En Java, comment rejoindre Arrays ? 3 façons : Apache Commons ArrayUtils, Java 8 Streams et Simple APIs
Publié: 2022-01-20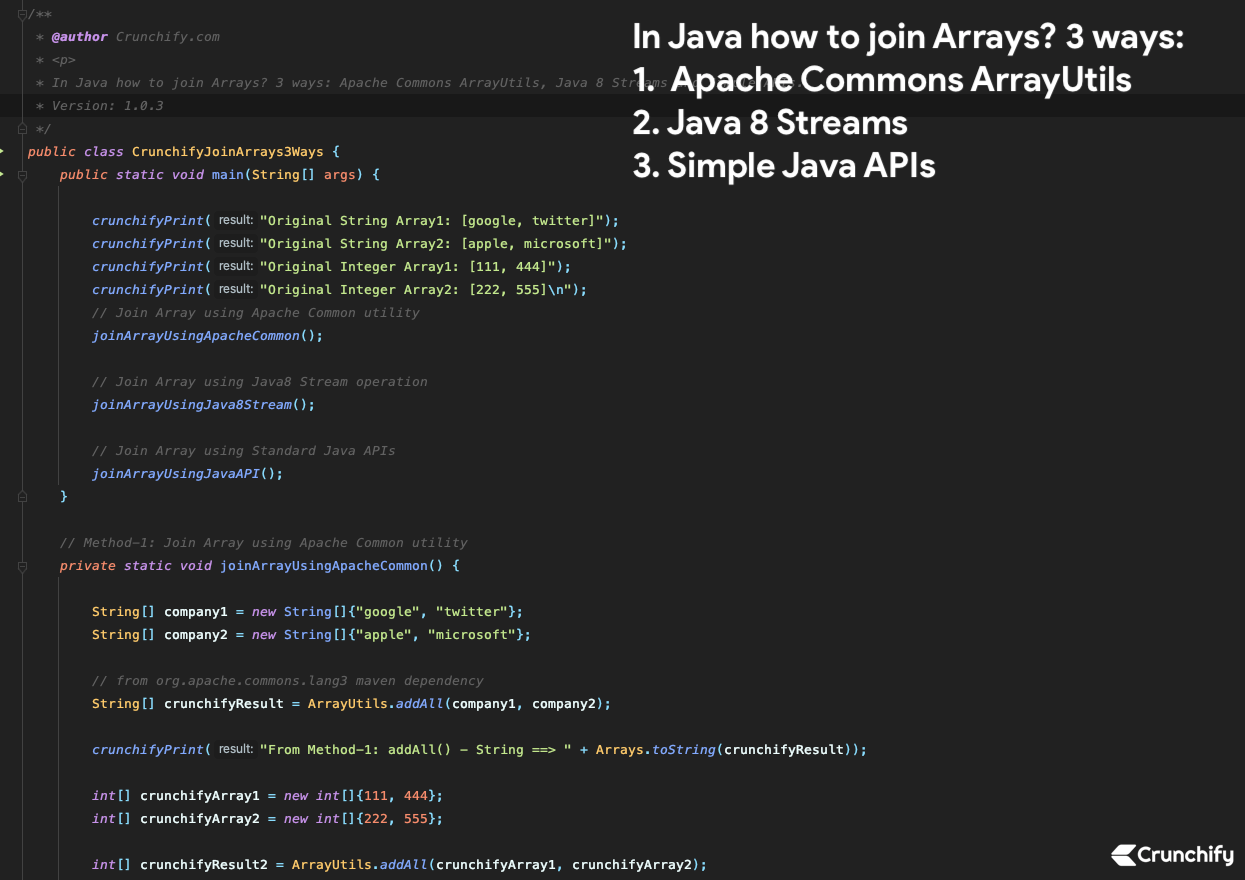
Dans ce didacticiel, nous allons passer en revue différentes manières de joindre des tableaux Java.
Si vous avez l'une des questions ci-dessous, vous êtes au bon endroit :
- Comment concaténer deux tableaux en Java ?
- Comment fusionner deux tableaux en Java ?
- 3 façons de combiner des tableaux en Java
- Joindre un tableau de primitives avec un séparateur en Java
Voici les trois façons dont vous pouvez joindre des tableaux en Java.
- Join Array à l'aide de l'utilitaire Apache Common
- Join Array à l'aide de l'opération Java8 Stream
- Rejoindre Array à l'aide des API Java standard
Commençons:
Créez la classe Java CrunchifyJoinArrays3Ways.java .
Mettez le code Java ci-dessous dans le fichier.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 |
package crunchify . com . tutorial ; import org . apache . commons . lang3 . ArrayUtils ; import java . lang . reflect . Array ; import java . util . Arrays ; import java . util . stream . IntStream ; import java . util . stream . Stream ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * <p> * In Java how to join Arrays? 3 ways: Apache Commons ArrayUtils, Java 8 Streams and Simple APIs. * Version: 1.0.3 */ public class CrunchifyJoinArrays3Ways { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { crunchifyPrint ( "Original String Array1: [google, twitter]" ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "Original String Array2: [apple, microsoft]" ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "Original Integer Array1: [111, 444]" ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "Original Integer Array2: [222, 555]\n" ) ; // Join Array using Apache Common utility joinArrayUsingApacheCommon ( ) ; // Join Array using Java8 Stream operation joinArrayUsingJava8Stream ( ) ; // Join Array using Standard Java APIs joinArrayUsingJavaAPI ( ) ; } // Method-1: Join Array using Apache Common utility private static void joinArrayUsingApacheCommon ( ) { String [ ] company1 = new String [ ] { "google" , "twitter" } ; String [ ] company2 = new String [ ] { "apple" , "microsoft" } ; // from org.apache.commons.lang3 maven dependency String [ ] crunchifyResult = ArrayUtils . addAll ( company1 , company2 ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "From Method-1: addAll() - String ==> " + Arrays . toString ( crunchifyResult ) ) ; int [ ] crunchifyArray1 = new int [ ] { 111 , 444 } ; int [ ] crunchifyArray2 = new int [ ] { 222 , 555 } ; int [ ] crunchifyResult2 = ArrayUtils . addAll ( crunchifyArray1 , crunchifyArray2 ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "From Method-1: addAll() - Integer ==> " + Arrays . toString ( crunchifyResult2 ) ) ; } // Simple Java Print Method private static void crunchifyPrint ( String result ) { System . out . println ( result ) ; } // Method-2: Join Array using Java8 Stream operation private static void joinArrayUsingJava8Stream ( ) { String [ ] company1 = new String [ ] { "google" , "twitter" } ; String [ ] company2 = new String [ ] { "apple" , "microsoft" } ; // Stream.of() - returns a sequential ordered stream whose elements are the specified values. // A sequence of elements supporting sequential and parallel aggregate operations. The following example illustrates an aggregate operation using Stream and IntStream: // // int sum = widgets.stream() // .filter(w -> w.getColor() == RED) // .mapToInt(w -> w.getWeight()) // .sum(); String [ ] result = Stream . of ( company1 , company2 ) . flatMap ( Stream : : of ) . toArray ( String [ ] : : new ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "\nFrom Method-2: Stream.of() ==> " + Arrays . toString ( result ) ) ; int [ ] crunchifyArray1 = new int [ ] { 111 , 444 } ; int [ ] crunchifyArray2 = new int [ ] { 222 , 555 } ; // Arrays.stream() - returns a sequential IntStream with the specified array as its source. int [ ] crunchifyResult2 = IntStream . concat ( Arrays . stream ( crunchifyArray1 ) , Arrays . stream ( crunchifyArray2 ) ) . toArray ( ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "From Method-2: IntStream.concat() ==> " + Arrays . toString ( crunchifyResult2 ) ) ; } // Method-3: Join Array using Standard Java APIs private static void joinArrayUsingJavaAPI ( ) { String [ ] company1 = new String [ ] { "google" , "twitter" } ; String [ ] company2 = new String [ ] { "apple" , "microsoft" } ; String [ ] crunchifyResult = crunchifyJoinGenericArray ( company1 , company2 ) ; crunchifyPrint ( "\nFrom Method-3: crunchifyJoinArrayusingGeneric() ==> " + Arrays . toString ( crunchifyResult ) ) ; int [ ] crunchifyArray1 = new int [ ] { 111 , 444 } ; int [ ] crunchifyArray2 = new int [ ] { 222 , 555 } ; int [ ] crunchifyResult2 = crunchifyJoinIntegerArray ( crunchifyArray1 , crunchifyArray2 ) ; // Arrays.toString() Returns a string representation of the contents of the specified array. // The string representation consists of a list of the array's elements, enclosed in square brackets ("[]"). // Adjacent elements are separated by the characters ", " (a comma followed by a space). // Elements are converted to strings as by String.valueOf(int). Returns "null" if a is null. crunchifyPrint ( "From Method-3: joinArray() ==> " + Arrays . toString ( crunchifyResult2 ) ) ; } @ SafeVarargs private static < T > T [ ] crunchifyJoinGenericArray ( T [ ] . . . crunchifyArrays ) { int crunchify = 0 ; for ( T [ ] crunchifyArray : crunchifyArrays ) { crunchify += crunchifyArray . length ; } //T[] result = new T[crunchify]; final T [ ] crunchifyResult = ( T [ ] ) Array . newInstance ( crunchifyArrays [ 0 ] . getClass ( ) . getComponentType ( ) , crunchify ) ; int crunchifyOffset = 0 ; for ( T [ ] crunchifyArray : crunchifyArrays ) { // Copies an array from the specified source array, beginning at the specified position, to the specified position of the destination array. // A subsequence of array components are copied from the source array referenced by src to the destination array referenced by dest. // The number of components copied is equal to the length argument. // The components at positions srcPos through srcPos+length-1 in the source array are copied into positions destPos through destPos+length-1, respectively, of the destination array. System . arraycopy ( crunchifyArray , 0 , crunchifyResult , crunchifyOffset , crunchifyArray . length ) ; crunchifyOffset += crunchifyArray . length ; } return crunchifyResult ; } private static int [ ] crunchifyJoinIntegerArray ( int [ ] . . . crunchifyArrays ) { int crunchify = 0 ; for ( int [ ] crunchifyArray : crunchifyArrays ) { crunchify += crunchifyArray . length ; } final int [ ] crunchifyResult = new int [ crunchify ] ; int crunchifyOffset = 0 ; for ( int [ ] crunchifyArray : crunchifyArrays ) { System . arraycopy ( crunchifyArray , 0 , crunchifyResult , crunchifyOffset , crunchifyArray . length ) ; crunchifyOffset += crunchifyArray . length ; } return crunchifyResult ; } } |
Jetons un coup d'œil à certains détails de l'API Java.

java.lang.System.arraycopy() :

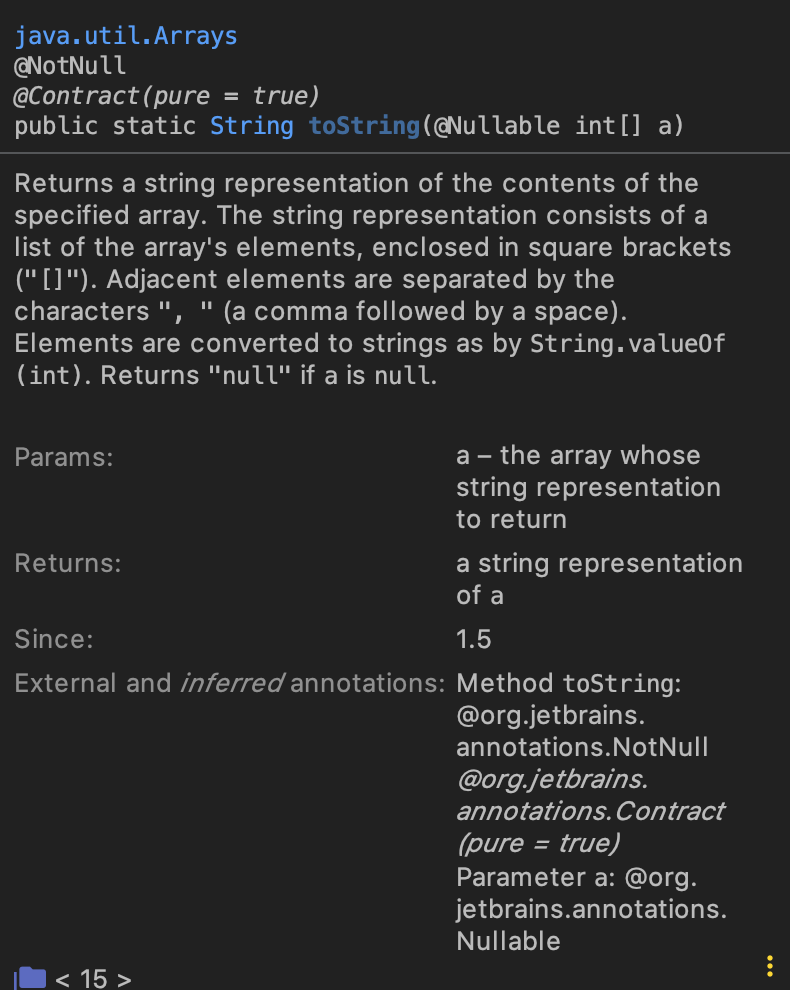
java.util.Arrays.toString() :
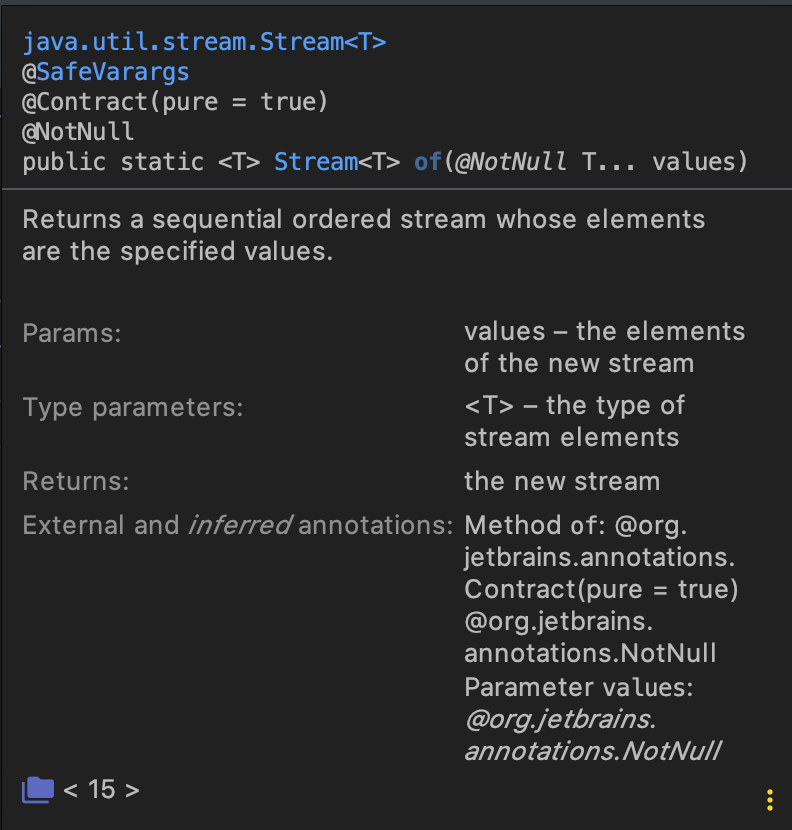
java.util.stream() :

Exécutez simplement le programme en tant que programme Java et vous devriez voir un résultat identique à celui ci-dessous.
Sortie de la console IntelliJ IDEA :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
/ Library / Java / JavaVirtualMachines / jdk - 15.jdk / Contents / Home / bin / java - javaagent : / Applications / IntelliJ IDEA . app / Contents / lib / idea_rt . jar = 50249 : / Applications / IntelliJ IDEA . app / Contents / bin - Dfile . encoding = UTF - 8 - classpath / Users / app / crunchify / github / CrunchifyTutorials / target / classes : / Users / app / crunchify / github / CrunchifyTutorials / WebContent / WEB - INF / lib / zxing - 2.1.jar / Users / app / . m2 / repository / commons - collections / commons - collections / 3.2.1 / commons - collections - 3.2.1.jar / spring - context - support - 5.1.3.RELEASE.jar crunchify . com . tutorial . CrunchifyJoinArrays3Ways Original String Array1 : [ google , twitter ] Original String Array2 : [ apple , microsoft ] Original Integer Array1 : [ 111 , 444 ] Original Integer Array2 : [ 222 , 555 ] From Method - 1 : addAll ( ) - String == > [ google , twitter , apple , microsoft ] From Method - 1 : addAll ( ) - Integer == > [ 111 , 444 , 222 , 555 ] From Method - 2 : Stream . of ( ) == > [ google , twitter , apple , microsoft ] From Method - 2 : IntStream . concat ( ) == > [ 111 , 444 , 222 , 555 ] From Method - 3 : crunchifyJoinArrayusingGeneric ( ) == > [ google , twitter , apple , microsoft ] From Method - 3 : joinArray ( ) == > [ 111 , 444 , 222 , 555 ] Process finished with exit code 0 |
Veuillez me faire savoir si vous avez un autre moyen de fusionner des tableaux Java ou si vous obtenez une exception.
