Java에서 버블 정렬 알고리즘을 구현하는 방법 – 오름차순 및 내림차순 예제
게시 됨: 2019-01-19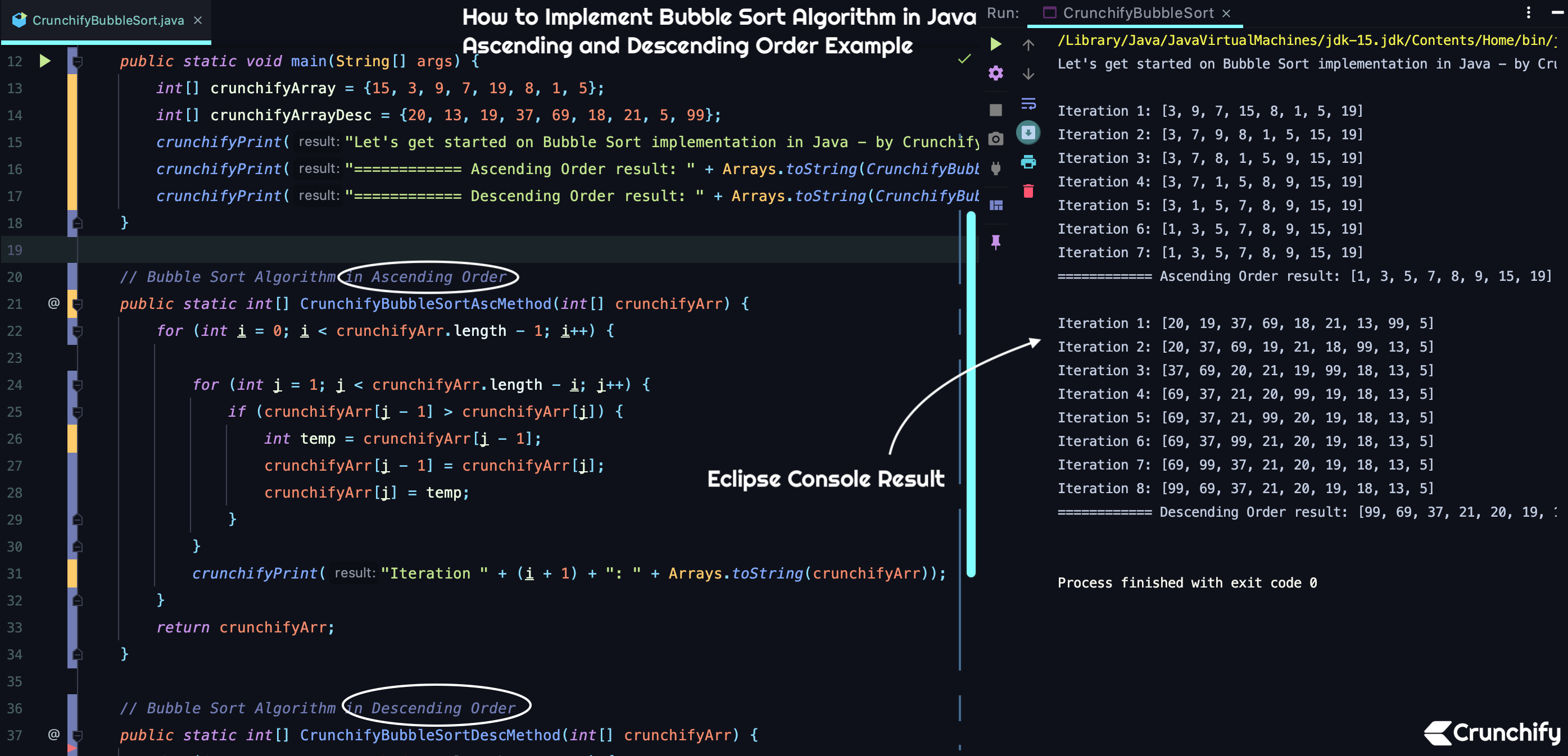
때때로 sinking sort 이라고 잘못 언급되는 Bubble sort 은 정렬할 목록을 반복적으로 단계별로 실행하고 인접한 항목의 각 쌍을 비교하고 순서가 잘못된 경우 교체하여 작동하는 간단한 정렬 알고리즘입니다.
목록을 통한 전달은 스왑이 필요하지 않을 때까지 반복되며 이는 목록이 정렬되었음을 나타냅니다. 알고리즘은 더 작은 요소가 목록의 맨 위로 bubble 되는 방식에서 이름을 얻습니다.
요소에 대해 작업하기 위해 비교만 사용하기 때문에 비교 정렬입니다. 알고리즘은 간단하지만 대부분의 다른 정렬 알고리즘은 큰 목록에 더 효율적입니다.
논리는 간단합니다.
버블 정렬에서는 기본적으로 배열 목록을 첫 번째 위치에서 (크기 – 1) 위치로 탐색하고 요소를 다음 위치와 비교합니다. 다음 요소가 더 큰 경우에만 요소를 다음 요소로 교체합니다.
다음은 자바 코드입니다.
-
CrunchifyBubbleSort.java파일을 생성합니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . util . Arrays ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * How to Implement Bubble sort algorithm in Java? Ascending and Descending Order Tutorial */ public class CrunchifyBubbleSort { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { int [ ] crunchifyArray = { 15 , 3 , 9 , 7 , 19 , 8 , 1 , 5 } ; int [ ] crunchifyArrayDesc = { 20 , 13 , 19 , 37 , 69 , 18 , 21 , 5 , 99 } ; crunchifyPrint ( "Let's get started on Bubble Sort implementation in Java - by Crunchify \n" ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "============ Ascending Order result: " + Arrays . toString ( CrunchifyBubbleSortAscMethod ( crunchifyArray ) ) + "\n" ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "============ Descending Order result: " + Arrays . toString ( CrunchifyBubbleSortDescMethod ( crunchifyArrayDesc ) ) + "\n" ) ; } // Bubble Sort Algorithm in Ascending Order public static int [ ] CrunchifyBubbleSortAscMethod ( int [ ] crunchifyArr ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyArr . length - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 1 ; j < crunchifyArr . length - i ; j ++ ) { if ( crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] > crunchifyArr [ j ] ) { int temp = crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] ; crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] = crunchifyArr [ j ] ; crunchifyArr [ j ] = temp ; } } crunchifyPrint ( "Iteration " + ( i + 1 ) + ": " + Arrays . toString ( crunchifyArr ) ) ; } return crunchifyArr ; } // Bubble Sort Algorithm in Descending Order public static int [ ] CrunchifyBubbleSortDescMethod ( int [ ] crunchifyArr ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < crunchifyArr . length - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 1 ; j < crunchifyArr . length - i ; j ++ ) { if ( crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] < crunchifyArr [ j ] ) { int temp = crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] ; crunchifyArr [ j - 1 ] = crunchifyArr [ j ] ; crunchifyArr [ j ] = temp ; } } crunchifyPrint ( "Iteration " + ( i + 1 ) + ": " + Arrays . toString ( crunchifyArr ) ) ; } return crunchifyArr ; } // Simple log util private static void crunchifyPrint ( String result ) { System . out . println ( result ) ; } } |
Eclipse 콘솔 결과:
Eclipse 콘솔 또는 IntelliJ IDE에서 Bubble Sort Java 프로그램 위를 실행하면 아래와 같은 결과가 표시됩니다.

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
Let ' s get started on Bubble Sort implementation in Java - by Crunchify Iteration 1 : [ 3 , 9 , 7 , 15 , 8 , 1 , 5 , 19 ] Iteration 2 : [ 3 , 7 , 9 , 8 , 1 , 5 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 3 : [ 3 , 7 , 8 , 1 , 5 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 4 : [ 3 , 7 , 1 , 5 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 5 : [ 3 , 1 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 6 : [ 1 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 7 : [ 1 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] ============ Ascending Order result : [ 1 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 19 ] Iteration 1 : [ 20 , 19 , 37 , 69 , 18 , 21 , 13 , 99 , 5 ] Iteration 2 : [ 20 , 37 , 69 , 19 , 21 , 18 , 99 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 3 : [ 37 , 69 , 20 , 21 , 19 , 99 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 4 : [ 69 , 37 , 21 , 20 , 99 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 5 : [ 69 , 37 , 21 , 99 , 20 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 6 : [ 69 , 37 , 99 , 21 , 20 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 7 : [ 69 , 99 , 37 , 21 , 20 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Iteration 8 : [ 99 , 69 , 37 , 21 , 20 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] ============ Descending Order result : [ 99 , 69 , 37 , 21 , 20 , 19 , 18 , 13 , 5 ] Process finished with exit code 0 |
버블 정렬 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도란?
-
Best case시나리오를 고려한다면O(n)이 될 것입니다. -
Worst case시나리오를 고려한다면O(n 2 )
프로그램 위에서 실행되는 문제나 예외가 있으면 알려주십시오.
