자바 세마포어와 뮤텍스란 무엇인가 – 자바 동시성 멀티스레드가 예제로 설명됨
게시 됨: 2015-03-12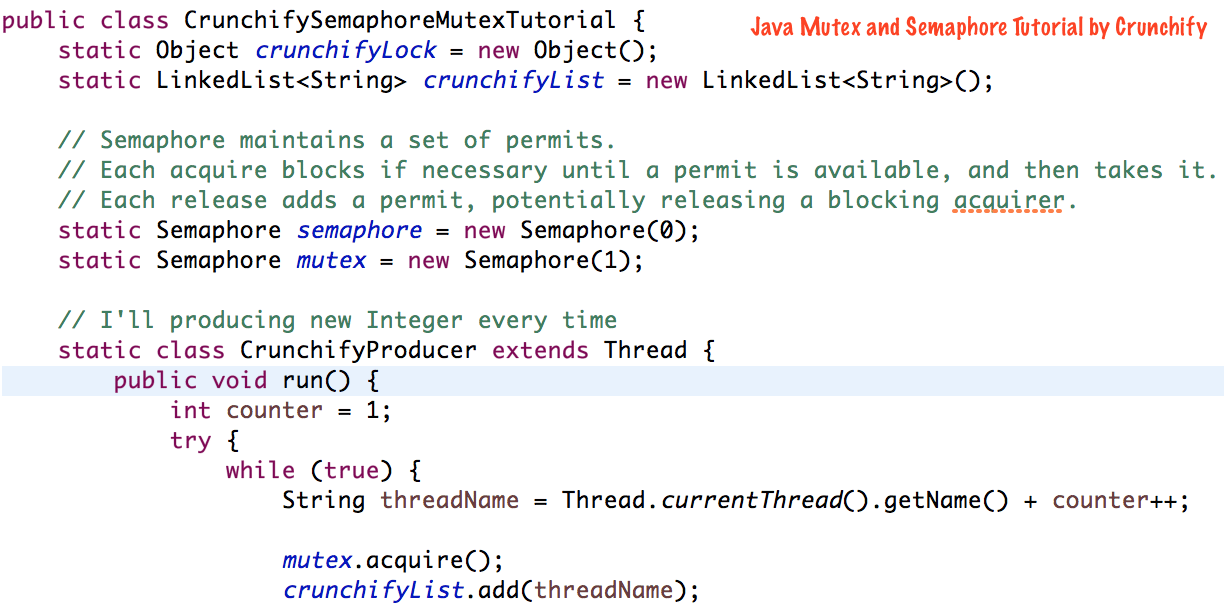
Java 동시성은 매우 광범위한 주제입니다. 사용할 수 있는 수백 개의 자습서와 예제가 있습니다. 얼마 전에 Java 및 다양한 유형의 동기화된 블록에서 동시에 여러 스레드 실행에 대한 몇 가지 자습서를 작성했습니다.
이 튜토리얼에서 우리는 다음을 다룰 것입니다:
- 뮤텍스에 대한 설명
- 세마포어 설명
- 세부사항이 있는 두 가지 예
시작하자
아래 설명을 읽는 동안 Let's keep this in mind .
- 구매자와 고객을 예로 들어
- 쇼핑객이 노트북을 빌리고 있습니다.
- 고객이 방문하여 노트북을 사용할 수 있습니다. 고객이 노트북을 사용하려면 키가 필요합니다.
- 사용 후 – 고객은 노트북을 구매자에게 반품할 수 있습니다.
뮤텍스란 무엇입니까(단 1개의 스레드):
쇼핑객은 노트북의 열쇠를 가지고 있습니다. 한 고객이 그 시간에 열쇠를 가질 수 있습니다. 랩탑을 빌릴 수 있습니다. 작업이 완료되면 구매자는 대기열의 다음 고객에게 키를 제공(해제)합니다.
Official Definition :
"Mutex는 일반적으로 둘 이상의 스레드에서 cannot be executed concurrently re-entrant code 섹션에 대한 액세스를 직렬화하는 데 사용됩니다. 뮤텍스 개체는 한 스레드만 제어 섹션으로 들어갈 수 있도록 허용하므로 해당 섹션에 대한 액세스 권한을 얻으려는 다른 스레드는 첫 번째 스레드가 해당 섹션에서 종료될 때까지 대기해야 합니다."
즉, Mutex = Mutually Exclusive Semaphore
세마포어란 무엇입니까(N개의 지정된 스레드):
이제 구매자에게 3개의 동일한 랩탑과 3개의 동일한 키가 있다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 세마포어는 free identical Laptop keys 의 수입니다. 세마포어 카운트(키 수)는 처음에 3으로 설정되고(3개의 랩탑 모두 무료임) 고객이 들어올 때 카운트 값이 감소합니다. 모든 랩탑이 사용 중이면 즉 랩탑, 세마포어 수는 0입니다. 이제 고객 중 한 명이 랩탑을 반환하면 세마포어가 1(무료 키 1개)로 증가하고 대기열의 다음 고객에게 제공됩니다.
Official Definition : “세마포어는 공유 리소스의 동시 사용자 수를 최대 수로 제한합니다. 스레드는 리소스에 대한 액세스를 요청할 수 있고(세마포 감소), 리소스 사용을 완료했음을 알릴 수 있습니다(세마포 증가)."
다른 사람은 읽어야 합니다: Singleton ThreadSafe 인스턴스의 지연 생성
예-1: (아래 설명)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 |
package crunchify . com . tutorial ; import java . util . LinkedList ; import java . util . concurrent . Semaphore ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifySemaphoreMutexTutorial { static Object crunchifyLock = new Object ( ) ; static LinkedList <String> crunchifyList = new LinkedList <String> ( ) ; // Semaphore maintains a set of permits. // Each acquire blocks if necessary until a permit is available, and then takes it. // Each release adds a permit, potentially releasing a blocking acquirer. static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore ( 0 ) ; static Semaphore mutex = new Semaphore ( 1 ) ; // I'll producing new Integer every time static class CrunchifyProducer extends Thread { public void run ( ) { int counter = 1 ; try { while ( true ) { String threadName = Thread . currentThread ( ) . getName ( ) + counter ++ ; mutex . acquire ( ) ; crunchifyList . add ( threadName ) ; System . out . println ( "Producer is prdoucing new value: " + threadName ) ; mutex . release ( ) ; // release lock semaphore . release ( ) ; Thread . sleep ( 500 ) ; } } catch ( Exception x ) { x . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } } // I'll be consuming Integer every stime static class CrunchifyConsumer extends Thread { String consumerName ; public CrunchifyConsumer ( String name ) { this . consumerName = name ; } public void run ( ) { try { while ( true ) { // acquire lock. Acquires the given number of permits from this semaphore, blocking until all are // available // process stops here until producer releases the lock semaphore . acquire ( ) ; // Acquires a permit from this semaphore, blocking until one is available mutex . acquire ( ) ; String result = "" ; for ( String value : crunchifyList ) { result = value + "," ; } System . out . println ( consumerName + " consumes value: " + result + "crunchifyList.size(): " + crunchifyList . size ( ) + "\n" ) ; mutex . release ( ) ; } } catch ( Exception e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } } public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { new CrunchifyProducer ( ) . start ( ) ; new CrunchifyConsumer ( "Crunchify" ) . start ( ) ; new CrunchifyConsumer ( "Google" ) . start ( ) ; new CrunchifyConsumer ( "Yahoo" ) . start ( ) ; } } |
위의 튜토리얼 CrunchifySemaphoreMutexTutorial.java 에서 CrunchifyProducer 가 crunchifyList linkedList 객체에 threadName 을 추가하면 세마포어 신호를 보낼 수 있습니다.
그런 다음 CrunchifyConsumer 는 세마포어 획득을 시도할 수 있으므로 CrunchifyProducer가 threadID가 추가되었다는 신호를 보낼 때까지 대기합니다. 추가된 데이터에 신호를 보내면 소비자 중 하나가 깨어나 crunchifyList 개체를 읽을 수 있음을 알게 됩니다. 목록을 읽은 다음 세마포어에서 획득 시도로 돌아갈 수 있습니다.
그 시간에 생산자가 다른 패킷을 작성했다면 다시 신호를 보냈고 소비자 중 하나는 계속해서 다른 패킷을 읽는 등…
다시 말해:
|
1 2 3 |
CrunchifyProducer : Add an object o List - Semaphore . release ( 1 ) CrunchifyConsumer x N ) - Semaphore . acquire ( 1 ) - Read an object from List |

결과:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
Producer is prdoucing new value : Thread - 01 Crunchify consumes value : Thread - 01 , crunchifyList . size ( ) : 1 Producer is prdoucing new value : Thread - 02 Google consumes value : Thread - 02 , crunchifyList . size ( ) : 2 Producer is prdoucing new value : Thread - 03 Yahoo consumes value : Thread - 03 , crunchifyList . size ( ) : 3 Producer is prdoucing new value : Thread - 04 Crunchify consumes value : Thread - 04 , crunchifyList . size ( ) : 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
경쟁 조건을 방지하는 방법:
What if you have multiple Consumers? 위의 Java Tutorial에서 소비자(생산자가 아님)는 경쟁 조건을 방지하기 위해 패킷을 읽을 때 버퍼를 잠가야 합니다(세마포어를 획득할 때는 아님). 아래 예에서 생산자는 모든 것이 동일한 JVM에 있기 때문에 목록을 잠급니다.
예-2:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 |
package crunchify . com . tutorial ; import java . util . concurrent . Semaphore ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyJavaSemaphoreTutorial { private static final int MAX_CONCURRENT_THREADS = 2 ; private final Semaphore crunchifyAdminLOCK = new Semaphore ( MAX_CONCURRENT_THREADS , true ) ; public void crunchifyStartTest ( ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++ ) { CrunchifyPerson person = new CrunchifyPerson ( ) ; person . start ( ) ; } } public class CrunchifyPerson extends Thread { @Override public void run ( ) { try { // Acquire Lock crunchifyAdminLOCK . acquire ( ) ; } catch ( InterruptedException e ) { System . out . println ( "received InterruptedException" ) ; return ; } System . out . println ( "Thread " + this . getId ( ) + " start using Crunchify's car - Acquire()" ) ; try { sleep ( 1000 ) ; } catch ( Exception e ) { } finally { // Release Lock crunchifyAdminLOCK . release ( ) ; } System . out . println ( "Thread " + this . getId ( ) + " stops using Crunchify's car - Release()\n" ) ; } } public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { CrunchifyJavaSemaphoreTutorial test = new CrunchifyJavaSemaphoreTutorial ( ) ; test . crunchifyStartTest ( ) ; } } |
결과:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
Thread 11 start using Crunchify 's car - Acquire() Thread 10 start using Crunchify' s car - Acquire ( ) Thread 10 stops using Crunchify 's car - Release() Thread 12 start using Crunchify' s car - Acquire ( ) Thread 13 start using Crunchify 's car - Acquire() Thread 11 stops using Crunchify' s car - Release ( ) Thread 13 stops using Crunchify 's car - Release() Thread 15 start using Crunchify' s car - Acquire ( ) Thread 14 start using Crunchify 's car - Acquire() Thread 12 stops using Crunchify' s car - Release ( ) Thread 14 stops using Crunchify 's car - Release() Thread 16 start using Crunchify' s car - Acquire ( ) Thread 15 stops using Crunchify 's car - Release() Thread 17 start using Crunchify' s car - Acquire ( ) Thread 17 stops using Crunchify 's car - Release() Thread 18 start using Crunchify' s car - Acquire ( ) Thread 19 start using Crunchify 's car - Acquire() Thread 16 stops using Crunchify' s car - Release ( ) Thread 18 stops using Crunchify 's car - Release() Thread 19 stops using Crunchify' s car - Release ( ) |
