Cómo acelerar WordPress aprovechando el almacenamiento en caché del navegador a través de .htaccess
Publicado: 2017-08-04
Aproveche el almacenamiento en caché del navegador para que sus páginas web sean más rápidas. Si puede aprovechar el almacenamiento en caché del navegador , puede aumentar considerablemente la velocidad del sitio web. A medida que Google comienza a considerar la velocidad del sitio como un parámetro de SEO, los webmasters pueden aprovechar el almacenamiento en caché del navegador para mejorar la velocidad del sitio y obtener una mejor clasificación en los motores de búsqueda.
Aquí hay un archivo .htaccess completo que tenemos en la carpeta raíz de Crunchify.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 |
######### CRUNCHIFY SETTING - START ########## Options All - Indexes # Disable ETags < IfModule mod_headers . c > Header unset ETag Header set Connection keep - alive < / IfModule > FileETag None ############## MaxCDN Fix ############# < IfModule mod_headers . c > < FilesMatch "\.(ttf|ttc|otf|eot|woff|woff2|font.css|css|js)$" > Header set Access - Control - Allow - Origin "*" < / FilesMatch > < / IfModule > ########### REDIRECT TRAFFIC TO HTTPS ############ # RewriteEngine On # RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off # RewriteRule (.*) https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L] ############ SECURITY ########### < FilesMatch "\.(md|exe|sh|bak|inc|pot|po|mo|log|sql)$" > Order allow , deny Deny from all < / FilesMatch > < Files robots . txt > Allow from all < / Files > ############## CACHING-GZIP ############ < IfModule mod_expires . c > ExpiresActive On ExpiresDefault A2592000 < FilesMatch "\.(txt|xml|js)$" > ExpiresDefault A2592000 < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(css)$" > ExpiresDefault A2592000 < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(flv|ico|pdf|avi|mov|ppt|doc|mp3|wmv|wav|mp4|m4v|ogg|webm|aac)$" > ExpiresDefault A2592000 < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|swf|webp)$" > ExpiresDefault A2592000 < / FilesMatch > < / IfModule > < IfModule mod_headers . c > < FilesMatch "\.(txt|xml|js)$" > Header set Cache - Control "max-age=2592000" < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(css)$" > Header set Cache - Control "max-age=2592000" < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(flv|ico|pdf|avi|mov|ppt|doc|mp3|wmv|wav|mp4|m4v|ogg|webm|aac)$" > Header set Cache - Control "max-age=2592000" < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|swf|webp)$" > Header set Cache - Control "max-age=2592000" < / FilesMatch > < / IfModule > < IfModule mod_deflate . c > < IfModule mod_setenvif . c > < IfModule mod_headers . c > SetEnvIfNoCase ^ ( Accept - EncodXng | X - cept - Encoding | X { 15 } | ~ { 15 } | - { 15 } ) $ ^ ( ( gzip | deflate ) \ s* , ? \ s* ) + | [ X ~ - ] { 4 , 13 } $ HAVE_Accept - Encoding RequestHeader append Accept - Encoding "gzip,deflate" env = HAVE_Accept - Encoding < / IfModule > < / IfModule > < IfModule mod_filter . c > AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE "application/atom+xml" \ "application/javascript" \ "application/json" \ "application/ld+json" \ "application/manifest+json" \ "application/rdf+xml" \ "application/rss+xml" \ "application/schema+json" \ "application/vnd.geo+json" \ "application/vnd.ms-fontobject" \ "application/x-font-ttf" \ "application/x-javascript" \ "application/x-web-app-manifest+json" \ "application/xhtml+xml" \ "application/xml" \ "font/eot" \ "font/opentype" \ "image/bmp" \ "image/svg+xml" \ "image/vnd.microsoft.icon" \ "image/x-icon" \ "text/cache-manifest" \ "text/css" \ "text/html" \ "text/javascript" \ "text/plain" \ "text/vcard" \ "text/vnd.rim.location.xloc" \ "text/vtt" \ "text/x-component" \ "text/x-cross-domain-policy" \ "text/xml" < / IfModule > < IfModule mod_mime . c > AddEncoding gzip svgz < / IfModule > < / IfModule > ######### CRUNCHIFY SETTING END ############ # BEGIN WordPress < IfModule mod_rewrite . c > RewriteEngine On RewriteBase / RewriteRule ^ index \ . php $ - [ L ] RewriteCond % { REQUEST_FILENAME } ! - f RewriteCond % { REQUEST_FILENAME } ! - d RewriteRule . / index . php [ L ] < / IfModule > # END WordPress |

NOTA : elimine el redireccionamiento al bloque HTTPS si no está en HTTPS :). Aunque ya lo he comentado. Si ya ha habilitado HTTPS en el sitio y aún permite que el usuario visite el sitio a través de HTTP, entonces está bien.
Comprendamos cada sección del archivo .htaccess:
Paso-1 Deshacerse de ETag
En primer lugar, debemos disable ETag header ya que vamos a utilizar la duración de Expires. La tecnología ETag es conocida como lenta y problemática, incluso otros sitios de alto rango se quejan de ello.
Agregar a .htaccess : (ubicado en la ubicación raíz del blog)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# Disable ETags < IfModule mod_headers . c > Header unset ETag Header set Connection keep - alive < / IfModule > FileETag None |
También mantenemos la conexión keep-alive . Se llama persistent connection . Si se debe abrir una nueva conexión para cada solicitud o archivo, podría llevar mucho más tiempo.
Otro debe leer:
- 5 trucos útiles para acelerar WordPress y aumentar el rendimiento
- 9 recursos esenciales de WordPress que quizás te hayas perdido
Paso 2 Habilitar el almacenamiento en caché del navegador
Si establece una fecha de caducidad o una antigüedad máxima en los encabezados HTTP para los recursos estáticos, los navegadores modernos cargarán los recursos estáticos descargados previamente, como imágenes, css, javascript, pdf, swf, etc., desde discos locales en lugar de a través de la red.
Entonces, si configura su servidor web para establecer encabezados de almacenamiento en caché y aplicarlos a todos los recursos estáticos almacenables en caché, su sitio parecerá cargarse mucho más rápido. Agregar a continuación a .htaccess
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
< IfModule mod_expires . c > ExpiresActive On ExpiresDefault A2592000 < FilesMatch "\.(txt|xml|js)$" > ExpiresDefault A2592000 < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(css)$" > ExpiresDefault A2592000 < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(flv|ico|pdf|avi|mov|ppt|doc|mp3|wmv|wav|mp4|m4v|ogg|webm|aac)$" > ExpiresDefault A2592000 < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|swf|webp)$" > ExpiresDefault A2592000 < / FilesMatch > < / IfModule > < IfModule mod_headers . c > < FilesMatch "\.(txt|xml|js)$" > Header set Cache - Control "max-age=2592000" < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(css)$" > Header set Cache - Control "max-age=2592000" < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(flv|ico|pdf|avi|mov|ppt|doc|mp3|wmv|wav|mp4|m4v|ogg|webm|aac)$" > Header set Cache - Control "max-age=2592000" < / FilesMatch > < FilesMatch "\.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|swf|webp)$" > Header set Cache - Control "max-age=2592000" < / FilesMatch > < / IfModule > |
Lo que esto hace es agregar un encabezado de vencimiento lejano en el futuro (asegúrese de que mod_expires esté cargado en su configuración de apache si tiene problemas) a su contenido estático (imágenes, js, css, etc.).
Dos cosas aquí:
- ExpiresDefault A2592000 = 1 mes en el futuro
- Control de caché “max-age=2592000” = 1 mes
Si lo desea, también puede establecer el valor en 1 año = 31536000
Paso 3 Agregue gzip y deflate los encabezados de compresión
Comprimir cosas siempre termina haciéndolas más pequeñas y se cargan más rápido, por lo que es imprescindible implementar algún tipo de compresión en sus componentes.
Es posible que este paso de optimización no funcione para usted si su servidor no tiene mod_deflate o mod_gzip instalados como parte de Apache.
Básicamente, estamos comprimiendo la mayoría de los recursos para que se carguen con menos ancho de banda y muy rápido.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 |
< IfModule mod_deflate . c > < IfModule mod_setenvif . c > < IfModule mod_headers . c > SetEnvIfNoCase ^ ( Accept - EncodXng | X - cept - Encoding | X { 15 } | ~ { 15 } | - { 15 } ) $ ^ ( ( gzip | deflate ) \ s* , ? \ s* ) + | [ X ~ - ] { 4 , 13 } $ HAVE_Accept - Encoding RequestHeader append Accept - Encoding "gzip,deflate" env = HAVE_Accept - Encoding < / IfModule > < / IfModule > < IfModule mod_filter . c > AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE "application/atom+xml" \ "application/javascript" \ "application/json" \ "application/ld+json" \ "application/manifest+json" \ "application/rdf+xml" \ "application/rss+xml" \ "application/schema+json" \ "application/vnd.geo+json" \ "application/vnd.ms-fontobject" \ "application/x-font-ttf" \ "application/x-javascript" \ "application/x-web-app-manifest+json" \ "application/xhtml+xml" \ "application/xml" \ "font/eot" \ "font/opentype" \ "image/bmp" \ "image/svg+xml" \ "image/vnd.microsoft.icon" \ "image/x-icon" \ "text/cache-manifest" \ "text/css" \ "text/html" \ "text/javascript" \ "text/plain" \ "text/vcard" \ "text/vnd.rim.location.xloc" \ "text/vtt" \ "text/x-component" \ "text/x-cross-domain-policy" \ "text/xml" < / IfModule > < IfModule mod_mime . c > AddEncoding gzip svgz < / IfModule > < / IfModule > |
Paso 4 Verifique si su configuración funciona correctamente
Echa un vistazo a continuación captura de pantalla. Debería ver todos los parámetros establecidos en el encabezado de respuesta de su archivo.
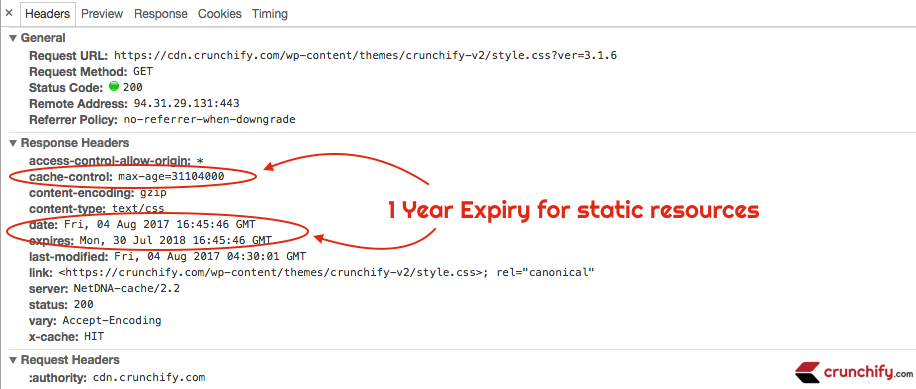

Pregunta abierta: ¿Puedo cambiar la fecha de caducidad de algunos recursos como el script de Google Adsense o el script de Google Analytics?
- https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js
- https://www.google-analytics.com/analytics.js
Answer is NO . Solo puede establecer el valor de caducidad de los recursos que se cargan desde su sitio.
