Meilleure journalisation pour votre application Java d'entreprise – CrunchifyBetterLog4jLogging.java
Publié: 2019-08-29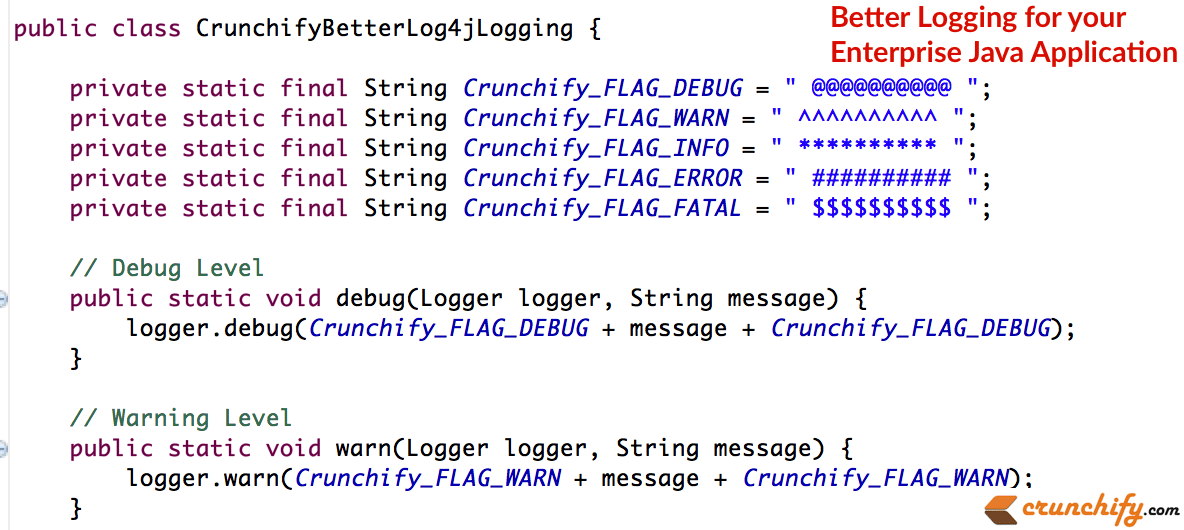
Si vous développez une application Java où vous devez utiliser la fonctionnalité de journalisation, il existe plusieurs façons d'améliorer l'utilitaire de journalisation.
Pour s'assurer que la journalisation peut être laissée dans un programme de production, l'API de journalisation Java est conçue pour rendre la journalisation aussi peu coûteuse que possible. Pour permettre au code de produire une journalisation fine en cas de besoin, mais sans ralentir l'application dans le cadre d'une utilisation normale en production, l'API fournit des mécanismes permettant de modifier dynamiquement les messages de journal produits, de sorte que l'impact du code de journalisation soit minimisé pendant le fonctionnement normal.
Commençons maintenant à écrire un simple utilitaire Logger qui améliorera la qualité globale de la journalisation de votre production.
Mettre à jour Log4j vers la dernière version
CVE-2021-44228 : Apache Log4j2 <=2.14.1 Les fonctionnalités JNDI utilisées dans la configuration, les messages de journal et les paramètres ne protègent pas contre LDAP contrôlé par l'attaquant et d'autres points de terminaison liés à JNDI.
Depuis log4j 2.16.0, ce comportement a été désactivé par défaut.
Étape 1:
Créer le fichier CrunchifyBetterLog4jLogging.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
package com . crunchify . tutorial ; import org . apache . log4j . Logger ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * */ public class CrunchifyBetterLog4jLogging { private static final String Crunchify_FLAG_DEBUG = " ---------- " ; private static final String Crunchify_FLAG_WARN = " ^^^^^^^^^^ " ; private static final String Crunchify_FLAG_INFO = " ********** " ; private static final String Crunchify_FLAG_ERROR = " ########## " ; private static final String Crunchify_FLAG_FATAL = " $$$$$ " ; // Debug Level public static void debug ( Logger logger , String message ) { logger . debug ( Crunchify_FLAG_DEBUG + message + Crunchify_FLAG_DEBUG ) ; } // Warning Level public static void warn ( Logger logger , String message ) { logger . warn ( Crunchify_FLAG_WARN + message + Crunchify_FLAG_WARN ) ; } // Info Level public static void info ( Logger logger , String message ) { logger . info ( Crunchify_FLAG_INFO + message + Crunchify_FLAG_INFO ) ; } // Error Level public static void error ( Logger Logger , String message ) { Logger . error ( Crunchify_FLAG_ERROR + message + Crunchify_FLAG_ERROR ) ; } // Fatal Level public static void fatal ( Logger Logger , String message ) { Logger . fatal ( Crunchify_FLAG_FATAL + message + Crunchify_FLAG_FATAL ) ; } } |
Fondamentalement, ce que nous faisons, c'est que lorsque, dans votre programme Java, vous dites log.info ou log.error ou log.fatal , le code ajoutera automatiquement des caractères spéciaux comme vous le voyez ci-dessus.
Étape 2
Cas de test (exemple de programme Java) – CrunchifyBetterLog4jLoggingTest.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
package com . crunchify . tutorial ; import org . apache . log4j . Logger ; public class CrunchifyBetterLog4jLoggingTest { private static Logger logger = Logger . getLogger ( CrunchifyBetterLog4jLoggingTest . class ) ; public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { int a = 20 ; int b = 30 ; int c = 3 ; int d = 4 ; CrunchifyBetterLog4jLoggingTest . SwapVairablesMethod1 ( a , b ) ; CrunchifyBetterLog4jLoggingTest . SwapVairablesMethod2 ( c , d ) ; } public static void SwapVairablesMethod1 ( int a , int b ) { CrunchifyBetterLog4jLogging . debug ( logger , "value of a and b before swapping, a: " + a + " b: " + b ) ; // swapping value of two numbers without using temp variable a = a + b ; // now a is 50 and b is 20 b = a - b ; // now a is 50 but b is 20 (original value of a) a = a - b ; // now a is 30 and b is 20, numbers are swapped CrunchifyBetterLog4jLogging . warn ( logger , "Result Method1 => a: " + a + " b: " + b ) ; } public static void SwapVairablesMethod2 ( int c , int d ) { CrunchifyBetterLog4jLogging . info ( logger , "value of c and d before swapping, c: " + c + " d: " + d ) ; // swapping value of two numbers without using temp variable using // multiplication and division c = c * d ; d = c / d ; c = c / d ; CrunchifyBetterLog4jLogging . error ( logger , "Result Method2 => c: " + c + " d: " + d ) ; } } |
Ici, nous imprimons différents types de résultats de journalisation.

Résultat:
|
1 2 3 4 |
2014 - 06 - 21 00 : 23 : 19 , 463 DEBUG [ CrunchifyBetterLog4jLoggingTest ] @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ value of a and b before swapping , a : 20 b : 30 @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ 2014 - 06 - 21 00 : 23 : 19 , 464 WARN [ CrunchifyBetterLog4jLoggingTest ] ^^^^^^^^^^ Result Method1 = > a : 30 b : 20 ^^^^^^^^^^ 2014 - 06 - 21 00 : 23 : 19 , 464 INFO [ CrunchifyBetterLog4jLoggingTest ] ********** value of c and d before swapping , c : 3 d : 4 ********** 2014 - 06 - 21 00 : 23 : 19 , 464 ERROR [ CrunchifyBetterLog4jLoggingTest ] ########## Result Method2 => c: 4 d: 3 ########## |
