java.lang.NullPointerException(NPE)을 눈치채셨나요? Java에서 런타임 NPE를 피하기 위한 8가지 모범 사례
게시 됨: 2020-10-07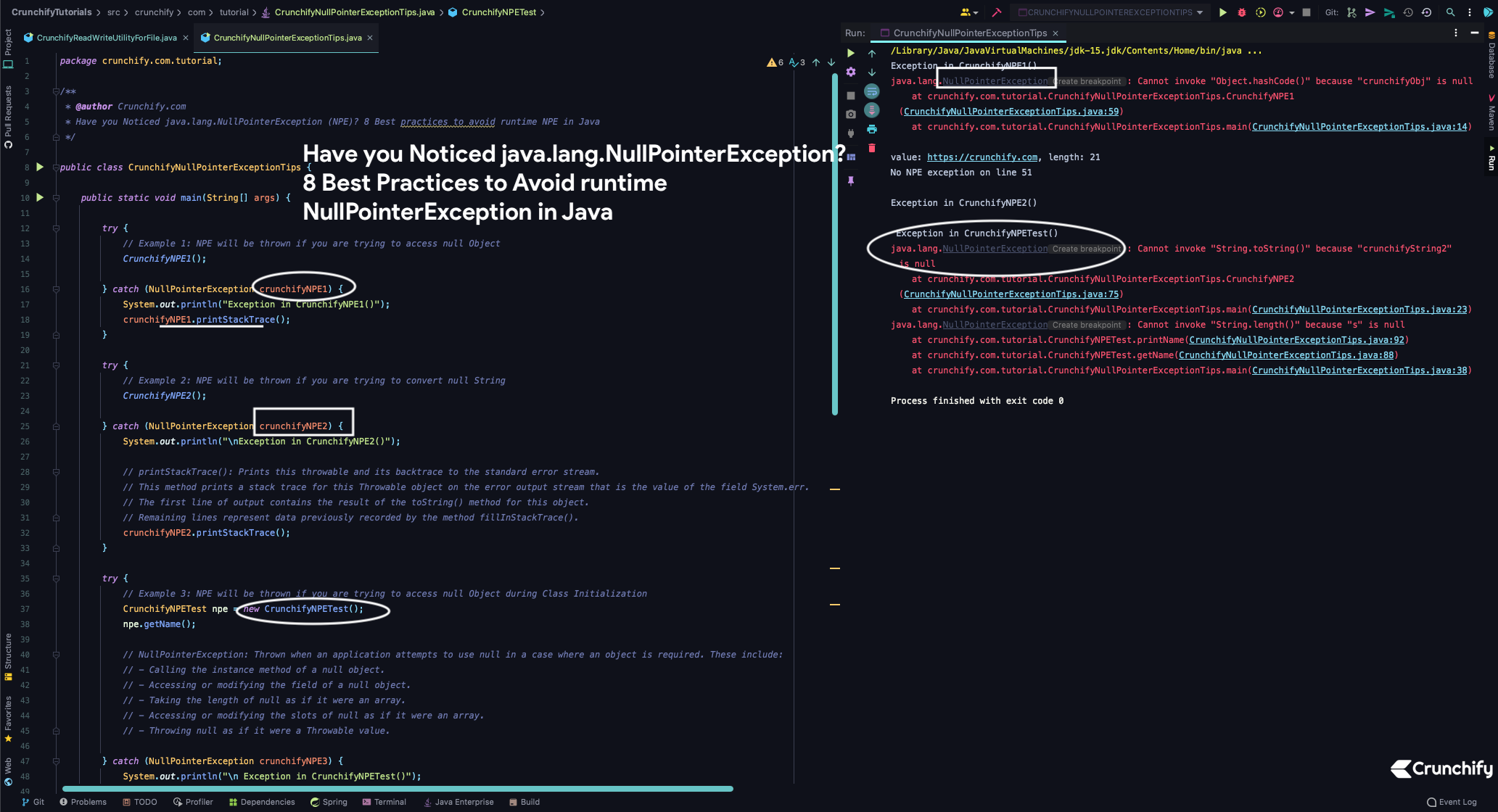
Java 및 Java에서 Null 포인터 예외 방지 Java에서 NullPointerException을 방지하기 위한 팁 및 모범 사례.
Java 개발자로서 첫날부터 NPE(Null Pointer Exception)에 직면했을 것입니다. 대부분의 경우 NPE 예외는 동일한 근본 원인을 핀으로 가리키는 명확한 스택 추적을 보여주지만 수백 개의 클래스가 있는 대규모 엔터프라이즈 수준 응용 프로그램의 경우 실제 근본 원인을 찾는 것은 악몽이 됩니다.
NPE(널 포인터 예외)란 무엇입니까?
NullPointerException (NPE) 은 개체를 참조하는 것처럼 메모리(null)의 아무 위치도 가리키지 않는 참조를 사용하려고 할 때 발생하는 예외입니다.
null 참조에서 메서드를 호출하거나 null 참조 필드에 액세스하려고 하면 NPE가 트리거됩니다. 이것이 가장 흔한 원인입니다.
JavaDoc에 따르면 NPE의 주요 원인은 다음과 같습니다.
-
Throwable값인 것처럼null을 throw합니다. -
null개체의 인스턴스 메서드를 호출합니다. -
null개체의 필드에 액세스하거나 수정합니다. - 배열인 것처럼
null의 길이를 취합니다. - 배열인 것처럼
null슬롯에 액세스하거나 수정합니다.
이제 진짜 질문은 런타임에 java.lang.NullPointerException을 피하는 방법입니다. 이 튜토리얼에서는 런타임에 NPE를 생성하는 몇 가지 예제와 이를 해결하기 위해 수행해야 하는 단계를 살펴보겠습니다.
런타임 1일에 NPE를 생성해 봅시다. 아래의 CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips.java 예를 살펴보십시오.
우리는 NPE를 3가지 다른 방법으로 만들 것입니다
- null 개체에 액세스하려고 하면 NPE가 발생합니다.
- null 문자열을 변환하려고 하면 NPE가 발생합니다.
- 클래스 초기화 중에 null 개체에 액세스하려고 하면 NPE가 throw됩니다.
클래스 CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips.java 만들기
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 |
package crunchify . com . tutorial ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * Have you Noticed java.lang.NullPointerException (NPE)? 8 Best practices to avoid runtime NPE in Java */ public class CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { try { // Example 1: NPE will be thrown if you are trying to access null Object CrunchifyNPE1 ( ) ; } catch ( NullPointerException crunchifyNPE1 ) { System . out . println ( "Exception in CrunchifyNPE1()" ) ; crunchifyNPE1 . printStackTrace ( ) ; } try { // Example 2: NPE will be thrown if you are trying to convert null String CrunchifyNPE2 ( ) ; } catch ( NullPointerException crunchifyNPE2 ) { System . out . println ( "\nException in CrunchifyNPE2()" ) ; // printStackTrace(): Prints this throwable and its backtrace to the standard error stream. // This method prints a stack trace for this Throwable object on the error output stream that is the value of the field System.err. // The first line of output contains the result of the toString() method for this object. // Remaining lines represent data previously recorded by the method fillInStackTrace(). crunchifyNPE2 . printStackTrace ( ) ; } try { // Example 3: NPE will be thrown if you are trying to access null Object during Class Initialization CrunchifyNPETest npe = new CrunchifyNPETest ( ) ; npe . getName ( ) ; // NullPointerException: Thrown when an application attempts to use null in a case where an object is required. These include: // - Calling the instance method of a null object. // - Accessing or modifying the field of a null object. // - Taking the length of null as if it were an array. // - Accessing or modifying the slots of null as if it were an array. // - Throwing null as if it were a Throwable value. } catch ( NullPointerException crunchifyNPE3 ) { System . out . println ( "\n Exception in CrunchifyNPETest()" ) ; crunchifyNPE3 . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } private static void CrunchifyNPE1 ( ) { Object crunchifyObj = null ; // hasCode(): Returns a hash code value for the object. // This method is supported for the benefit of hash tables such as those provided by java.util.HashMap. crunchifyObj . hashCode ( ) ; } private static void CrunchifyNPE2 ( ) { String crunchifyString ; crunchifyString = "https://crunchify.com" ; // The line 40 declares a variable named "crunchifyString", but, it does not contain a primitive value. Instead it contains a pointer (because the type is String // which is a reference type). Since you did not say as yet what to point to Java sets it to null, meaning "I am pointing at nothing". // In line 41, the new keyword is used to instantiate (or create) an object of type String and the pointer variable "crunchifyString" is assigned this // object. You can now reference the object using the dereferencing operator . (a dot). System . out . println ( "\nvalue: " + crunchifyString . toString ( ) + ", length: " + crunchifyString . length ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( "No NPE exception on line 51" ) ; // Now Let's create NPE String crunchifyString2 = null ; System . out . println ( crunchifyString2 . toString ( ) ) ; } } class CrunchifyNPETest { private String crunchifyName ; public void setName ( String name ) { this . crunchifyName = name ; } public void getName ( ) { printName ( crunchifyName ) ; } private void printName ( String s ) { System . out . println ( s + " (" + s . length ( ) + ")" ) ; } } |
결과:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
Exception in CrunchifyNPE1 ( ) java . lang . NullPointerException : Cannot invoke "Object.hashCode()" because "crunchifyObj" is null at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . CrunchifyNPE1 ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 59 ) at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . main ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 14 ) value : https : //crunchify.com, length: 21 No NPE exception on line 51 Exception in CrunchifyNPE2 ( ) Exception in CrunchifyNPETest ( ) java . lang . NullPointerException : Cannot invoke "String.toString()" because "crunchifyString2" is null at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . CrunchifyNPE2 ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 75 ) at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . main ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 23 ) java . lang . NullPointerException : Cannot invoke "String.length()" because "s" is null at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNPETest . printName ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 92 ) at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNPETest . getName ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 88 ) at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . main ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 38 ) Process finished with exit code 0 |
글쎄, 런타임에 NullPointerException을 피하기 위해 사용할 수 있는 몇 가지 팁과 트릭이 있습니다. 한 번 보자.

힌트 1:
Eclipse / IntelliJ IDE는 작업 공간에 NPE를 표시하려고 합니다. 개발 중에만 코드를 수정하십시오.
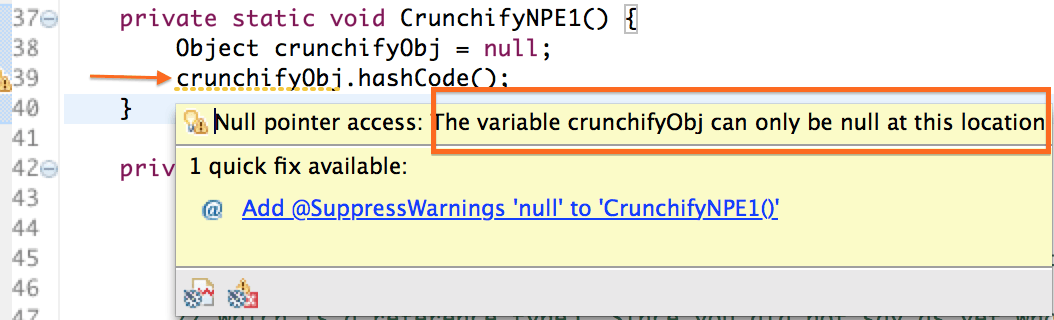
힌트 2:
개체에 대한 작업 전에 crunchifyI sNullorEmpty () 검사를 추가합니다. 이것을 CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips.java 에 추가하십시오.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
public static boolean crunchifyIsNullOrEmpty ( String crunchifyStr ) { if ( crunchifyStr == null ) return true ; else if ( crunchifyStr . trim ( ) . equals ( "" ) ) return true ; else return false ; } |
위의 자바 프로그램 라인 55와 56은 이것으로 대체될 것입니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
String crunchifyString2 = null ; if ( ! crunchifyIsNullOrEmpty ( crunchifyString2 ) ) { System . out . println ( crunchifyString2 . toString ( ) ) ; } else { System . out . println ( "crunchifyString2 is null" ) ; } |
힌트 3:
trim() 작업 후 null 이 비어 있는지 확인하십시오.
|
1 2 3 |
public static boolean isNullOrEmptyAfterTrim ( String crunchifyStr ) { return ( crunchifyStr == null | | crunchifyStr . trim ( ) . length ( ) == 0 ) ; } |
힌트 4:
중단 없는 런타임 프로세스를 방지하려면 항상 Try Catch block 을 사용하십시오.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
try { CrunchifyNPE1 ( ) ; } catch ( NullPointerException npe ) { System . out . println ( "Exception in CrunchifyNPE1()" + npe ) ; } |
힌트 5:
Collections.emptyList() 는 더 나은 제네릭 처리로 인해 선호됩니다.
힌트 6:
Java Assertions 사용
어설션은 코드에 대한 가정을 테스트할 수 있는 문입니다. 예를 들어 시스템에서 이름을 반환하는 메서드를 작성하는 경우 String이 null인 경우 otherName을 반환한다고 주장할 수 있습니다.
어설션의 기본 사용법은 다음과 같습니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
assert < Expression > ; // or another usage is assert < Expression1 > : < Expression2 > ; // in our program add line below. private void printName ( String s ) { assert ( s ! = null ) : "Name must be not null" ; System . out . println ( s + " (" + s . length ( ) + ")" ) ; } |
하지만 문제가 있습니다. Assertion은 프로덕션 환경에서 사용할 수 없으며 비즈니스 로직과 함께 Assertion을 사용해서는 안 됩니다.
힌트 7:
containsKey() , containsValue() , contains() 검사를 사용해보십시오.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
package com . crunchify . tutorial ; import java . util . * ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyContainsKeyExample { public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { HashMap < Integer , String > crunchifyMap = new HashMap < Integer , String > ( ) ; // populate hash map crunchifyMap . put ( 1 , "Crunchify" ) ; crunchifyMap . put ( 2 , "wordpress" ) ; crunchifyMap . put ( 3 , "java tutorials" ) ; // check existence of key 4 if ( crunchifyMap . containsKey ( 4 ) ) { System . out . println ( "Check if key 2 exists: " + crunchifyMap . get ( 4 ) ) ; } else { System . out . println ( "NPE for value 4 avoided" ) ; } } } |
힌트 8:
결론적으로 런타임에 프로덕션에서 디버깅하는 것보다 개발하는 동안 NPE를 처리하는 것이 항상 좋은 습관입니다. Spring Framework Annotation, Factory Pattern , Null Object Pattern 등을 사용하여 사용할 수 있는 다른 팁과 트릭이 많이 있습니다. 하지만 지금은 이만 줄이겠습니다.
아마 일주일 안에 이것에 대한 새로운 튜토리얼을 게시할 것입니다. 계속 지켜봐 주세요.
이 튜토리얼에 추가하고 싶은 것이 있거나 문제를 발견한 경우, 차임벨을 들고 의견을 제공하십시오.
