Ansible – Como Grep (ps -few) e matar qualquer processo linux em execução no host remoto?
Publicados: 2022-02-24
Ansible é uma ferramenta de administração de sistema incrível. Publicamos vários artigos no Ansible nas últimas semanas sobre como copiar arquivos em um host remoto, como executar comandos em hosts remotos, como instalar Java, Python em um host remoto e assim por diante.
Neste tutorial, veremos como grep o processo java em execução no host remoto e matar esse processo remoto usando o simples manual do ansible.
Aqui estão os passos que faremos neste tutorial:
- No host remoto, execute CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram.java
- Siga o tutorial sobre Como executar um programa para sempre em Java
- execute o programa java usando
nohup java CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram &
|
1 2 3 |
ubuntu @ ip - 172 - 31 - 10 - 150 : ~ $ nohup java CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram & [ 1 ] 18174 ubuntu @ ip - 172 - 31 - 10 - 150 : ~ $ nohup : ignoring input and appending output to 'nohup.out' |
Como verificar se o processo está iniciado e em execução no host remoto?
confira o processo ID 18174 .
|
1 2 3 |
ubuntu @ ip - 172 - 31 - 10 - 150 : ~ $ ps - few | grep CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram ubuntu 18174 15069 1 15 : 15 pts / 0 00 : 00 : 00 java CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram ubuntu 18187 15069 0 15 : 16 pts / 0 00 : 00 : 00 grep -- color = auto CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram |
- criar arquivo
crunchify-hostsque possui IP de host remoto - crie o arquivo
crunchify-grep-kill-process.ymlcom tarefas ansible para grep e kill java process - execute o comando: ansible-playbook -i ./crunchify-hosts crunchify-grep-kill-process.yml
- verifique o resultado no console do terminal do macOS
arquivo crunchify-hosts
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
[ local ] localhost ansible_connection = local ansible_python_interpreter = python [ crunchify ] 3.16.83.84 [ crunchify : vars ] ansible_ssh_user = ubuntu ansible_ssh_private_key_file =/ Users / crunchify / Documents / ansible / crunchify . pem ansible_python_interpreter =/ usr / bin / python3 |
O arquivo contém o endereço IP remoto e as credenciais que ajudarão o ansible a fazer login sem senha.
arquivo crunchify-grep-kill-process.yml
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
--- - hosts : crunchify become : yes tasks : - name : Get running processes list from remote host ignore_errors : yes shell : "ps -few | grep CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram | awk '{print $2}'" register : running_processes - name : Kill running processes ignore_errors : yes shell : "kill {{ item }}" with_items : "{{ running_processes.stdout_lines }}" - wait_for : path : "/proc/{{ item }}/status" state : absent with_items : "{{ running_processes.stdout_lines }}" ignore_errors : yes register : crunchify_processes - name : Force kill stuck processes ignore_errors : yes shell : "kill -9 {{ item }}" with_items : "{{ crunchify_processes.results | select('failed') | map(attribute='item') | list }}" |
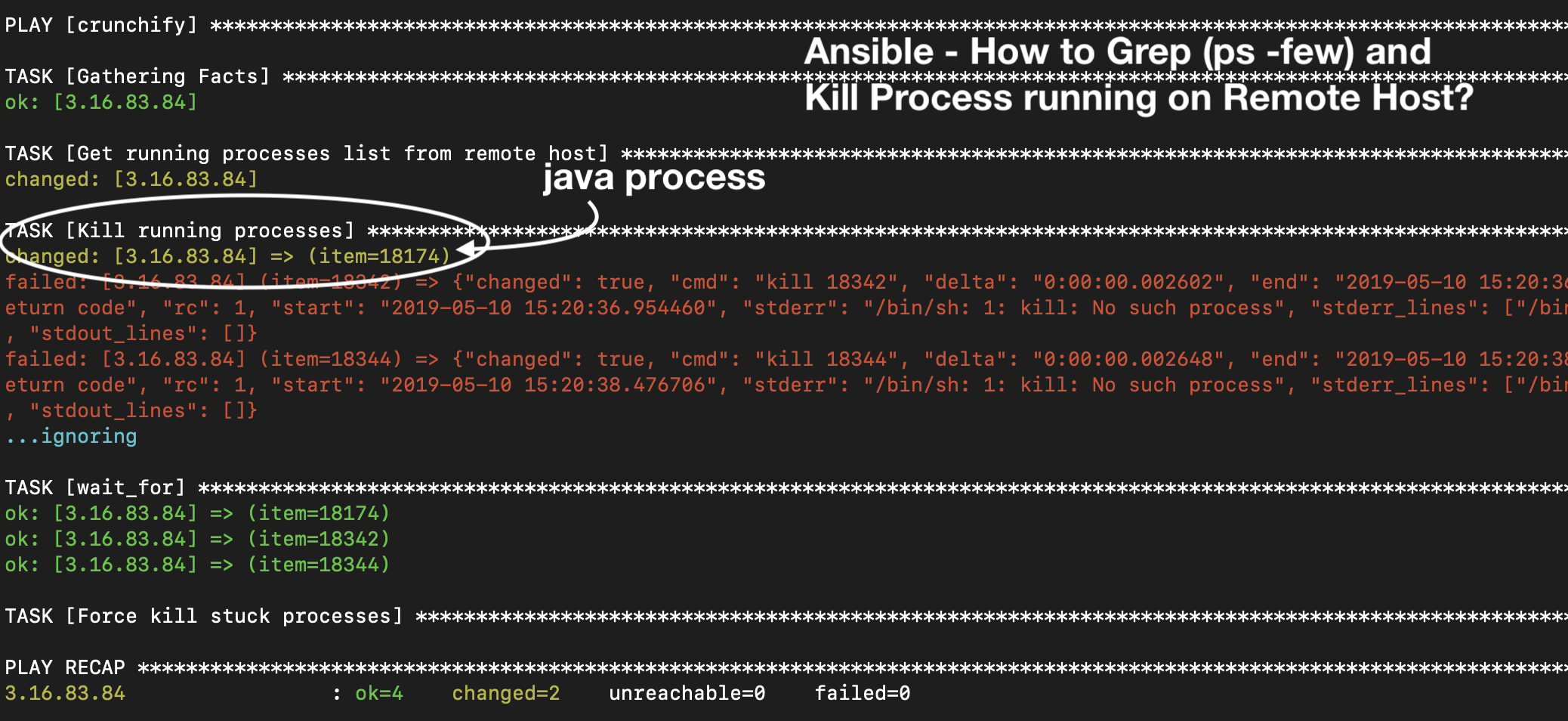
Aqui o arquivo de playbook ansible está obtendo todos os processos Java, matando-o usando o comando kill -9 simples.

Execute o Ansible Playbook:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
bash1 . 2 $ ansible - playbook - i . / crunchify - hosts crunchify - grep - kill - process . yml PLAY [ crunchify ] ************************************************************************************************************************************************************** TASK [ Gathering Facts ] ******************************************************************************************************************************************************** ok : [ 3.16.83.84 ] TASK [ Get running processes list from remote host ] **************************************************************************************************************************** changed : [ 3.16.83.84 ] TASK [ Kill running processes ] ************************************************************************************************************************************************* changed : [ 3.16.83.84 ] = > ( item = 18174 ) failed : [ 3.16.83.84 ] ( item = 18342 ) = > { "changed" : true , "cmd" : "kill 18342" , "delta" : "0:00:00.002602" , "end" : "2019-05-10 15:20:36.957062" , "item" : "18342" , "msg" : "non-zero return code" , "rc" : 1 , "start" : "2019-05-10 15:20:36.954460" , "stderr" : "/bin/sh: 1: kill: No such process" , "stderr_lines" : [ "/bin/sh: 1: kill: No such process" ] , "stdout" : "" , "stdout_lines" : [ ] } failed : [ 3.16.83.84 ] ( item = 18344 ) = > { "changed" : true , "cmd" : "kill 18344" , "delta" : "0:00:00.002648" , "end" : "2019-05-10 15:20:38.479354" , "item" : "18344" , "msg" : "non-zero return code" , "rc" : 1 , "start" : "2019-05-10 15:20:38.476706" , "stderr" : "/bin/sh: 1: kill: No such process" , "stderr_lines" : [ "/bin/sh: 1: kill: No such process" ] , "stdout" : "" , "stdout_lines" : [ ] } . . . ignoring TASK [ wait_for ] *************************************************************************************************************************************************************** ok : [ 3.16.83.84 ] = > ( item = 18174 ) ok : [ 3.16.83.84 ] = > ( item = 18342 ) ok : [ 3.16.83.84 ] = > ( item = 18344 ) TASK [ Force kill stuck processes ] ********************************************************************************************************************************************* PLAY RECAP * ******************************************************************************************************************************************************************* 3.16.83.84 : ok = 4 changed = 2 unreachable = 0 failed = 0 |
Como verificar?
Apenas tente grep process novamente no host remoto.
|
1 2 |
ubuntu @ ip - 172 - 31 - 10 - 150 : ~ $ ps - few | grep CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram ubuntu 18484 15069 0 15 : 22 pts / 0 00 : 00 : 00 grep -- color = auto CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram |
Como você percebe, você não verá o process ID 18174 na lista e não há nenhum processo Java em execução.
É isso.
Esta é a maneira mais simples de grep e matar o processo Java usando o Ansible. Deixe-me saber se você enfrentar algum problema ao executar este Ansible playbook .
