En Java Comment créer votre propre niveau de journalisation à l'aide de Log4j (Configuration de Log4j 2)
Publié: 2017-07-26
Si vous devez ajouter votre propre niveau de journalisation dans Log4j, vous pouvez le faire comme suit. Vous devrez créer votre propre classe qui s'étendra de Level , Custom Log Levels with Apache Log4j 2.
Log4j est un logging framework simple et flexible. La journalisation fournit au développeur un contexte détaillé pour les échecs d'application. Avec log4j, il est possible d'activer la journalisation au moment de l'exécution sans modifier le binaire de l'application.
Le package log4j est conçu pour que ces instructions puissent rester dans le code livré sans entraîner de coût de performances élevé.
Log4j permet aux demandes de journalisation d'imprimer vers plusieurs destinations. En langage log4j, une destination de sortie est appelée un appender . Ils varient de la console, des fichiers, des composants GUI, des serveurs de socket distants à JMS.
Fichier Jar dont vous avez besoin.
Voici une dépendance Maven :
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
< dependency > < groupId > log4j < / groupId > < artifactId > log4j < / artifactId > < version > 2.16.0 < / version > < / dependency > |
Mettre à jour Log4j vers la dernière version
CVE-2021-44228 : Apache Log4j2 <=2.14.1 Les fonctionnalités JNDI utilisées dans la configuration, les messages de journal et les paramètres ne protègent pas contre LDAP contrôlé par l'attaquant et d'autres points de terminaison liés à JNDI.
Depuis log4j 2.16.0, ce comportement a été désactivé par défaut.
Vous devez placer le fichier log4j.xml sous le dossier /resources :

Voici un exemple de code Java pour :
- Journalisation Log4j pour les niveaux de journalisation personnalisés en Java
- Créer votre propre niveau de journalisation dans log4j
- exemple d'enregistreur personnalisé log4j
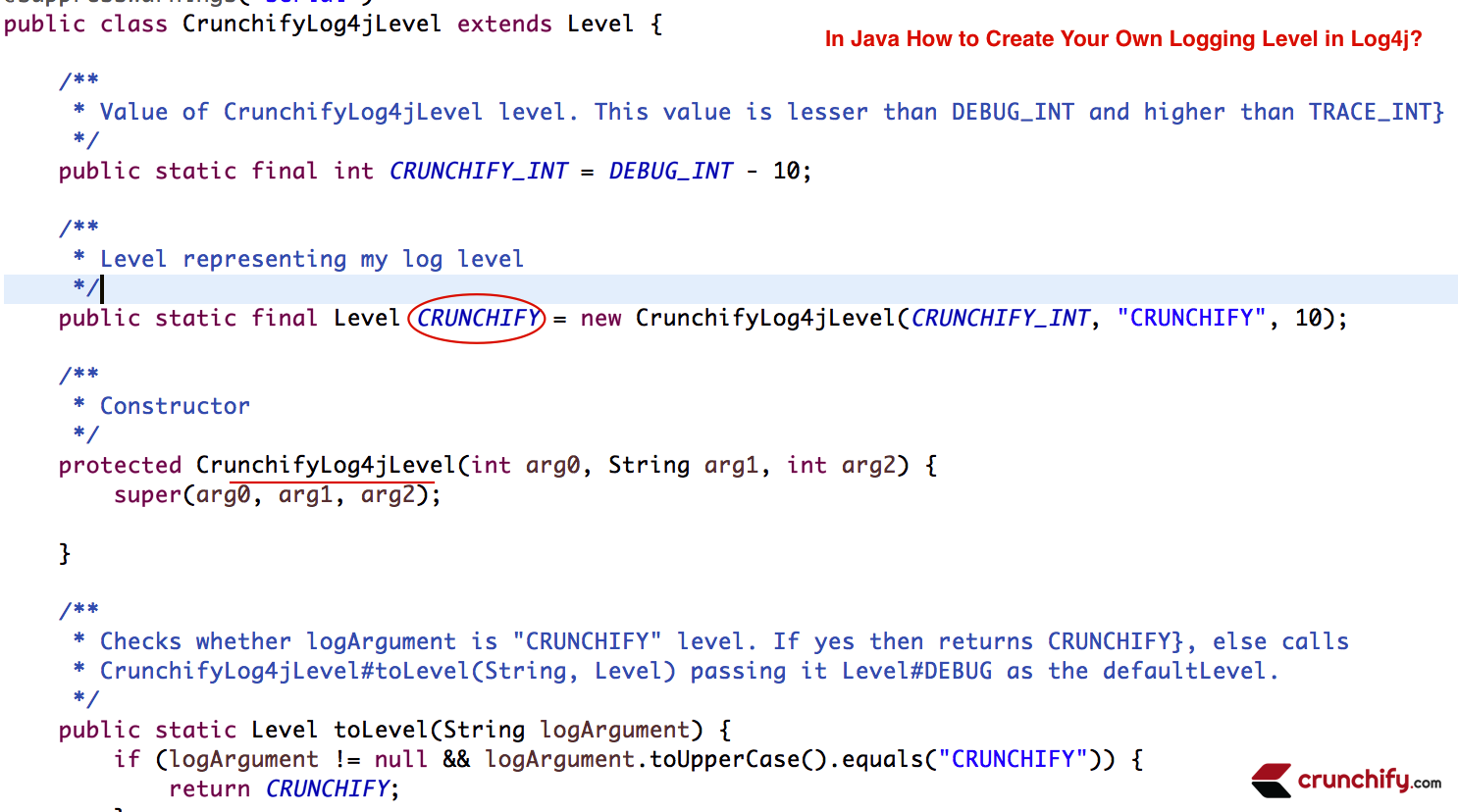
CrunchifyLog4jLevel.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import org . apache . log4j . Level ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ @SuppressWarnings ( "serial" ) public class CrunchifyLog4jLevel extends Level { /** * Value of CrunchifyLog4jLevel level. This value is lesser than DEBUG_INT and higher * than TRACE_INT} */ public static final int CRUNCHIFY_INT = DEBUG_INT - 10 ; /** * Level representing my log level */ public static final Level CRUNCHIFY = new CrunchifyLog4jLevel ( CRUNCHIFY_INT , "CRUNCHIFY" , 10 ) ; /** * Constructor */ protected CrunchifyLog4jLevel ( int arg0 , String arg1 , int arg2 ) { super ( arg0 , arg1 , arg2 ) ; } /** * Checks whether logArgument is "CRUNCHIFY" level. If yes then returns * CRUNCHIFY}, else calls CrunchifyLog4jLevel#toLevel(String, Level) passing * it Level#DEBUG as the defaultLevel. */ public static Level toLevel ( String logArgument ) { if ( logArgument ! = null && logArgument.toUpperCase().equals("CRUNCHIFY")) { return CRUNCHIFY; } return ( Level ) toLevel ( logArgument , Level . DEBUG ) ; } /** * Checks whether val is CrunchifyLog4jLevel#CRUNCHIFY_INT. If yes then * returns CrunchifyLog4jLevel#CRUNCHIFY, else calls * CrunchifyLog4jLevel#toLevel(int, Level) passing it Level#DEBUG as the * defaultLevel * */ public static Level toLevel ( int val ) { if ( val == CRUNCHIFY_INT ) { return CRUNCHIFY ; } return ( Level ) toLevel ( val , Level . DEBUG ) ; } /** * Checks whether val is CrunchifyLog4jLevel#CRUNCHIFY_INT. If yes * then returns CrunchifyLog4jLevel#CRUNCHIFY, else calls Level#toLevel(int, org.apache.log4j.Level) * */ public static Level toLevel ( int val , Level defaultLevel ) { if ( val == CRUNCHIFY_INT ) { return CRUNCHIFY ; } return Level . toLevel ( val , defaultLevel ) ; } /** * Checks whether logArgument is "CRUNCHIFY" level. If yes then returns * CrunchifyLog4jLevel#CRUNCHIFY, else calls * Level#toLevel(java.lang.String, org.apache.log4j.Level) * */ public static Level toLevel ( String logArgument , Level defaultLevel ) { if ( logArgument ! = null && logArgument.toUpperCase().equals("CRUNCHIFY")) { return CRUNCHIFY; } return Level . toLevel ( logArgument , defaultLevel ) ; } } |
Un autre doit lire:

- Comment démarrer le serveur Stop Apache Tomcat via la ligne de commande ? (Configuration en tant que service Windows)
- Créer et déployer un service Web simple et un client de service Web dans Eclipse
Voici un contenu du fichier log4j.xml
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
<? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" ?> < ! DOCTYPE log4j : configuration SYSTEM "log4j.dtd" > < log4j : configuration xmlns : log4j = "http://jakarta.apache.org/log4j/" debug = "false" > < ! -- FILE Appender -- > < appender name = "FILE" class = "org.apache.log4j.FileAppender" > < param name = "File" value = "c:/crunchify.log" / > < param name = "Append" value = "false" / > < layout class = "org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout" > < param name = "ConversionPattern" value = "%t %-5p %c - %m%n" / > < / layout > < / appender > < ! -- CONSOLE Appender -- > < appender name = "CONSOLE" class = "org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender" > < layout class = "org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout" > < param name = "ConversionPattern" value = "%d{ISO8601} %-5p [%c{1}] %m%n" / > < / layout > < / appender > < ! -- Limit Category and Specify Priority -- > < category name = "com.crunchify" > < priority value = "CRUNCHIFY" class = "com.crunchify.tutorials.CrunchifyLog4jLevel" / > < appender - ref ref = "CONSOLE" / > < / category > < ! -- Setup the Root category -- > < root > < appender - ref ref = "CONSOLE" / > < / root > < / log4j : configuration > |
CrunchifyLog4jLevelTest.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import org . apache . log4j . Level ; import org . apache . log4j . Logger ; import com . crunchify . tutorials . CrunchifyLog4jLevel ; /** * Tests whether the new log level * com.crunchify.tutorials.CrunchifyLog4jLevel#CRUNCHIFY} is working * * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyLog4jLevelTest { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { Logger logger = Logger . getLogger ( CrunchifyLog4jLevelTest . class ) ; logger . log ( CrunchifyLog4jLevel . CRUNCHIFY , "I am CrunchifyLog4jLevelTest log" ) ; logger . log ( Level . DEBUG , "I am a DEBUG message" ) ; } } |
Exécutez le programme de test et vous devriez voir le type de résultat ci-dessous dans Eclipse's Console .
|
1 2 |
2013 - 08 - 01 15 : 22 : 36 , 758 CRUNCHIFY [ CrunchifyLog4jLevelTest ] I am CrunchifyLog4jLevelTest log 2013 - 08 - 01 15 : 22 : 36 , 758 DEBUG [ CrunchifyLog4jLevelTest ] I am a DEBUG message |
La valeur int que vous spécifiez pour votre niveau de journalisation est importante. Ici, j'ai défini le niveau de journalisation " CRUNCHIFY " qui doit être supérieur au niveau DEBUG mais inférieur au niveau TRACE fourni par log4j.
Ainsi, chaque fois que vous avez défini un niveau de priorité sur DEBUG sur la catégorie (dans votre fichier log4j.xml ), les journaux de niveau CRUNCHIFY ne parviendront PAS au fichier journal.
