HashMap의 clone(), putIfAbsent(), computeIfAbsent(), computeIfPresent() Java의 메소드(예제)
게시 됨: 2021-05-11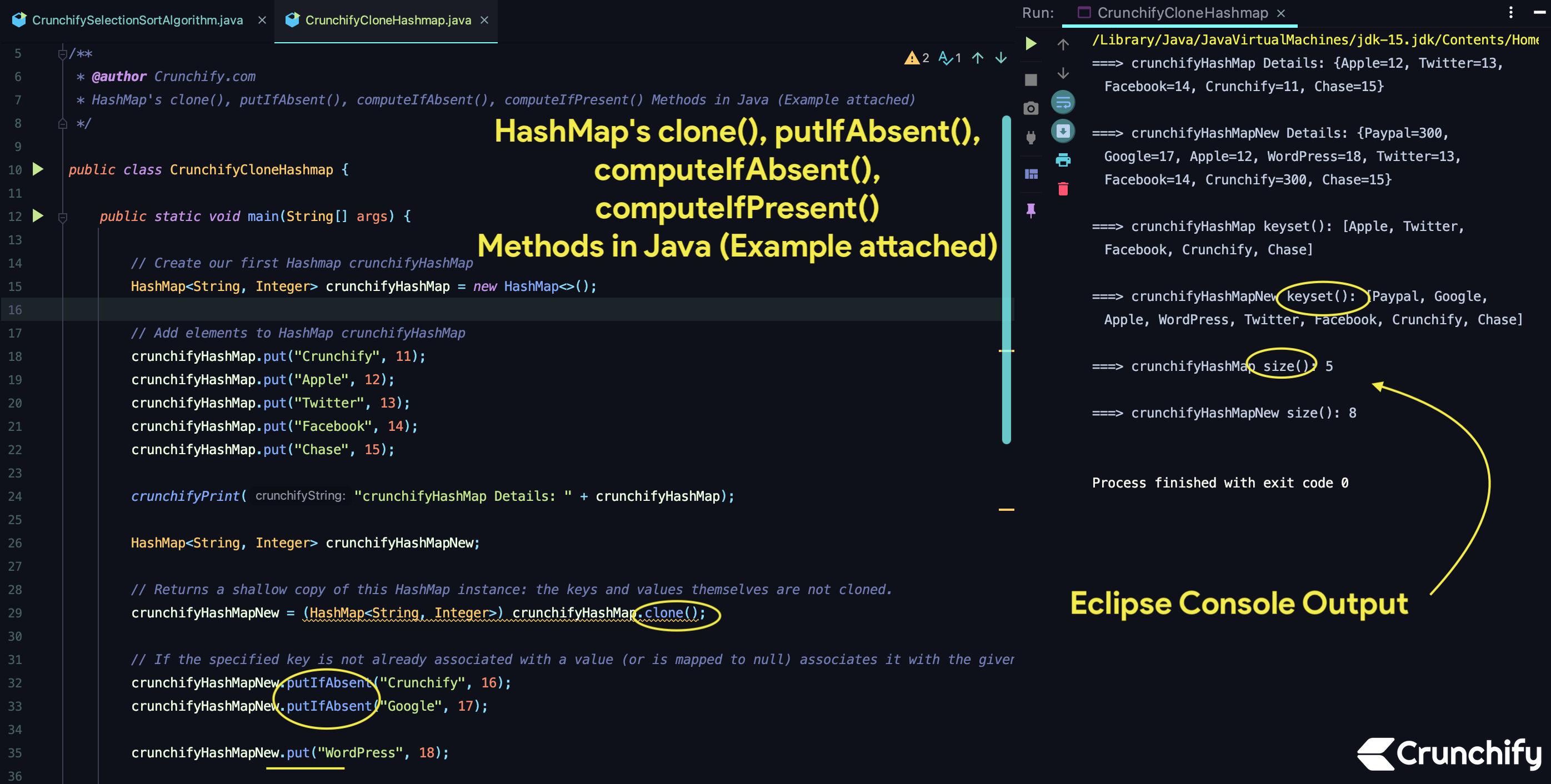
이 Java Tutorial에서는 HashMap의 아래 메서드를 사용하는 방법에 대해 자세히 설명합니다.
- 클론()
- putIfAbsent(K 키, V 값)
- computeIfAbsent(K 키, java.util.function.Function mappingFunction)
- computeIfPresent(K 키, java.util.function.
BiFunctionremappingFunction)
hashMap.clone():
이 HashMap 인스턴스의 얕은 복사본을 반환합니다. 키와 값 자체는 복제되지 않습니다.
hashMap.putIfAbsent():
지정된 키가 이미 값과 연결되어 있지 않은 경우(또는 null에 매핑된 경우) 이를 주어진 값과 연결하고 null을 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 현재 값을 반환합니다.
hashMap.computeIfAbsent():
지정된 키가 아직 값과 연결되어 있지 않은 경우(또는 null에 매핑된 경우) 지정된 매핑 함수를 사용하여 해당 값을 계산하려고 시도하고 null이 아닌 경우 이 맵에 입력합니다.
hashMap.computeIfPresent():
지정된 키의 값이 존재하고 null이 아닌 경우 키와 현재 매핑된 값이 지정된 새 매핑을 계산하려고 시도합니다.
시작하자:
- Java 클래스
CrunchifyCloneHashmap.java 만들기 - 거기에 아래 코드를 넣어
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 |
package crunchify . com . java . tutorials ; import java . util . HashMap ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * HashMap's clone(), putIfAbsent(), computeIfAbsent(), computeIfPresent() Methods in Java (Example attached) */ public class CrunchifyCloneHashmap { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { // Create our first Hashmap crunchifyHashMap HashMap < String , Integer > crunchifyHashMap = new HashMap < > ( ) ; // Add elements to HashMap crunchifyHashMap crunchifyHashMap . put ( "Crunchify" , 11 ) ; crunchifyHashMap . put ( "Apple" , 12 ) ; crunchifyHashMap . put ( "Twitter" , 13 ) ; crunchifyHashMap . put ( "Facebook" , 14 ) ; crunchifyHashMap . put ( "Chase" , 15 ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "crunchifyHashMap Details: " + crunchifyHashMap ) ; HashMap < String , Integer > crunchifyHashMapNew ; // Returns a shallow copy of this HashMap instance: the keys and values themselves are not cloned. crunchifyHashMapNew = ( HashMap < String , Integer > ) crunchifyHashMap . clone ( ) ; // If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null) associates it with the given value and returns null, else returns the current value. crunchifyHashMapNew . putIfAbsent ( "Crunchify" , 16 ) ; crunchifyHashMapNew . putIfAbsent ( "Google" , 17 ) ; crunchifyHashMapNew . put ( "WordPress" , 18 ) ; // If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null), attempts to compute its value using the given mapping function and enters it into this map unless null. //If the mapping function returns null, no mapping is recorded. If the mapping function itself throws an (unchecked) exception, the exception is rethrown, and no mapping is recorded. The most common usage is to construct a new object serving as an initial mapped value or memoized result, as in: // // map.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new Value(f(k))); // //Or to implement a multi-value map, Map<K,Collection<V>>, supporting multiple values per key: // // map.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new HashSet<V>()).add(v); crunchifyHashMapNew . computeIfAbsent ( "Paypal" , k - > 100 + 200 ) ; // If the value for the specified key is present and non-null, attempts to compute a new mapping given the key and its current mapped value. //If the remapping function returns null, the mapping is removed. If the remapping function itself throws an (unchecked) exception, the exception is rethrown, and the current mapping is left unchanged. //The remapping function should not modify this map during computation. //This method will, on a best-effort basis, throw a ConcurrentModificationException if it is detected that the remapping function modifies this map during computation. crunchifyHashMapNew . computeIfPresent ( "Crunchify" , ( key , val ) - > 300 ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "crunchifyHashMapNew Details: " + crunchifyHashMapNew ) ; // Returns a Set view of the keys contained in this map. The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through the iterator's own remove operation), // the results of the iteration are undefined. The set supports element removal, which removes the corresponding mapping from the map, via // the Iterator.remove, Set.remove, removeAll, retainAll, and clear operations. It does not support the add or addAll operations. crunchifyPrint ( "crunchifyHashMap keyset(): " + crunchifyHashMap . keySet ( ) ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "crunchifyHashMapNew keyset(): " + crunchifyHashMapNew . keySet ( ) ) ; // Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map. crunchifyPrint ( "crunchifyHashMap size(): " + crunchifyHashMap . size ( ) ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "crunchifyHashMapNew size(): " + crunchifyHashMapNew . size ( ) ) ; } private static void crunchifyPrint ( String crunchifyString ) { System . out . println ( "===> " + crunchifyString + "\n" ) ; } } |
위의 Java 코드에서 crunchifyHashMapNew.putIfAbsent("Crunchify", 16); 새로운 HashMap에 추가되었습니다.

Eclipse IDE 또는 IntelliJ IDEA에서 위의 프로그램을 Java 응용 프로그램으로 실행하기만 하면 됩니다.
다음과 유사한 콘솔 결과가 표시되어야 합니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
/ Library / Java / JavaVirtualMachines / jdk - 15.jdk / Contents / Home / bin / java - javaagent : / Applications / IntelliJ 5.1.3.RELEASE.jar crunchify . com . java . tutorials . CrunchifyCloneHashmap === > crunchifyHashMap Details : { Apple = 12 , Twitter = 13 , Facebook = 14 , Crunchify = 11 , Chase = 15 } === > crunchifyHashMapNew Details : { Paypal = 300 , Google = 17 , Apple = 12 , WordPress = 18 , Twitter = 13 , Facebook = 14 , Crunchify = 300 , Chase = 15 } === > crunchifyHashMap keyset ( ) : [ Apple , Twitter , Facebook , Crunchify , Chase ] === > crunchifyHashMapNew keyset ( ) : [ Paypal , Google , Apple , WordPress , Twitter , Facebook , Crunchify , Chase ] === > crunchifyHashMap size ( ) : 5 === > crunchifyHashMapNew size ( ) : 8 Process finished with exit code 0 |

코드 실행에 문제가 있으면 알려주십시오.
