在 Java 中如何使用 DOM 解析器創建 XML 文件? 將 DOM 寫為 XML 文件
已發表: 2019-01-11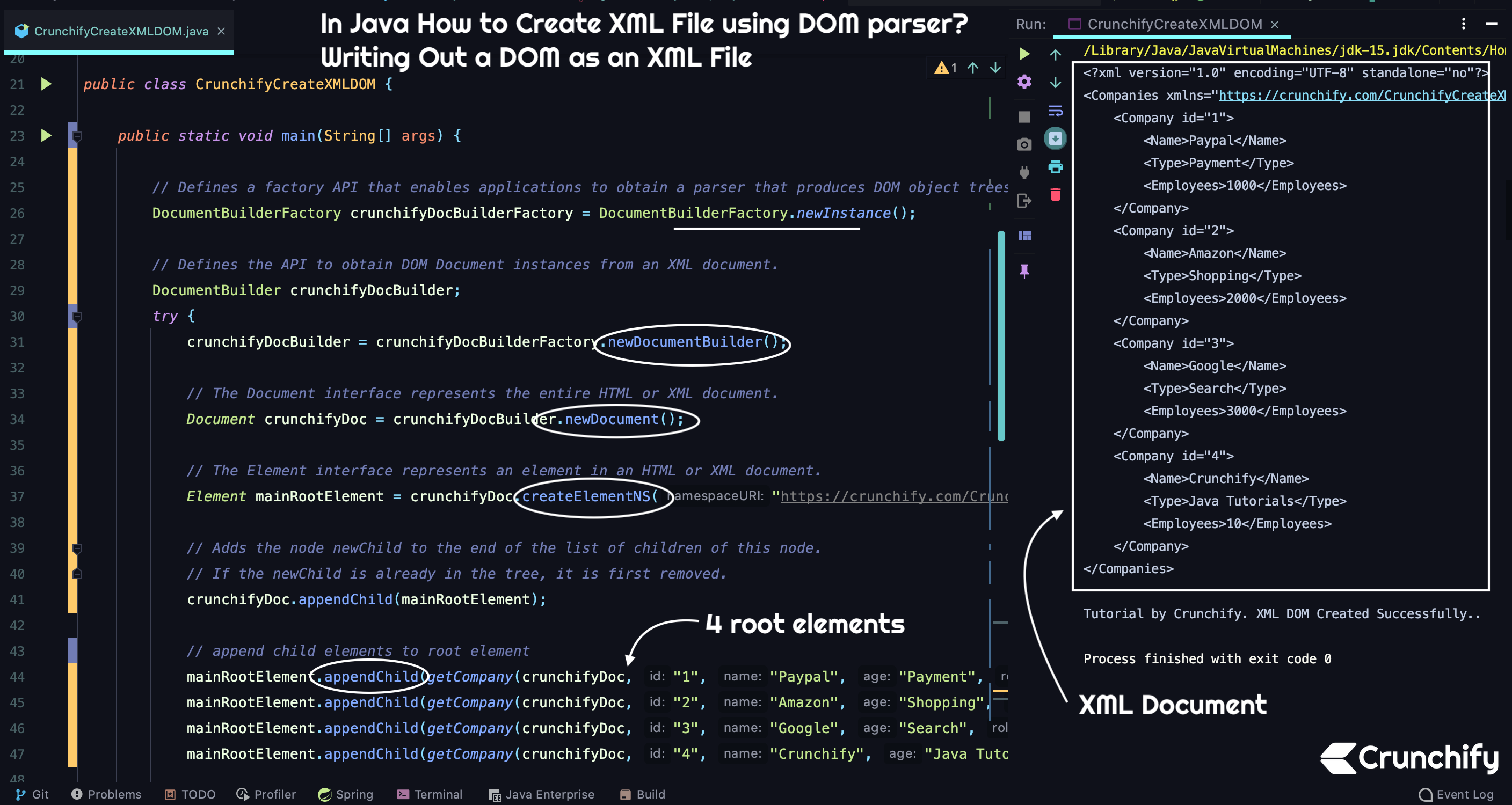
正如我們之前學習的“在 Java 中計算 XML 元素數量的簡單方法”,這裡是另一個用 Java 編寫 XML 文件的簡單 Java 代碼(DOM Parser)。
- 將 DOM 寫為 XML 文件
- Java DOM 教程 – 在 Java 中使用 DOM 編寫 XML
- 如何在 Java 中編寫 XML 文件(DOM 解析器)
- Java:用 Java 編寫 XML (DOM) 文件的簡單方法
這就是我在這裡所做的:
- 使用名稱創建根 XML 元素:
Companies - 創建 4 個
Company元素 - 每個公司元素都有一個屬性
id - 每個公司元素都有 3 個元素——
Name, Type, Employee
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 |
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import org . w3c . dom . Document ; import org . w3c . dom . Element ; import org . w3c . dom . Node ; import javax . xml . parsers . DocumentBuilder ; import javax . xml . parsers . DocumentBuilderFactory ; import javax . xml . transform . OutputKeys ; import javax . xml . transform . Transformer ; import javax . xml . transform . TransformerFactory ; import javax . xml . transform . dom . DOMSource ; import javax . xml . transform . stream . StreamResult ; /** * @author Crunchify.com * In Java How to Create XML File using DOM parser? Writing Out a DOM as an XML File. * Version: 1.1 */ public class CrunchifyCreateXMLDOM { public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { // Defines a factory API that enables applications to obtain a parser that produces DOM object trees from XML documents. DocumentBuilderFactory crunchifyDocBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory . newInstance ( ) ; // Defines the API to obtain DOM Document instances from an XML document. DocumentBuilder crunchifyDocBuilder ; try { crunchifyDocBuilder = crunchifyDocBuilderFactory . newDocumentBuilder ( ) ; // The Document interface represents the entire HTML or XML document. Document crunchifyDoc = crunchifyDocBuilder . newDocument ( ) ; // The Element interface represents an element in an HTML or XML document. Element mainRootElement = crunchifyDoc . createElementNS ( "https://crunchify.com/CrunchifyCreateXMLDOM" , "Companies" ) ; // Adds the node newChild to the end of the list of children of this node. // If the newChild is already in the tree, it is first removed. crunchifyDoc . appendChild ( mainRootElement ) ; // append child elements to root element mainRootElement . appendChild ( getCompany ( crunchifyDoc , "1" , "Paypal" , "Payment" , "1000" ) ) ; mainRootElement . appendChild ( getCompany ( crunchifyDoc , "2" , "Amazon" , "Shopping" , "2000" ) ) ; mainRootElement . appendChild ( getCompany ( crunchifyDoc , "3" , "Google" , "Search" , "3000" ) ) ; mainRootElement . appendChild ( getCompany ( crunchifyDoc , "4" , "Crunchify" , "Java Tutorials" , "10" ) ) ; // output DOM XML to console // An instance of this abstract class can transform a source tree into a result tree. Transformer crunchifyTransformer = TransformerFactory . newInstance ( ) . newTransformer ( ) ; crunchifyTransformer . setOutputProperty ( OutputKeys . INDENT , "yes" ) ; // Acts as a holder for a transformation Source tree in the form of a Document Object Model (DOM) tree. DOMSource source = new DOMSource ( crunchifyDoc ) ; // Acts as an holder for a transformation result, which may be XML, plain Text, HTML, or some other form of markup. StreamResult console = new StreamResult ( System . out ) ; crunchifyTransformer . transform ( source , console ) ; System . out . println ( "\nTutorial by Crunchify. XML DOM Created Successfully.." ) ; } catch ( TransformerException | ParserConfigurationException e ) { e . printStackTrace ( ) ; } } // The Node interface is the primary datatype for the entire Document Object Model. // It represents a single node in the document tree. private static Node getCompany ( Document doc , String id , String name , String age , String role ) { Element crunchifyCompany = doc . createElement ( "Company" ) ; crunchifyCompany . setAttribute ( "id" , id ) ; crunchifyCompany . appendChild ( getCrunchifyCompanyElements ( doc , crunchifyCompany , "Name" , name ) ) ; crunchifyCompany . appendChild ( getCrunchifyCompanyElements ( doc , crunchifyCompany , "Type" , age ) ) ; crunchifyCompany . appendChild ( getCrunchifyCompanyElements ( doc , crunchifyCompany , "Employees" , role ) ) ; return crunchifyCompany ; } // Utility method to create text node private static Node getCrunchifyCompanyElements ( Document doc , Element element , String name , String value ) { Element node = doc . createElement ( name ) ; node . appendChild ( doc . createTextNode ( value ) ) ; return node ; } } |
文檔生成器工廠:
定義一個工廠 API,使應用程序能夠獲得一個解析器,該解析器從 XML 文檔生成 DOM 對象樹。

文檔生成器:
定義 API 以從 XML 文檔中獲取 DOM 文檔實例。
附加孩子():
將節點 newChild 添加到該節點的子節點列表的末尾。 如果 newChild 已經在樹中,則首先將其移除。
變壓器:
此抽像類的實例可以將源樹轉換為結果樹。
DOM來源:
充當文檔對像模型 (DOM) 樹形式的轉換源樹的持有者。
流結果:
充當轉換結果的持有者,它可能是 XML、純文本、HTML 或某種其他形式的標記。
-
The Node接口是整個文檔對像模型的主要數據類型。 它表示文檔樹中的單個節點。 -
The Document接口代表整個 HTML 或 XML 文檔。 -
The ElementJava 接口表示 HTML 或 XML 文檔中的元素。
Eclipse 控制台輸出:
將上述程序作為 Java 應用程序運行以獲得類似的結果,如下所示。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
<? xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8" standalone = "no" ?> < Companies xmlns = "https://crunchify.com/CrunchifyCreateXMLDOM" > < Company id = "1" > < Name > Paypal < / Name > < Type > Payment < / Type > < Employees > 1000 < / Employees > < / Company > < Company id = "2" > < Name > Amazon < / Name > < Type > Shopping < / Type > < Employees > 2000 < / Employees > < / Company > < Company id = "3" > < Name > Google < / Name > < Type > Search < / Type > < Employees > 3000 < / Employees > < / Company > < Company id = "4" > < Name > Crunchify < / Name > < Type > Java Tutorials < / Type > < Employees > 10 < / Employees > < / Company > < / Companies > Tutorial by Crunchify . XML DOM Created Successfully . . Process finished with exit code 0 |
