Java Timer, TimerTask, Tutorial de classe de lembrete com exemplo
Publicados: 2021-02-04
java.util.Timer é uma classe de utilitário que pode ser usada para agendar uma thread para ser executada em um determinado momento no futuro. A classe Java Timer pode ser usada para agendar uma tarefa para ser executada uma única vez ou em intervalos regulares.
java.util.TimerTask é uma classe abstrata que implementa a interface Runnable e precisamos estender essa classe para criar nossa própria TimerTask que pode ser agendada usando a classe java Timer .
A classe Timer é thread-safe e vários threads podem compartilhar um único objeto Timer sem necessidade de sincronização externa. A classe Timer usa java.util.TaskQueue para adicionar tarefas em um determinado intervalo regular e a qualquer momento pode haver apenas um encadeamento executando o TimerTask, por exemplo, se você estiver criando um Timer para ser executado a cada 10 segundos, mas a execução de um único encadeamento leva 20 segundos, então o objeto Timer continuará adicionando tarefas à fila e assim que um encadeamento for concluído, ele notificará a fila e outro encadeamento começará a ser executado.
A classe Timer usa os métodos Object wait e notify para agendar as tarefas. TimerTask é uma abstract class e nós a herdamos para fornecer implementação concreta. A classe TimerTask implements a interface Runnable , portanto, é um thread e, portanto, sua implementação de TimerTask também é um thread.
Exemplo de Timer e TimerTask muito simples: A tarefa é executada após 5 seconds .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
package com . crunchify . tutorials ; import java . util . Timer ; import java . util . TimerTask ; /** * Author: Crunchify.com */ public class CrunchifyTimerTaskExample { Timer timer ; public CrunchifyTimerTaskExample ( int seconds ) { timer = new Timer ( ) ; timer . schedule ( new CrunchifyReminder ( ) , seconds * 1000 ) ; } class CrunchifyReminder extends TimerTask { public void run ( ) { System . out . format ( "Timer Task Finished..!%n" ) ; timer . cancel ( ) ; // Terminate the timer thread } } public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { new CrunchifyTimerTaskExample ( 5 ) ; System . out . format ( "Task scheduled.. Now wait for 5 sec to see next message..%n" ) ; } } |
Resultado:
|
1 2 |
Task scheduled . . Now wait for 5 sec to see next message . . Time ' s up ! |
Este programa simples ilustra as seguintes partes básicas da implementação e agendamento de uma tarefa a ser executada por um thread de timer:
- Implemente uma subclasse personalizada de
TimerTask. O métodoruncontém o código que executa a tarefa. Neste exemplo, a subclasse é denominada CrunchifyReminder. - Crie um thread instanciando a classe
Timer. - Instancie o objeto
TimerTask(new CrunchifyReminder()). - Agende a tarefa de timer para execução.
Como posso executar este TimerTask repetidamente?
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 |
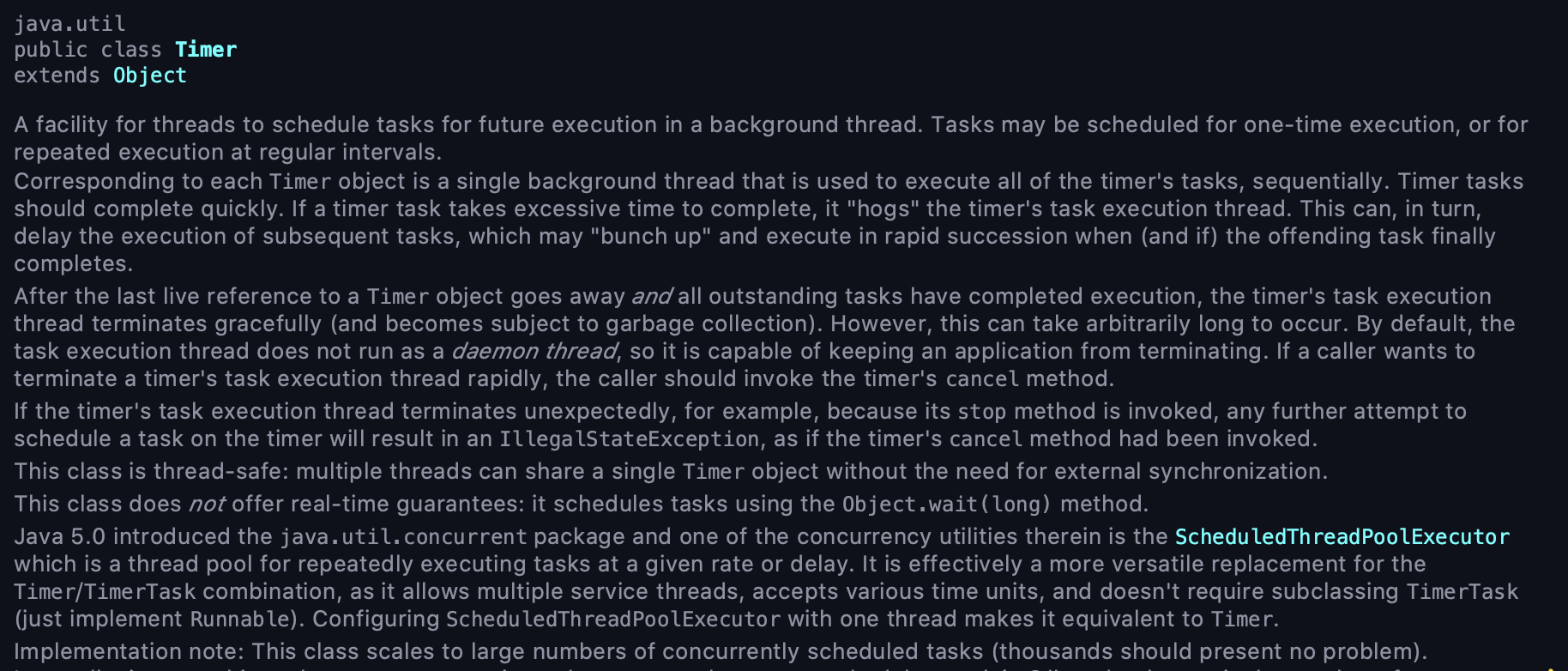
package crunchify . com . tutorials ; import java . util . Timer ; import java . util . TimerTask ; import java . awt . Toolkit ; /** * Author: Crunchify.com * Java Timer and TimerTask - Reminder Class Tutorials */ public class CrunchifyTimerTaskExample { // Toolkit This class is the abstract superclass of all actual implementations of the Abstract Window Toolkit. // Subclasses of the Toolkit class are used to bind the various components to particular native toolkit implementations. Toolkit toolkit ; // Timer A facility for threads to schedule tasks for future execution in a background thread. // Tasks may be scheduled for one-time execution, or for repeated execution at regular intervals. Timer timer ; public CrunchifyTimerTaskExample ( ) { toolkit = Toolkit . getDefaultToolkit ( ) ; timer = new Timer ( ) ; // schedule() Schedules the specified task for repeated fixed-delay execution, beginning after the specified delay. // Subsequent executions take place at approximately regular intervals separated by the specified period. timer . schedule ( new CrunchifyReminder ( ) , 0 , // initial delay 1 * 1000 ) ; // subsequent rate } // TimerTask A task that can be scheduled for one-time or repeated execution by a Timer. // A timer task is not reusable. Once a task has been scheduled for execution on a Timer or cancelled, // subsequent attempts to schedule it for execution will throw IllegalStateException. class CrunchifyReminder extends TimerTask { int loop = 5 ; public void run ( ) { if ( loop > 0 ) { // beep() Emits an audio beep depending on native system settings and hardware capabilities. toolkit . beep ( ) ; System . out . format ( "Knock Knock..!\n" ) ; loop -- ; } else { toolkit . beep ( ) ; System . out . format ( "\nThat's it.. Done..!" ) ; // cancel() Terminates this timer, discarding any currently scheduled tasks. Does not interfere with a currently executing task (if it exists). Once a timer has been terminated, // its execution thread terminates gracefully, and no more tasks may be scheduled on it. timer . cancel ( ) ; } } } public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { new CrunchifyTimerTaskExample ( ) ; System . out . format ( "Task scheduled..!%n \n" ) ; } } |
Resultado:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
Task scheduled . . ! Knock Knock . . ! Knock Knock . . ! Knock Knock . . ! Knock Knock . . ! Knock Knock . . ! That ' s it . . Done . . ! |
Por padrão, um programa continua em execução enquanto seus threads de timer estiverem em execução. Você pode encerrar um thread de timer de quatro maneiras:

- Invoca
cancelno temporizador. Você pode fazer isso em qualquer lugar do programa, como no método derunde uma tarefa de timer. - Faça do thread do timer um “daemon” criando o timer assim:
new Timer(true). Se os únicos encadeamentos restantes no programa forem encadeamentos daemon, o programa será encerrado. - Após a execução de todas as tarefas agendadas do timer, remova todas as referências ao objeto
Timer. Eventualmente, o encadeamento do temporizador será encerrado. - Invoque o método
System.exit, que faz com que o programa inteiro (e todos os seus threads) saia.
