So sortieren Sie eine HashMap nach Schlüssel und Wert in Java 8 – Vollständiges Tutorial
Veröffentlicht: 2020-09-18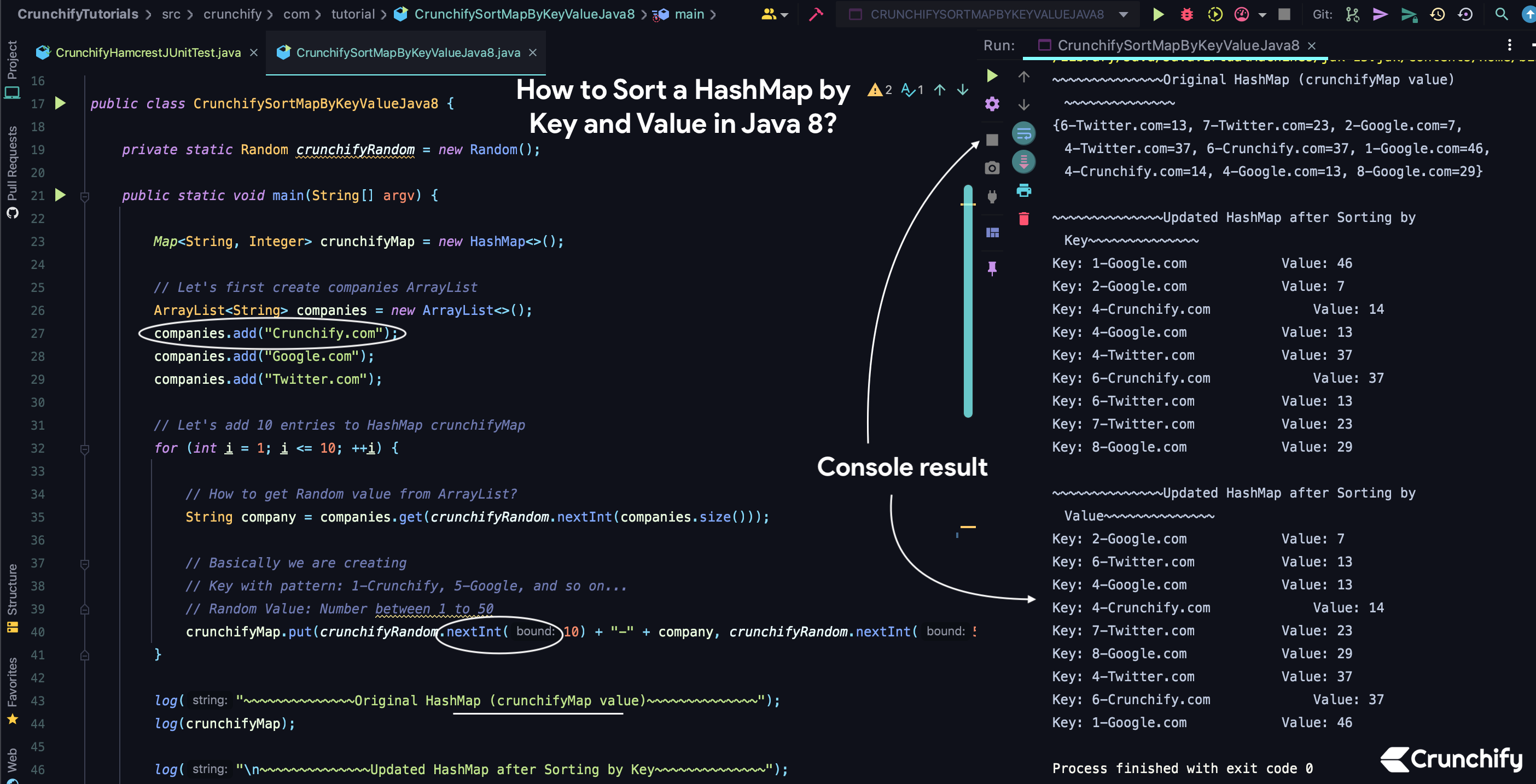
In Java 8 – Wie sortiere ich eine Karte?
Auf Crunchify haben wir fast 400 Java-Tutorials geschrieben und dieses ist eine Ergänzung zur Java8-Kategorie.
Ich liebe die Java-Sammlung und habe mehrere Tutorials zum Durchlaufen von Map and List, LinkedList, JSONArray und vielem mehr.
In diesem Tutorial gehen wir auf die beste Methode zum Sortieren von HashMap nach Schlüssel und Wert in Java8 ein.
Lass uns anfangen:
- Wir werden die Klasse CrunchifySortMapByKeyValueJava8.java erstellen
- Erstellen Sie HashMap<String, Integer> crunchifyMap und das werden wir zum Sortieren nach Schlüssel und Wert verwenden.
-
For KEY: Wir werden zufällige Unternehmen aus der Liste hinzufügen- Muster: Zufallszahl zwischen 1 bis 10 + (-) + 1 Unternehmen aus der Liste
- Firmenliste: crunchify.com, google.com, twitter.com
-
For VALUE: Wir fügen eine Zufallszahl zwischen 1 und 50 hinzu - Wir drucken die Originalkarte, sortiert nach Schlüsselkarte und sortiert nach Wertkarte
Karte.Eintrag. matchingByKey
comparingByKey()gibt einen Komparator zurück, der Map.Entry in natürlicher Reihenfolge auf Schlüssel vergleicht.Karte.Eintrag. matchingByValue
comparingByValue()gibt einen Komparator zurück, der Map.Entry in natürlicher Reihenfolge nach Wert vergleicht.
Hier ist ein vollständiger Java-Code:
Bitte werfen Sie einen Blick auf zwei Fragen, die im folgenden Code erwähnt werden. Dies sind einfache Dienstprogramme, nur für den Fall, dass Sie sie in Ihrem Projekt verwenden möchten.
- Wie bekomme ich einen Zufallswert von ArrayList?
- Wie iteriere ich durch HashMap in Java 8?
CrunchifySortMapByKeyValueJava8.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 |
package crunchify . com . tutorial ; import java . util . ArrayList ; import java . util . HashMap ; import java . util . LinkedHashMap ; import java . util . Map ; import java . util . Random ; import java . util . stream . Stream ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * * Best way to sort HashMap by Key and Value in Java8 - Tutorial by App Shah * */ public class CrunchifySortMapByKeyValueJava8 { private static final Random crunchifyRandom = new Random ( ) ; public static void main ( String [ ] argv ) { Map < String , Integer > crunchifyMap = new HashMap < > ( ) ; // Let's first create companies ArrayList ArrayList <String> companies = new ArrayList < > ( ) ; companies . add ( "Crunchify.com" ) ; companies . add ( "Google.com" ) ; companies . add ( "Twitter.com" ) ; // Let's add 10 entries to HashMap crunchifyMap for ( int i = 1 ; i < = 10 ; ++ i ) { // How to get Random value from ArrayList? String company = companies . get ( crunchifyRandom . nextInt ( companies . size ( ) ) ) ; // Basically we are creating // Key with pattern: 1-Crunchify, 5-Google, and so on... // Random Value: Number between 1 to 50 crunchifyMap . put ( crunchifyRandom . nextInt ( 10 ) + "-" + company , crunchifyRandom . nextInt ( 50 ) ) ; } crunchifyLog ( "~~~~~~~~~~~~~~Original HashMap (crunchifyMap value)~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" ) ; crunchifyLog ( crunchifyMap ) ; crunchifyLog ( "\n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~Updated HashMap after Sorting by Key~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" ) ; // Map: An object that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value. Map < String , Integer > key = crunchifySortByKey ( crunchifyMap ) ; iterateThroughHashMapJava8 ( key ) ; crunchifyLog ( "\n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~Updated HashMap after Sorting by Value~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" ) ; Map < String , Integer > value = crunchifySortByValue ( crunchifyMap ) ; iterateThroughHashMapJava8 ( value ) ; } // Simple Log Statement private static void crunchifyLog ( Object string ) { System . out . println ( string ) ; } // How to Iterate through HashMap in Java 8? private static void iterateThroughHashMapJava8 ( Map < String , Integer > crunchifyMap ) { crunchifyMap . forEach ( ( k , v ) - > { System . out . println ( "Key: " + k + "\t\t\t Value: " + v ) ; } ) ; } // Let's sort HashMap by Key // Comparable: This interface imposes a total ordering on the objects of each class that implements it. // This ordering is referred to as the class's natural ordering, and the class's compareTo method is referred to as its natural comparison method. public static < K extends Comparable < ? super K > , V > Map < K , V > crunchifySortByKey ( Map < K , V > crunchifyMap ) { Map < K , V > crunchifyResult = new LinkedHashMap < > ( ) ; Stream < Map . Entry < K , V > > sequentialStream = crunchifyMap . entrySet ( ) . stream ( ) ; // comparingByKey() returns a comparator that compares Map.Entry in natural order on key. sequentialStream . sorted ( Map . Entry . comparingByKey ( ) ) . forEachOrdered ( c - > crunchifyResult . put ( c . getKey ( ) , c . getValue ( ) ) ) ; return crunchifyResult ; } // Let's sort HashMap by Value public static < K , V extends Comparable < ? super V > > Map < K , V > crunchifySortByValue ( Map < K , V > crunchifyMap ) { Map < K , V > crunchifyResult = new LinkedHashMap < > ( ) ; // Stream: A sequence of elements supporting sequential and parallel aggregate operations. // The following example illustrates an aggregate operation using Stream and IntStream. Stream < Map . Entry < K , V > > sequentialStream = crunchifyMap . entrySet ( ) . stream ( ) ; // comparingByValue() returns a comparator that compares Map.Entry in natural order on value. // sorted(): Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, sorted according to the provided Comparator. sequentialStream . sorted ( Map . Entry . comparingByValue ( ) ) . forEachOrdered ( c - > crunchifyResult . put ( c . getKey ( ) , c . getValue ( ) ) ) ; // getValue(): Returns the value corresponding to this entry. If the mapping has been removed from the backing map (by the iterator's remove operation), the results of this call are undefined. // getKey(): Returns the key corresponding to this entry. return crunchifyResult ; } } |
Ausgabe der Eclipse-Konsole:
Führen Sie einfach das obige Programm als Java-Anwendung aus und Sie sollten das Ergebnis wie unten sehen.

|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Original HashMap ( crunchifyMap value ) ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ { 9 - Google . com = 36 , 6 - Twitter . com = 17 , 3 - Google . com = 39 , 2 - Twitter . com = 43 , 5 - Crunchify . com = 2 , 8 - Google . com = 5 , 8 - Crunchify . com = 47 , 5 - Google . com = 10 , 7 - Google . com = 3 } ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Updated HashMap after Sorting by Key ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Key : 2 - Twitter . com Value : 43 Key : 3 - Google . com Value : 39 Key : 5 - Crunchify . com Value : 2 Key : 5 - Google . com Value : 10 Key : 6 - Twitter . com Value : 17 Key : 7 - Google . com Value : 3 Key : 8 - Crunchify . com Value : 47 Key : 8 - Google . com Value : 5 Key : 9 - Google . com Value : 36 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Updated HashMap after Sorting by Value ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Key : 5 - Crunchify . com Value : 2 Key : 7 - Google . com Value : 3 Key : 8 - Google . com Value : 5 Key : 5 - Google . com Value : 10 Key : 6 - Twitter . com Value : 17 Key : 9 - Google . com Value : 36 Key : 3 - Google . com Value : 39 Key : 2 - Twitter . com Value : 43 Key : 8 - Crunchify . com Value : 47 |
Lassen Sie uns wissen, wenn Sie auf ein Problem stoßen, das das obige Programm ausführt.
