Jak zaimplementować algorytm sortowania bąbelkowego w Javie – przykład kolejności rosnącej i malejącej
Opublikowany: 2019-01-19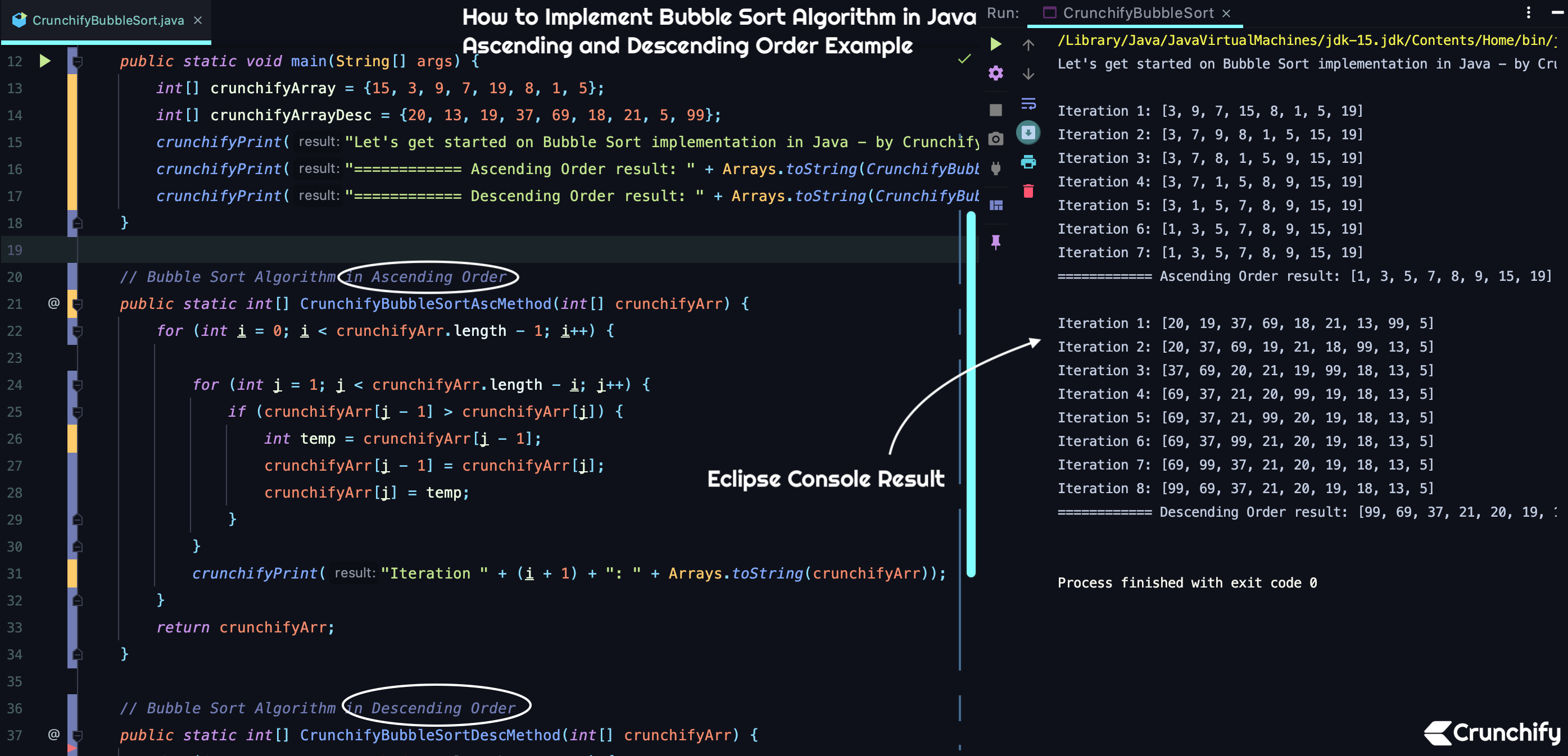
Bubble sort , czasami błędnie określane jako sinking sort , to prosty algorytm sortowania, który działa poprzez wielokrotne przechodzenie przez listę do posortowania, porównywanie każdej pary sąsiednich elementów i zamianę ich, jeśli są w złej kolejności.
Przechodzenie przez listę jest powtarzane, dopóki nie są potrzebne żadne zamiany, co oznacza, że lista jest posortowana. Algorytm bierze swoją nazwę od sposobu, w jaki mniejsze elementy bubble się na górze listy.
Ponieważ używa tylko porównań do operowania na elementach, jest to sortowanie porównawcze. Chociaż algorytm jest prosty, większość innych algorytmów sortowania jest bardziej wydajna w przypadku dużych list.
Logika jest prosta:
W sortowaniu bąbelkowym po prostu przechodzimy przez arraylist od pierwszej do (rozmiar – 1) pozycji i porównujemy element z następnym. Zamień element z następnym elementem tylko wtedy, gdy następny element jest większy.
Oto kod Java:
- Utwórz plik
CrunchifyBubbleSort.java.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . util . Arrays ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * How to Implement Bubble sort algorithm in Java? Ascending and Descending Order Tutorial */ public class CrunchifyBubbleSort { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { int [ ] crunchifyArray = { 15 , 3 , 9 , 7 , 19 , 8 , 1 , 5 } ; int [ ] crunchifyArrayDesc = { 20 , 13 , 19 , 37 , 69 , 18 , 21 , 5 , 99 } ; crunchifyPrint ( "Let's get started on Bubble Sort implementation in Java - by Crunchify \n" ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "============ Ascending Order result: " + Arrays . toString ( CrunchifyBubbleSortAscMethod ( crunchifyArray ) ) + "\n" ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "============ Descending Order result: " + Arrays . toString ( CrunchifyBubbleSortDescMethod ( crunchifyArrayDesc ) ) + "\n" ) ; } // Bubble Sort Algorithm in Ascending Order public static int [ ] CrunchifyBubbleSortAscMethod ( int [ ] crunchifyArr ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyArr . length - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 1 ; j < crunchifyArr . length - i ; j ++ ) { if ( crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] > crunchifyArr [ j ] ) { int temp = crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] ; crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] = crunchifyArr [ j ] ; crunchifyArr [ j ] = temp ; } } crunchifyPrint ( "Iteration " + ( i + 1 ) + ": " + Arrays . toString ( crunchifyArr ) ) ; } return crunchifyArr ; } // Bubble Sort Algorithm in Descending Order public static int [ ] CrunchifyBubbleSortDescMethod ( int [ ] crunchifyArr ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyArr . length - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 1 ; j < crunchifyArr . length - i ; j ++ ) { if ( crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] < crunchifyArr [ j ] ) { int temp = crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] ; crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] = crunchifyArr [ j ] ; crunchifyArr [ j ] = temp ; } } crunchifyPrint ( "Iteration " + ( i + 1 ) + ": " + Arrays . toString ( crunchifyArr ) ) ; } return crunchifyArr ; } // Simple log util private static void crunchifyPrint ( String result ) { System . out . println ( result ) ; } } |
Wynik konsoli Eclipse:
Po prostu uruchom powyżej program java Bubble Sort w konsoli Eclipse lub IntelliJ IDE i powinieneś zobaczyć wynik jak poniżej.

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
Let ' s get started on Bubble Sort implementation in Java - by Crunchify Iteration 1 : [ 3 , 9 , 7 , 15 , 8 , 1 , 5 , 19 ] Iteration 2 : [ 3 , 7 , 9 , 8 , 1 , 5 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 3 : [ 3 , 7 , 8 , 1 , 5 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 4 : [ 3 , 7 , 1 , 5 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 5 : [ 3 , 1 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 6 : [ 1 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 7 : [ 1 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] ============ Ascending Order result : [ 1 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 1 : [ 20 , 19 , 37 , 69 , 18 , 21 , 13 , 99 , 5 ] Iteration 2 : [ 20 , 37 , 69 , 19 , 21 , 18 , 99 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 3 : [ 37 , 69 , 20 , 21 , 19 , 99 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 4 : [ 69 , 37 , 21 , 20 , 99 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 5 : [ 69 , 37 , 21 , 99 , 20 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 6 : [ 69 , 37 , 99 , 21 , 20 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 7 : [ 69 , 99 , 37 , 21 , 20 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 8 : [ 99 , 69 , 37 , 21 , 20 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] ============ Descending Order result : [ 99 , 69 , 37 , 21 , 20 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Process finished with exit code 0 |
Czym jest złożoność czasowa algorytmu sortowania bąbelków?
- Jeśli rozważysz
Best casescenariusz, będzie toO(n) - Jeśli weźmiesz pod uwagę
Worst casescenariusz, będzie toO(n 2 )
Daj mi znać, jeśli masz jakiś problem lub wyjątek działający w powyższym programie.
