systemctl start/stop service: come configurare lo script Upstart e il processo di rigenerazione in Ubuntu, CentOS, Redhat Linux
Pubblicato: 2021-06-09
Come scrivere uno script di avvio per systemd?
systemd è l'ultima service management utility in tutte le ultime versioni della distribuzione Linux come Ubuntu OS, Redhat OS, CentOS.
Ecco perché la versione Ubuntu 17.4 e Redhat 7.4 ora supporta systemctl command come script upstart. Se utilizzi una versione precedente del sistema operativo Linux, potrebbe essere necessario guardare in fondo a questa pagina per vedere init.d script precedente
Discuteremo di seguito le cose in questo tutorial
- Configurazione dell'unità di servizio systemd
- Come
configuresystemd? - Come
enablesystemd? - Come avviare automaticamente il processo utilizzando systemd?
- Come fermare e
respawnil processo usando systemd?
Passaggi di installazione per questo tutorial:
Prerequisite: abbiamo compilato la versione del programma CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram.java nella cartella /tmp/crunchify . Questo processo Java continuerà a funzionare in background per sempre. È possibile scaricare il programma da qui.
Una volta scaricato, try to compile ed eseguirlo per assicurarti che funzioni.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
root @ crunchify : / tmp / crunchify # ls -ltr - rw - r -- r -- 1 root root 120 Oct 6 17 : 57 crunchify . tar . gz drwxr - xr - x 2 root root 4096 Oct 6 18 : 01 tomcat drwxr - xr - x 2 root root 4096 Oct 6 18 : 02 java - rw - r -- r -- 1 root root 621 Oct 7 16 : 06 package - rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 838 Oct 7 16 : 07 CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram . java - rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 1295 Oct 8 14 : 38 CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram . class root @ crunchify : / tmp / crunchify # javac CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram.java root @ crunchify : / tmp / crunchify # java CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram always running program == > Sun Oct 08 14 : 39 : 14 UTC 2017 always running program == > Sun Oct 08 14 : 39 : 16 UTC 2017 . . . . . . . . . |
Puoi digitare CTRL + C per uscire dal programma.
Ora iniziamo a configurare lo script di avvio automatico di systemd per il programma sopra.
Passo 1
- Vai alla cartella /lib/systemd/system
- Digita
cd /lib/systemd/system
Passo 2
- crea il file
crunchify.service(cambia il nome del file di conseguenza) - inserisci sotto il contenuto
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
[ Unit ] Description = Crunchify Java Process Restart Upstart Script After = auditd . service systemd - user - sessions . service time - sync . target [ Service ] User = root TimeoutStartSec = 0 Type = simple KillMode = process export JAVA_HOME =/ opt / java / jdk - 9 export PATH = $ PATH : $ JAVA_HOME / bin WorkingDirectory =/ tmp / crunchify ExecStart =/ opt / java / jdk - 9 / bin / java - cp / tmp / crunchify CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram Restart = always RestartSec = 2 LimitNOFILE = 5555 [ Install ] WantedBy = multi - user . target |

Passaggio 3
- Salvare il file
- Fornisci il permesso di esecuzione usando
chmod 755 crunchify.service
Passaggio 4
- Carica crunchify.service usando il comando
systemctl daemon-reload - Abilita crunchify.service utilizzando il comando
systemctl enable crunchify.service - Avvia crunchify.service usando il comando
systemctl start crunchify - Controlla lo stato di crunchify.service usando il comando
systemctl status crunchify
Passaggio 5
- Ora controlla se il processo è in esecuzione o no??
- Digita il comando
ps -few | grep javaps -few | grep javaper vedere tutti i processi Java in esecuzione - Dovresti vedere qualcosa del genere
|
1 2 3 |
root @ crunchify : / lib / systemd / system # ps -few | grep java root 28631 1 0 14 : 02 ? 00 : 00 : 03 / opt / java / jdk - 9 / bin / java - cp / tmp / crunchify CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram root 28853 28226 0 14 : 46 pts / 0 00 : 00 : 00 grep java |
Ciò significa che il processo 28631 sta iniziando a utilizzare lo script upstart. Potresti avere un ID processo diverso.
Come verificare se il tuo systemd crunchify.service funziona o meno?
- Prova a terminare il processo usando
kill -9 28631e dovresti vedere che il nuovo processo dovrebbe essere creato automaticamente. - Nel mio caso è stato creato un nuovo ID processo
28887
|
1 2 3 4 |
root @ crunchify : / lib / systemd / system # kill -9 28631 root @ crunchify : / lib / systemd / system # ps -few | grep java root 28887 1 17 14 : 48 ? 00 : 00 : 00 / opt / java / jdk - 9 / bin / java - cp / tmp / crunchify CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram root 28900 28226 0 14 : 48 pts / 0 00 : 00 : 00 grep java |
Video: esempio completo di configurazione dello script upstart di sistema live:
Questo video contiene: come configurare lo script di avvio/avvio di sistema in CentOS, Redhat, Ubuntu Linux OS?
- Come eseguire automaticamente lo script della shell all'avvio
- Come creare un servizio systemd in Linux (CentOS 7)
- Come configurare un servizio Linux per l'avvio automatico?
- Script di avvio di sistema Centos 7
- Script di avvio del sistema Ubuntu
Vuoi saperne di più su systemd? Ecco un cheat sheet come riferimento.
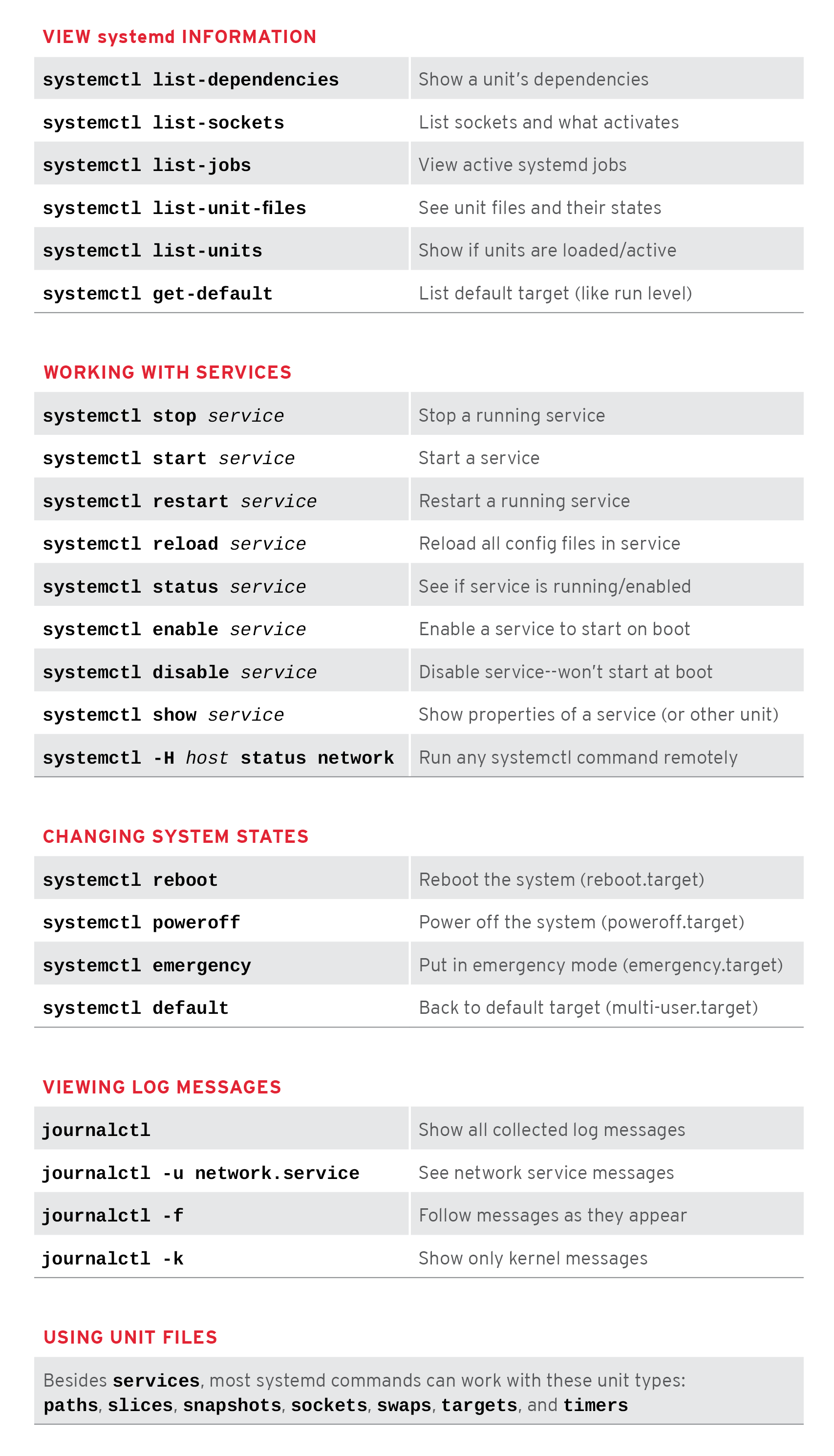
Spero che tu impari everything about systemd command e sulla configurazione dello script upstart su tutti i tipi di sistemi operativi Linux.
ARRESTO: SOLO per versioni precedenti del sistema operativo
Se stai utilizzando older version di Redhat, Ubuntu, CentOS, dovrai disporre di uno script in questo formato.
- Vai su
/etc/init - Crea file
crunchify.conf
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
# Run Crunchify's Java program indefinitely # description "Crunchify Java Process Restart Upstart Script" author "Crunchify.com (App Shah)" start on runlevel [ 2345 ] stop on runlevel [ ! 2345 ] respawn respawn limit 10 5 script su - root < < 'EOF' export JAVA_HOME =/ opt / java / jdk - 9 export PATH = $ PATH : $ JAVA_HOME / bin exec / opt / java / jdk - 9 / bin / java - cp / tmp / crunchify CrunchifyAlwaysRunningProgram EOF end script |
- Avvia il servizio usando il comando
service crunchify start - Segui gli stessi passaggi di verifica di cui sopra
Fammi sapere se riscontri problemi durante l'esecuzione dello script upstart nel tuo ambiente. Goditi la giornata e buona codifica.
