هل لاحظت java.lang.NullPointerException (NPE)؟ 8 أفضل الممارسات لتجنب وقت تشغيل NPE في Java
نشرت: 2020-10-07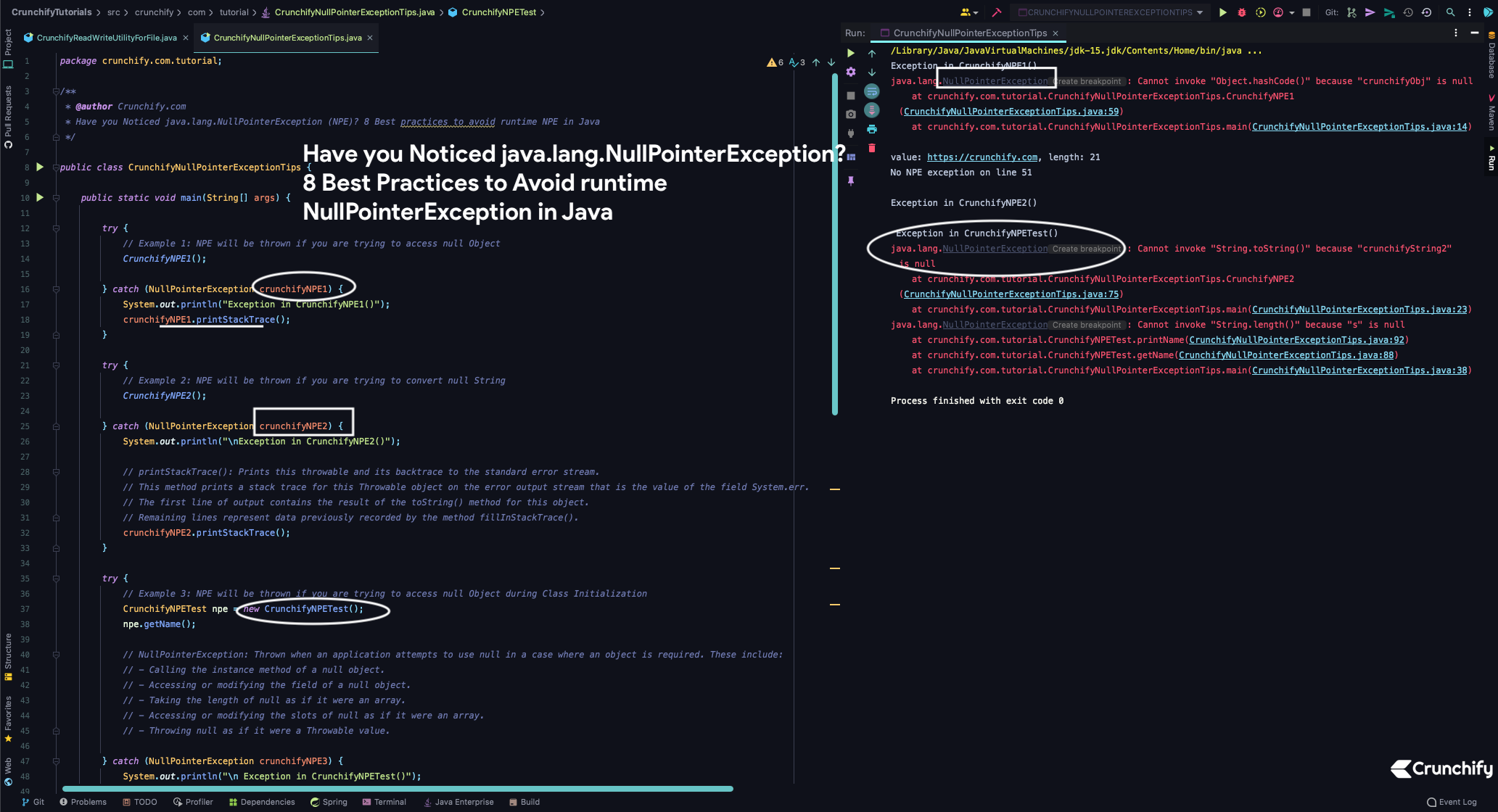
تجنب استثناء المؤشر الفارغ في Java و Java Tips وأفضل الممارسات لتجنب NullPointerException في Java.
بصفتي مطور Java ، أنا متأكد من أنك واجهت استثناء Null Pointer Exception (NPE) بدءًا من اليوم الأول. في معظم الحالات ، يُظهر استثناء NPE تتبعًا واضحًا للمكدس الذي يشير إلى السبب الجذري لنفسه ولكن في حالة التطبيق الكبير على مستوى المؤسسة الذي لديك فيه مئات الفئات ، يصبح اكتشاف السبب الجذري الحقيقي كابوسًا.
ما هو Null Pointer Exception (NPE)؟
NullPointerException (NPE) هو استثناء يحدث عند محاولة استخدام مرجع يشير إلى عدم وجود موقع في الذاكرة (فارغ) كما لو كان يشير إلى كائن.
سيؤدي استدعاء طريقة على مرجع null أو محاولة الوصول إلى حقل مرجعي فارغ إلى تشغيل NPE. هذا هو السبب الأكثر شيوعًا.
وفقًا لـ JavaDoc ، فيما يلي الأسباب الرئيسية لـ NPE:
- رمي
nullكما لو كان قيمةThrowable. - استدعاء طريقة المثيل لكائن
null. - الوصول إلى حقل كائن
nullأو تعديله. - أخذ الطول
nullكما لو كان مصفوفة. - الوصول إلى فتحات القيمة
nullأو تعديلها كما لو كانت مصفوفة.
السؤال الحقيقي الآن هو كيف تتجنب java.lang.NullPointerException في وقت التشغيل؟ في هذا البرنامج التعليمي ، سنلقي نظرة على بعض الأمثلة التي تنشئ NPE في وقت التشغيل والخطوات التي نحتاج إلى تنفيذها لحل هذه المشكلة.
لنقم بإنشاء NPE في وقت التشغيل الأول. ألق نظرة على المثال أدناه CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips.java
سنقوم بإنشاء NPE 3 طرق مختلفة
- سيتم طرح NPE إذا كنت تحاول الوصول إلى كائن فارغ
- سيتم طرح NPE إذا كنت تحاول تحويل سلسلة فارغة
- سيتم طرح NPE إذا كنت تحاول الوصول إلى كائن فارغ أثناء تهيئة الفئة
قم بإنشاء فئة CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 |
package crunchify . com . tutorial ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * Have you Noticed java.lang.NullPointerException (NPE)? 8 Best practices to avoid runtime NPE in Java */ public class CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { try { // Example 1: NPE will be thrown if you are trying to access null Object CrunchifyNPE1 ( ) ; } catch ( NullPointerException crunchifyNPE1 ) { System . out . println ( "Exception in CrunchifyNPE1()" ) ; crunchifyNPE1 . printStackTrace ( ) ; } try { // Example 2: NPE will be thrown if you are trying to convert null String CrunchifyNPE2 ( ) ; } catch ( NullPointerException crunchifyNPE2 ) { System . out . println ( "\nException in CrunchifyNPE2()" ) ; // printStackTrace(): Prints this throwable and its backtrace to the standard error stream. // This method prints a stack trace for this Throwable object on the error output stream that is the value of the field System.err. // The first line of output contains the result of the toString() method for this object. // Remaining lines represent data previously recorded by the method fillInStackTrace(). crunchifyNPE2 . printStackTrace ( ) ; } try { // Example 3: NPE will be thrown if you are trying to access null Object during Class Initialization CrunchifyNPETest npe = new CrunchifyNPETest ( ) ; npe . getName ( ) ; // NullPointerException: Thrown when an application attempts to use null in a case where an object is required. These include: // - Calling the instance method of a null object. // - Accessing or modifying the field of a null object. // - Taking the length of null as if it were an array. // - Accessing or modifying the slots of null as if it were an array. // - Throwing null as if it were a Throwable value. } catch ( NullPointerException crunchifyNPE3 ) { System . out . println ( "\n Exception in CrunchifyNPETest()" ) ; crunchifyNPE3 . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } private static void CrunchifyNPE1 ( ) { Object crunchifyObj = null ; // hasCode(): Returns a hash code value for the object. // This method is supported for the benefit of hash tables such as those provided by java.util.HashMap. crunchifyObj . hashCode ( ) ; } private static void CrunchifyNPE2 ( ) { String crunchifyString ; crunchifyString = "https://crunchify.com" ; // The line 40 declares a variable named "crunchifyString", but, it does not contain a primitive value. Instead it contains a pointer (because the type is String // which is a reference type). Since you did not say as yet what to point to Java sets it to null, meaning "I am pointing at nothing". // In line 41, the new keyword is used to instantiate (or create) an object of type String and the pointer variable "crunchifyString" is assigned this // object. You can now reference the object using the dereferencing operator . (a dot). System . out . println ( "\nvalue: " + crunchifyString . toString ( ) + ", length: " + crunchifyString . length ( ) ) ; System . out . println ( "No NPE exception on line 51" ) ; // Now Let's create NPE String crunchifyString2 = null ; System . out . println ( crunchifyString2 . toString ( ) ) ; } } class CrunchifyNPETest { private String crunchifyName ; public void setName ( String name ) { this . crunchifyName = name ; } public void getName ( ) { printName ( crunchifyName ) ; } private void printName ( String s ) { System . out . println ( s + " (" + s . length ( ) + ")" ) ; } } |
نتيجة:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
Exception in CrunchifyNPE1 ( ) java . lang . NullPointerException : Cannot invoke "Object.hashCode()" because "crunchifyObj" is null at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . CrunchifyNPE1 ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 59 ) at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . main ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 14 ) value : https : //crunchify.com, length: 21 No NPE exception on line 51 Exception in CrunchifyNPE2 ( ) Exception in CrunchifyNPETest ( ) java . lang . NullPointerException : Cannot invoke "String.toString()" because "crunchifyString2" is null at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . CrunchifyNPE2 ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 75 ) at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . main ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 23 ) java . lang . NullPointerException : Cannot invoke "String.length()" because "s" is null at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNPETest . printName ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 92 ) at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNPETest . getName ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 88 ) at crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . main ( CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips . java : 38 ) Process finished with exit code 0 |
حسنًا ، هناك بعض النصائح والحيل التي يمكننا استخدامها لتجنب NullPointerException في وقت التشغيل. لنلقي نظرة.

تلميح 1:
سيحاول Eclipse / IntelliJ IDE إظهار NPE في مساحة العمل. تصحيح التعليمات البرمجية الخاصة بك أثناء التطوير فقط.
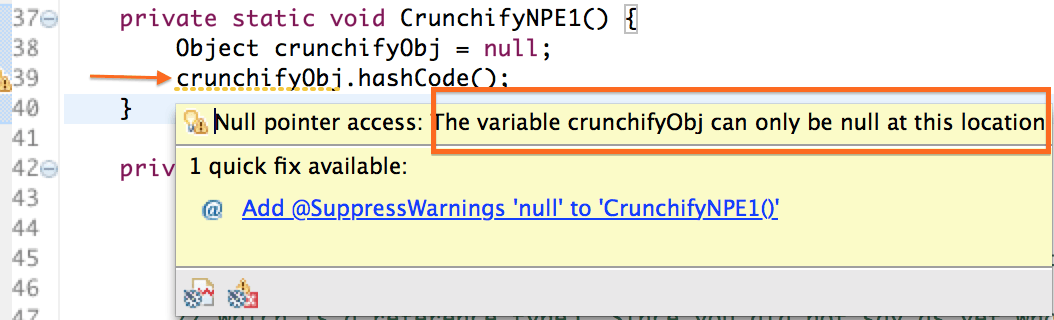
تلميح 2:
أضف crunchifyI sNullorEmpty () قبل إجراء عملية على الكائن. أضف هذا إلى CrunchifyNullPointerExceptionTips.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
public static boolean crunchifyIsNullOrEmpty ( String crunchifyStr ) { if ( crunchifyStr == null ) return true ; else if ( crunchifyStr . trim ( ) . equals ( "" ) ) return true ; else return false ; } |
في أعلاه ، سيتم استبدال السطر 55 و 56 من برنامج جافا بهذا.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
String crunchifyString2 = null ; if ( ! crunchifyIsNullOrEmpty ( crunchifyString2 ) ) { System . out . println ( crunchifyString2 . toString ( ) ) ; } else { System . out . println ( "crunchifyString2 is null" ) ; } |
تلميح 3:
تحقق مما إذا كانت السلسلة null أو فارغة بعد عملية القطع ().
|
1 2 3 |
public static boolean isNullOrEmptyAfterTrim ( String crunchifyStr ) { return ( crunchifyStr == null | | crunchifyStr . trim ( ) . length ( ) == 0 ) ; } |
تلميح 4:
استخدم دائمًا Try Catch block عملية Runtime غير المنقطعة.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
try { CrunchifyNPE1 ( ) ; } catch ( NullPointerException npe ) { System . out . println ( "Exception in CrunchifyNPE1()" + npe ) ; } |
تلميح 5:
يُفضل Collections.emptyList() بسبب التعامل الأفضل مع الأدوية الجنيسة.
تلميح 6:
استخدم Java Assertions
التأكيد هو بيان يمكّنك من اختبار افتراضاتك حول الكود الخاص بك. على سبيل المثال ، إذا قمت بكتابة طريقة تُرجع الاسم في النظام ، فقد تؤكد أن الاسم الآخر العائد إذا كانت السلسلة خالية.
الاستخدام الأساسي للتأكيدات سيكون:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
assert < Expression > ; // or another usage is assert < Expression1 > : < Expression2 > ; // in our program add line below. private void printName ( String s ) { assert ( s ! = null ) : "Name must be not null" ; System . out . println ( s + " (" + s . length ( ) + ")" ) ; } |
ولكن هناك مشكلة: التأكيد غير متوفر في بيئة الإنتاج ويجب ألا نستخدم التأكيد مع أي منطق أعمال.
تلميح 7:
حاول استخدام containsKey() ، و containsValue() ، contains() عمليات تحقق.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
package com . crunchify . tutorial ; import java . util . * ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyContainsKeyExample { public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { HashMap < Integer , String > crunchifyMap = new HashMap < Integer , String > ( ) ; // populate hash map crunchifyMap . put ( 1 , "Crunchify" ) ; crunchifyMap . put ( 2 , "wordpress" ) ; crunchifyMap . put ( 3 , "java tutorials" ) ; // check existence of key 4 if ( crunchifyMap . containsKey ( 4 ) ) { System . out . println ( "Check if key 2 exists: " + crunchifyMap . get ( 4 ) ) ; } else { System . out . println ( "NPE for value 4 avoided" ) ; } } } |
تلميح 8:
في الختام ، من الممارسات الجيدة دائمًا الاهتمام بـ NPE أثناء التطوير بدلاً من تصحيح الأخطاء في الإنتاج في وقت التشغيل. هناك عدد من النصائح والحيل الأخرى المتاحة باستخدام التعليق التوضيحي لـ Spring Framework ، Factory Pattern الكائن الفارغ وما إلى ذلك ، لكنني سأختصر هذا الآن.
سيتم نشر برنامج تعليمي جديد ربما في غضون أسبوع في هذا واحد. ابقوا متابعين.
هل تريد إضافة أي شيء إلى هذا البرنامج التعليمي أو وجدت مشكلة ، يرجى الاتصال وتقديم تعليقاتك.
