 경우
ConcurrentModificationException을 throw하지 않습니다. - ConcurrentHashMap은 다수의 잠금을 사용합니다.
동기화된 해시맵
- 개체 수준에서 동기화.
- 모든 읽기/쓰기 작업은 잠금을 획득해야 합니다.
- 전체 컬렉션을 잠그면 성능 오버헤드가 발생합니다.
- 이것은 본질적으로 전체 맵에 대한 하나의 스레드에만 액세스 권한을 부여하고 다른 모든 스레드를 차단합니다.
- 다툼의 원인이 됩니다.
- SynchronizedHashMap은 동시 수정 시 빠른 속도를 내는
Iterator를 반환합니다.
이제 코드를 살펴보자
-
CrunchifyConcurrentHashMapVsSynchronizedHashMap.java클래스 생성 - 각 HashTable, SynchronizedMap 및 CrunchifyConcurrentHashMap에 대한 객체 생성
- 지도에서 500,000개 항목 추가 및 검색
- 시작 및 종료 시간을 측정하고 시간을 밀리초 단위로 표시
- ExecutorService를 사용하여
5 threads를 병렬로 실행합니다.
다음은 자바 코드입니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . util . Collections ; import java . util . HashMap ; import java . util . Hashtable ; import java . util . Map ; import java . util . concurrent . ConcurrentHashMap ; import java . util . concurrent . ExecutorService ; import java . util . concurrent . Executors ; import java . util . concurrent . TimeUnit ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyConcurrentHashMapVsSynchronizedMap { public final static int THREAD_POOL_SIZE = 5 ; public static Map < String , Integer > crunchifyHashTableObject = null ; public static Map < String , Integer > crunchifySynchronizedMapObject = null ; public static Map < String , Integer > crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject = null ; public static void main ( String [ ] args ) throws InterruptedException { // Test with Hashtable Object crunchifyHashTableObject = new Hashtable < String , Integer > ( ) ; crunchifyPerformTest ( crunchifyHashTableObject ) ; // Test with synchronizedMap Object crunchifySynchronizedMapObject = Collections . synchronizedMap ( new HashMap < String , Integer > ( ) ) ; crunchifyPerformTest ( crunchifySynchronizedMapObject ) ; // Test with ConcurrentHashMap Object crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject = new ConcurrentHashMap < String , Integer > ( ) ; crunchifyPerformTest ( crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject ) ; } public static void crunchifyPerformTest ( final Map < String , Integer > crunchifyThreads ) throws InterruptedException { System . out . println ( "Test started for: " + crunchifyThreads . getClass ( ) ) ; long averageTime = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++ ) { long startTime = System . nanoTime ( ) ; ExecutorService crunchifyExServer = Executors . newFixedThreadPool ( THREAD_POOL_SIZE ) ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < THREAD_POOL_SIZE ; j ++ ) { crunchifyExServer . execute ( new Runnable ( ) { @SuppressWarnings ( "unused" ) @Override public void run ( ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < 500000 ; i ++ ) { Integer crunchifyRandomNumber = ( int ) Math . ceil ( Math . random ( ) * 550000 ) ; // Retrieve value. We are not using it anywhere Integer crunchifyValue = crunchifyThreads . get ( String . valueOf ( crunchifyRandomNumber ) ) ; // Put value crunchifyThreads . put ( String . valueOf ( crunchifyRandomNumber ) , crunchifyRandomNumber ) ; } } } ) ; } // Initiates an orderly shutdown in which previously submitted tasks are executed, but no new tasks will be accepted. Invocation // has no additional effect if already shut down. // This method does not wait for previously submitted tasks to complete execution. Use awaitTermination to do that. crunchifyExServer . shutdown ( ) ; // Blocks until all tasks have completed execution after a shutdown request, or the timeout occurs, or the current thread is // interrupted, whichever happens first. crunchifyExServer . awaitTermination ( Long . MAX_VALUE , TimeUnit . DAYS ) ; long entTime = System . nanoTime ( ) ; long totalTime = ( entTime - startTime ) / 1000000L ; averageTime += totalTime ; System . out . println ( "500K entried added/retrieved in " + totalTime + " ms" ) ; } System . out . println ( "For " + crunchifyThreads . getClass ( ) + " the average time is " + averageTime / 5 + " ms\n" ) ; } } |

shutdown()은 실행기 서비스가 더 이상 들어오는 작업을 수행하지 않음을 의미합니다.-
awaitTermination()은 종료 요청 후에 호출됩니다.
따라서 먼저 serviceExecutor를 종료한 다음 차단하고 스레드가 완료될 때까지 기다려야 합니다.
Eclipse 콘솔 결과:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
Test started for: class java.util.Hashtable 500K entried added/retrieved in 1832 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1723 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1782 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1607 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1851 ms For class java.util.Hashtable the average time is 1759 ms Test started for: class java.util.Collections$SynchronizedMap 500K entried added/retrieved in 1923 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 2032 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1621 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1833 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 2048 ms For class java.util.Collections$SynchronizedMap the average time is 1891 ms Test started for: class java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap 500K entried added/retrieved in 1068 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1029 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1165 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 840 ms 500K entried added/retrieved in 1017 ms For class java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap the average time is 1023 ms |
